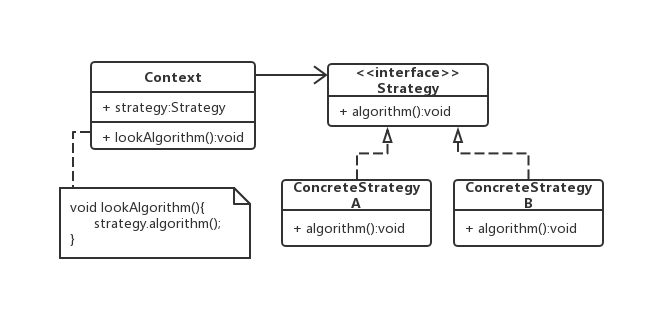
定义一系列算法,把它们一个个封装起来,并且使它们可以相互替换,本模式使得算法可以独立于使用它的客户而变化。策略模式包括以下三种角色
- 策略(Strategy):策略是一个接口,该接口定义若干个算法标识,定义了若干个抽象方法。
- 具体策略(ConcreteStrategy):具体策略是实现策略接口的类,具体策略实现策略接口所定义的抽象方法,给出算法标识的具体算法。
- 上下文(Context):上下文是依赖策略接口的类,即上下文包含有策略声明的变量。上下文中提供一个方法,该方法委托策略变量调用具体策略所实现的策略接口中方法。
策略模式的UML类图如下图所示:
策略模式的优点:
上下文和具体策略是松耦合的关系,上下文只知道它要使用某一个实现Strategy接口类的实例,但不需要知道具体是哪一类。
策略模式满足“开-闭原则”。当增加新的具体策略时,不需要修改上下文类的代码,上下文就可以引用新的具体策略实例。
策略模式的使用场景:
一个类定义了多种行为,并且这些行为在这个类的方法中以多个条件语句的形式出现,那么可以使用策略模式避免在类中使用大量的条件语句。
程序不希望暴露复杂的。与算法相关的数据结构,可以使用策略模式封装算法。
需要使用一个算法的不同实体。
应用举例 —— 加密、解密文件
用户需要对已有的文件进行加密处理,请提供几种加密方案。
设计实现可以使用策略模式,具体如下:
1. 策略接口的名称是EncryptStrategy,该接口有两个抽象方法,一个是加密,一个是解密
public interface EncryptStrategy {
public abstract void encryptFile(File file);
public abstract void decryptFile(File file);
}
2. 具体策略,有两个具体策略,StrategyONE和StrategyTWO
-
- StrategyONE使用一个字符串做密码,比如password,将这个字符串编码到一个字节数组,byte[] e = password.getBytes(); 假设e的长度是n,那么就将文件内容以n字节为一组,对每组中字节,用数组e对应字节做加法运算,解密的话就是相应的做减法运算。
- StrategyTWO使用一个字符串做密码,比如password,将这个字符串编码到一个字节数组,byte[] e = password.getBytes(); 假设e的长度是n,那么就将文件内容按顺序以n字节为一组对每组中字节,使用数组e的对应字节做异或运算
public class StrategyOne implements EncryptStrategy { String password; public StrategyOne(String password) { if(password == null||password.trim().length()==0) this.password = "I love java"; this.password = password; } public StrategyOne() { this.password = "I love java"; } public void encryptFile(File file) { try { byte[] a = this.password.getBytes(); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); long length = file.length(); byte[] c = new byte[(int)length]; int m = fis.read(); for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { int n = c[i]+a[i%a.length]; c[i] = (byte) n; } fis.close(); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file); fos.write(c, 0, m); fos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public void decryptFile(File file) { try { byte[] a = this.password.getBytes(); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); long length = file.length(); byte[] c = new byte[(int)length]; int m = fis.read(); for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { int n = c[i]-a[i%a.length]; c[i] = (byte) n; } fis.close(); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file); fos.write(c, 0, m); fos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
public class StrategyTWO implements EncryptStrategy { String password; public StrategyTWO(String password) { if(password == null||password.trim().length()==0) this.password = "I love java"; this.password = password; } public StrategyTWO() { this.password = "I love java"; }
@Override public void encryptFile(File file) { try { byte[] a = this.password.getBytes(); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); long length = file.length(); byte[] c = new byte[(int)length]; int m = fis.read(); for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { int n = c[i]^a[i%a.length]; c[i] = (byte) n; } fis.close(); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file); fos.write(c, 0, m); fos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override public void decryptFile(File file) { try { byte[] a = this.password.getBytes(); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); long length = file.length(); byte[] c = new byte[(int)length]; int m = fis.read(); for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { int n = c[i]^a[i%a.length]; c[i] = (byte) n; } fis.close(); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file); fos.write(c, 0, m); fos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
3. 上下文,该类包含策略声明用于保存具体策略的引用变量,代码如下
public class EncodeContext { public EncryptStrategy strategy; public void setStrategy(EncryptStrategy strategy) { this.strategy = strategy; } public void encryptFile(File file){ this.strategy.encryptFile(file); } public void decryptFile(File file){ this.strategy.decryptFile(file); } }
4. 应用程序
public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { File fileOne = new File("A.txt"); String s = ""; EncodeContext con = new EncodeContext(); con.setStrategy(new StrategyOne("Hello world!")); con.encryptFile(fileOne); System.out.println(fileOne.getName()+"加密后的內容:"); try { FileReader inOne = new FileReader(fileOne); BufferedReader inTwo = new BufferedReader(inOne); while((s=inTwo.readLine())!=null){ System.out.println(s); } inOne.close(); inTwo.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }