接下来,我们完成顺序存储结构线性表的抽象实现

抽象实现意味着SeqList是一个抽象类,在这一抽象类里面,我们仅仅把关键的操作实现了,但是还是不能生成具体的对象,这是因为顺序存储空间的指定并没有在SeqList中来完成,存储空间的最终指定在SeqList的两个子类中完成。
SeqList的设计要点如下:
抽象类模板,存储空间的位置和大小由子类完成
实现顺序存储结构线性表的关键操作(增、删、查等)
提供数组操作符,方便快速获取元素
抽象类模板的声明如下:

SeqList的实现代码如下:
1 #ifndef SEQLIST_H 2 #define SEQLIST_H 3 4 #include "List.h" 5 #include "Exception.h" 6 7 namespace DTLib 8 { 9 10 template <typename T> 11 class SeqList : public List<T> 12 { 13 protected: 14 T* m_array; //顺序存储空间,具体在子类中指定 15 int m_length; //当前线性表长度 16 public: 17 bool insert(int i, const T &e) 18 { 19 bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i <= m_length)); 20 21 ret = ret && (m_length < capacity()); 22 23 if( ret ) 24 { 25 for(int p = m_length -1; p >= i; p--) 26 { 27 m_array[p + 1] = m_array[p]; 28 } 29 30 m_array[i] = e; 31 32 m_length++; 33 } 34 35 return ret; 36 } 37 38 bool remove(int i) 39 { 40 bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < m_length)); 41 42 if( ret ) 43 { 44 for(int p = i; p < m_length - 1; p++) 45 { 46 m_array[p] = m_array[p + 1]; 47 } 48 49 m_length--; 50 } 51 52 return ret; 53 } 54 55 bool set(int i, const T &e) 56 { 57 bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < m_length)); 58 59 if( ret ) 60 { 61 m_array[i] = e; 62 } 63 64 return ret; 65 } 66 67 bool get(int i, T &e) const 68 { 69 bool ret = ((0 <= i) && i < m_length); 70 71 if( ret ) 72 { 73 e = m_array[i]; 74 } 75 76 return ret; 77 } 78 79 int length() const 80 { 81 return m_length; 82 } 83 84 void clear() 85 { 86 m_length = 0; 87 } 88 //顺序存储线性表的数组访问方式 89 T& operator[](int i) 90 { 91 if((0 <= i) && (i < m_length)) 92 { 93 return m_array[i]; 94 } 95 else 96 { 97 THROW_EXCEPTION(IndexOutOfBoundsException, "Parameter i is invalid ..."); 98 } 99 } 100 101 T operator[](int i) const 102 { 103 return (const_cast<SeqList<T>&>(*this))[i]; 104 } 105 106 //顺序存储空间的容量 107 virtual int capacity() const = 0; 108 }; 109 110 } 111 112 #endif // SEQLIST_H
SeqList是一个抽象类,不能实例化,但是可以定义SeqList的指针。
下一节我们实现SeqList的子类,关于StaticList和DynamicList我们先给出如下的思考:
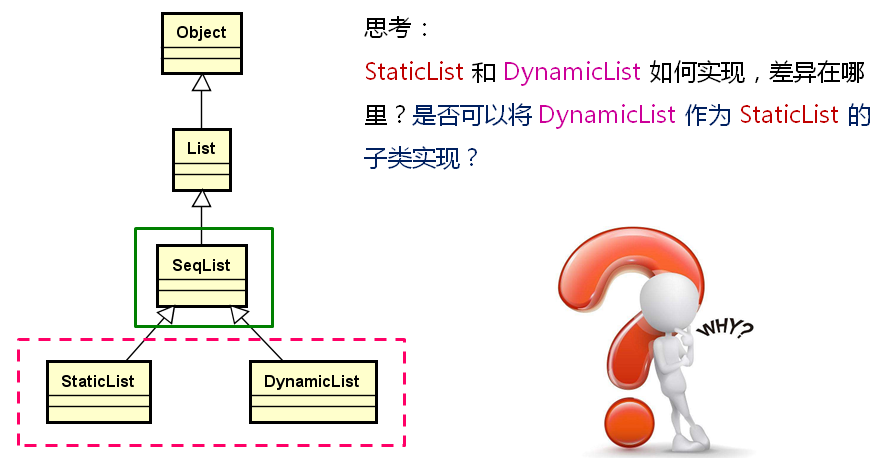
StaticList是静态的,在StaticList的具体实现当中就是将某个固定的存储空间作为顺序存储空间,指定到父类的m_array上去。DynamicList中是可以动态的指定顺序存储空间,并将这个存储空间指定到父类的m_array上去。