UNSUPERVISED REPRESENTATION LEARNING WITH DEEP CONVOLUTIONAL GENERATIVE ADVERSARIAL NETWORKS
ICLR 2016
摘要:近年来 CNN 在监督学习领域的巨大成功 和 无监督学习领域的无人问津形成了鲜明的对比,本文旨在链接上这两者之间的缺口。提出了一种 deep convolutional generative adversarial networks (DCGANs),that have certain architecture constraints。
引言:在计算机视觉领域,可以通过海量无标签数据,从中学习到好的表示(good immediate representation)然后将其应用到众多监督学习任务当中去,例如:image classification。一种较好的方法就是,利用产生式对抗网络来完成,然后利用 产生器 和 判别器的一部分来作为特征提取器,进行其他监督任务的学习。众所周知,GANs 的缺点是:unstable to train ,这样就会导致产生了毫无意义的输出。甚少有 paper 尝试去理解和可视化 GANs 到底学习到了什么,以及多层 GANs 的即可表示。
本文的贡献点在于:
1. 本文提出一些网络结构上的约束,使得训练过程更加稳定。并将此类型的结构称为:Deep Convolutional GANs (DCGAN)
2. 利用训练好的 discriminators 进行 image classification tasks,取得了和其他 unsupervised learning algorithm 相当的结果
3. 作者将 GANs 的 filter 进行了可视化处理,表明特定的 filter 学到了 draw specific objects
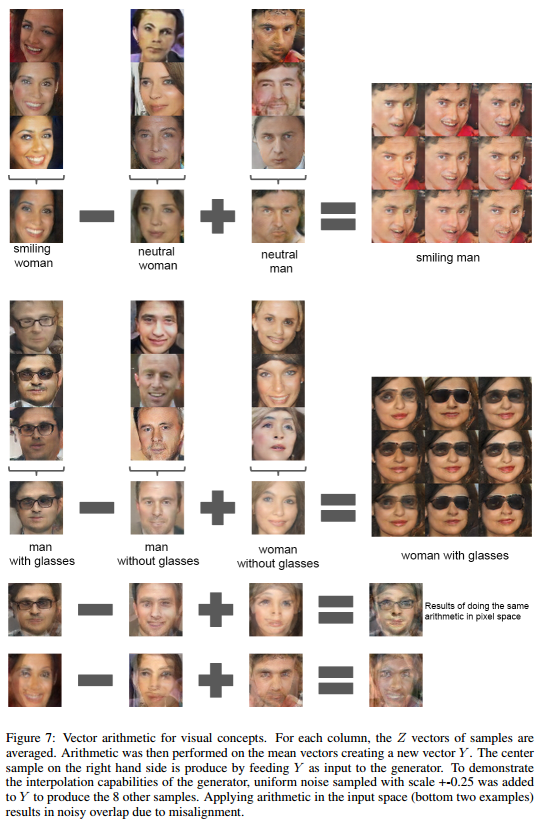
4. We show that generators have interesting vector arithmetic properties allowing for easy manipulation of many semantic qualities of generated samples
Approach to Model Architecture :
已经有很多尝试将 GANs 做 scale up,但是几乎都不怎么成功。作者在尝试用 supervised learning 常用的方法做 scale 时,也遇到了很多困难。但是,在作者做了很多模型探索之后(extensive model exploration)得到了一些结构上的技巧来改善训练的稳定性,并且允许得到更高分辨率的图像,采用更深的产生式模型。
本文核心的方法,主要从以下三个方面进行网络结构上的设计和改变 :
第一个是:the all convolutional net . 将 deteministic spatial pooling function (such as: maxpooling)with strided convolutions,使得网络可以学习其自己的 spatial downsampling。我们利用这种方法到我们的 generator 当中,允许其学习自己的 spatial upsampling,and discriminator 。
第二个是:the trend towards eliminating fully connected layers on top of convolutional features. 作者发现:global average pooling 增强了模型的稳定性,但是损害了收敛的速度。A middle ground of directly connecting the highest convolutional features to the input and output respectively of the generatively of the generator and discriminator worked well. 具体的网络结构见下图:
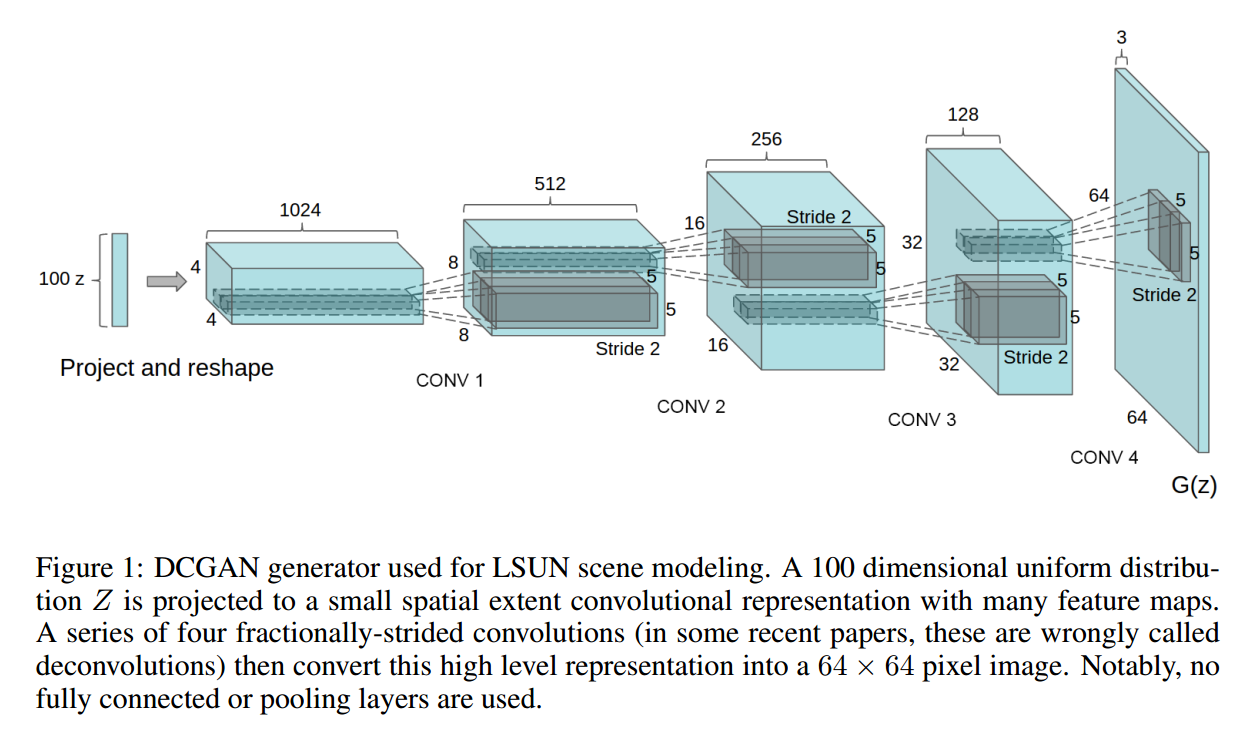
第三个是:Batch Normalizaiton,which stabilizes learning by normalizing the input to each unit to have zero mean and unit variance。但是,直接对所有的 layer 都使用这种技术,就会出现问题:resulted in sample oscillation and model instability 。这种困难是通过 不对 generator output layer 和 discriminator input layer 采用这种方法,就行了。
The ReLU activation is used in generator with the exception of the output layer which uses the Tanh function.
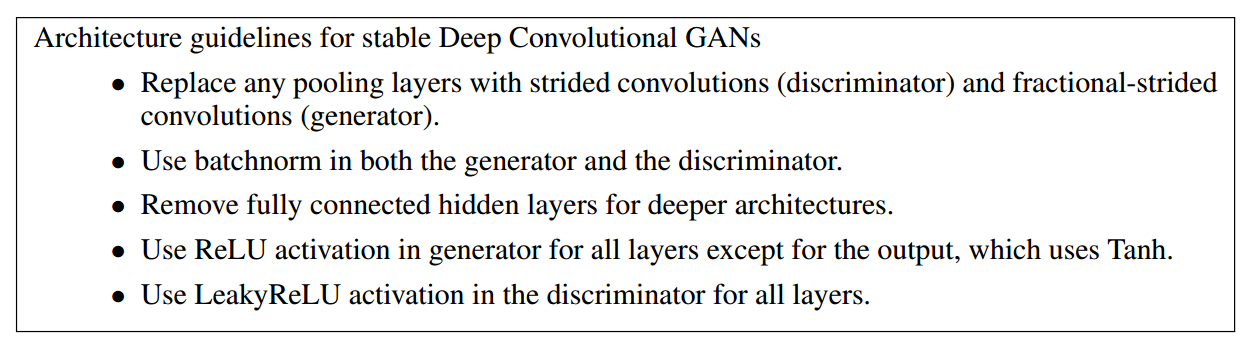
作者总结了一个列表,对稳定的训练 GANs 提供了下面的几条建议:
Details of Adversarial Training :
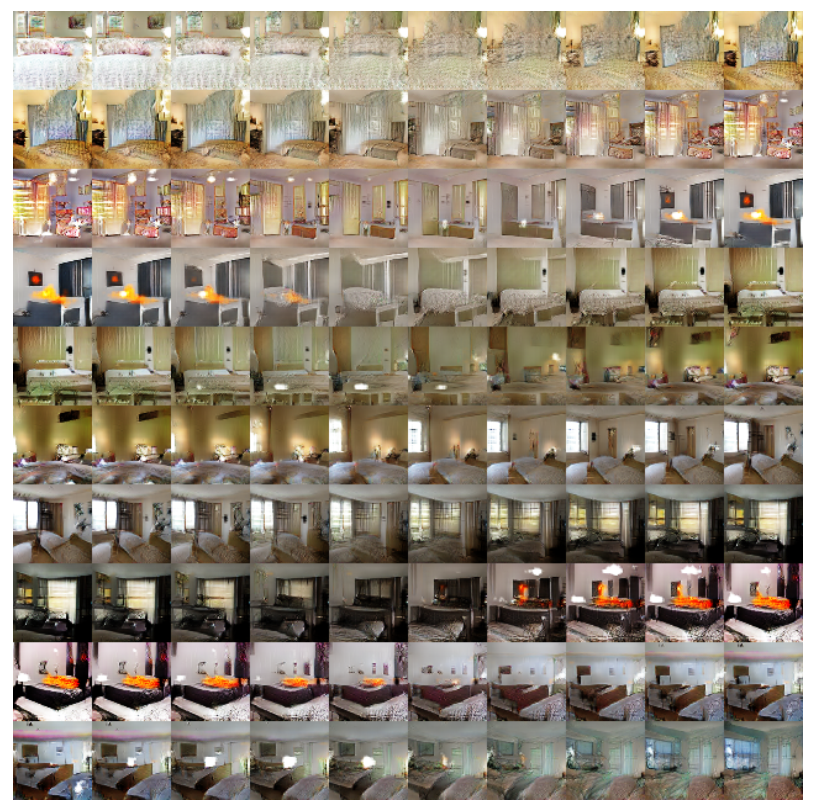
作者在三个数据集上进行了训练,分别是:Large-scale Scene Understanding (LSUN),Image Net-1k and Faces dataset 。


Expirical Validation of DCGANs Capabilities .
1. Classifying CIFAR-10 using GANs as a Feature Extractor :
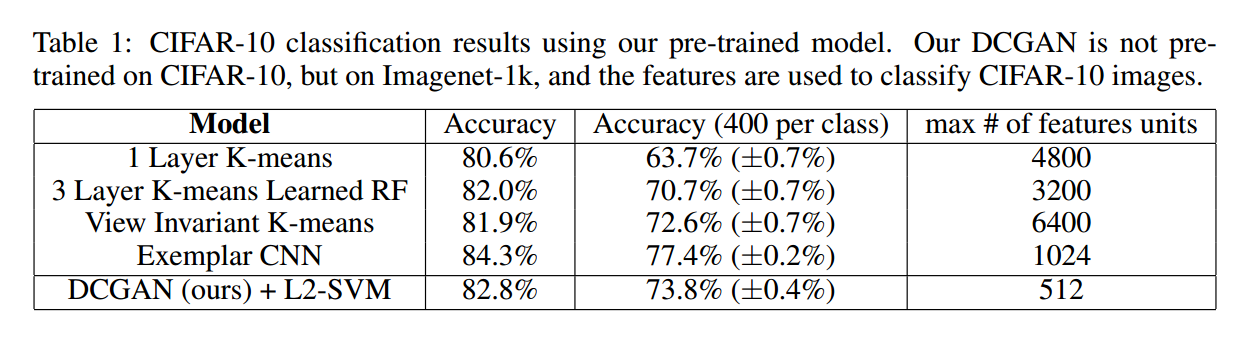
一种评价无监督表示学习算法的方式是:将其作为 特征提取器(feature extractor)在监督的 dataset 上,然后评价线性模型在这些特征上的拟合能力(evaluate the performance of linear models fitted on top of these features)。
作者将 K-means 这种无监督学习方法作为一种 baseline,并且与之在 cifar-10 数据集上进行了对比。
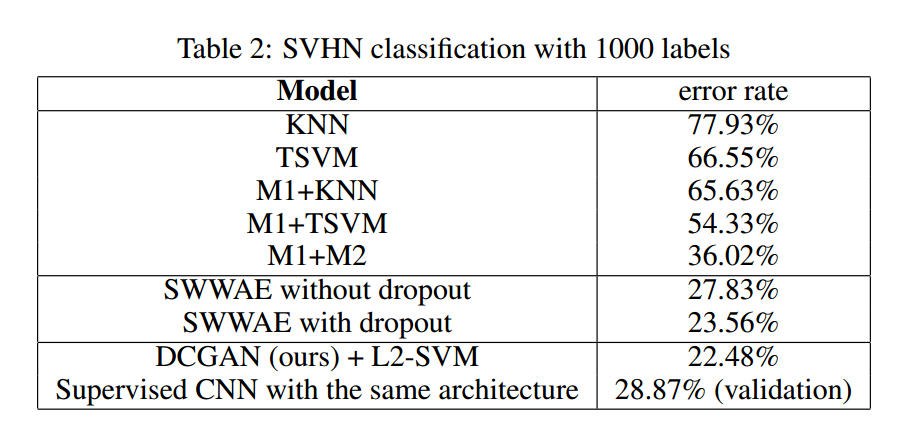
2. Classifying SVHN digits using GANs as a feature extractor .
在 SVHN dataset 上,作者将 DCGAN 的 discriminator 提取出来的特征,在 supervised learning 上做了测试。作者类似于监督学习的思路,将数据集划分开来。本文的方法取得了不错的效果,并且表明:the CNN architecture used in DCGANs is not the key contributing factor of the model‘s performance by training a purely supervised CNN with the same architecture on the same data and optimizing this model via random search over 64 hyperparameter trials .
Investgating and Visualizing the Intervals of the Networks .

Manipulating the Generator Representation :