应用技术点
flask源码上下文管理
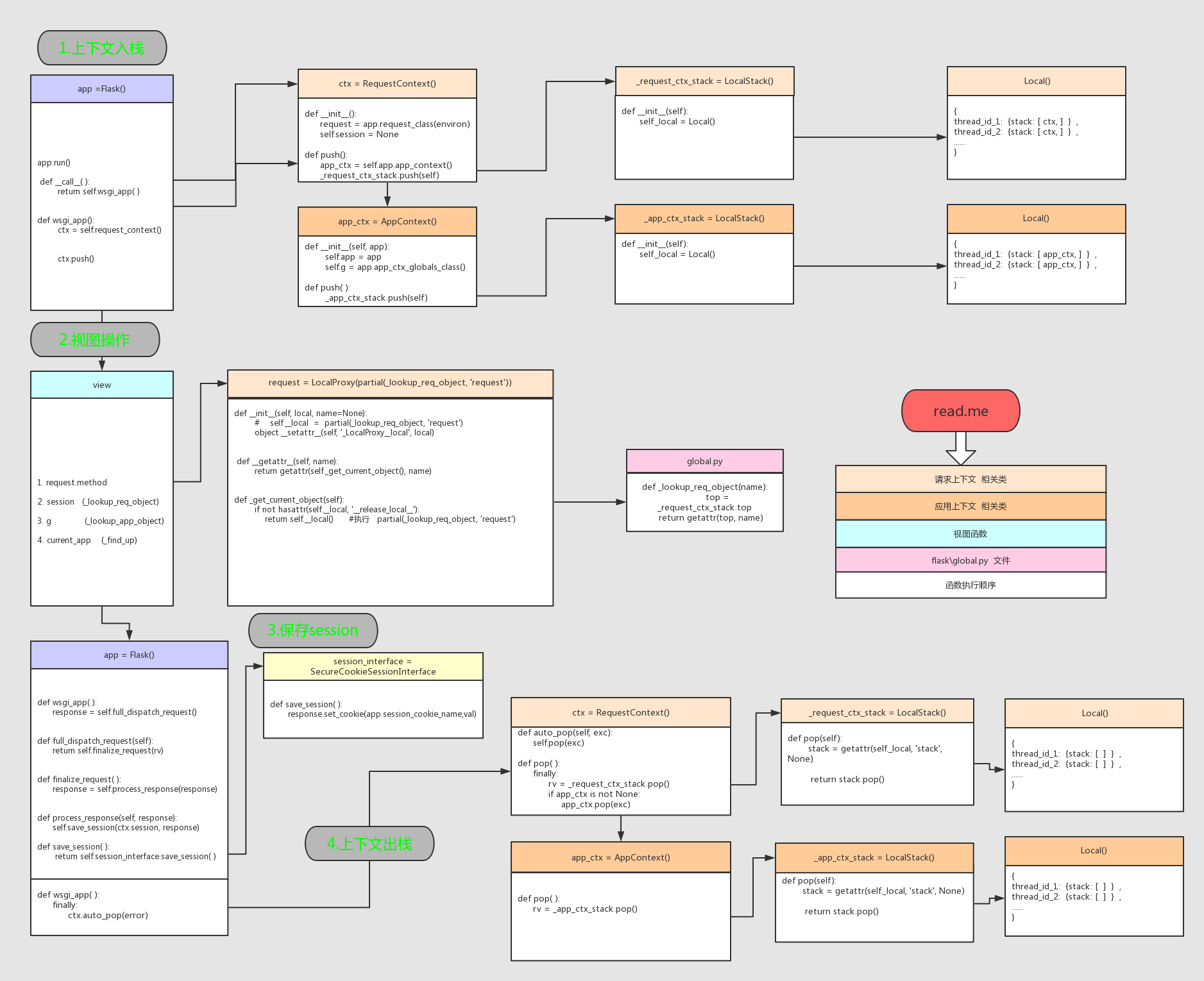
1、综述过程
将请求对象压入栈
1.请求进入
__call__ ---> wsgi_app ---> ctx = self.request_context(environ)
初始化请求对象
2.通过ctx.puth()建立2个请求堆栈(采用threading.local)
--app_ctx(app,g)
--ctx(request,session)
3._implicit_app_ctx_stack初始化
4._request_ctx_stack初始化
从栈中将请求对象调取出来
1.经过层层建立到达视图函数
--request
--session
--current_app
--g
2.以上四个对象通过localProxy(采用threading.local),调用
--_lookup_app_object
--_find_app
--_lookup_app
3.以上三个方法调用
_lookup_req_object ----> _implicit_app_ctx_stack
_find_app和_lookup_app ----> _request_ctx_stack
2、将请求对象压入栈
1.请求进入
__call__ ---> wsgi_app ---> ctx = self.request_context(environ)
初始化请求对象
wsgi_app源码
# Flask 类 def wsgi_app(self, environ, start_response): ctx = self.request_context(environ) ctx.push() error = None try: try: # 4 执行视图函数 response = self.full_dispatch_request() except Exception as e: # 异常处理试图报错,包含信号2345报错执行,got_request_exception信号 error = e response = self.handle_exception(e) except: error = sys.exc_info()[1] raise # 将处理的内容,返回给用户浏览器 return response(environ, start_response) finally: if self.should_ignore_error(error): error = None # 9、结束 ctx.auto_pop(error)
self.request_context(environ)
# Flask类 def request_context(self, environ): return RequestContext(self, environ)
RequestContext(self, environ)
# RequestContest类 def __init__(self, app, environ, request=None): self.app = app
# 初始化request请求对象 if request is None: request = app.request_class(environ) self.request = request self.url_adapter = app.create_url_adapter(self.request) self.flashes = None self.session = None
2.通过ctx.puth()建立2个请求堆栈(采用threading.local)
# RequestContext类 def push(self): top = _request_ctx_stack.top if top is not None and top.preserved: top.pop(top._preserved_exc) # Before we push the request context we have to ensure that there # is an application context. app_ctx = _app_ctx_stack.top if app_ctx is None or app_ctx.app != self.app: # app_ctx = AppContext(self.app) --> _implictit_app_ctx_stack(app,g) app_ctx = self.app.app_context() app_ctx.push() self._implicit_app_ctx_stack.append(app_ctx) else: self._implicit_app_ctx_stack.append(None) if hasattr(sys, 'exc_clear'): sys.exc_clear() ''' 请求相关数据,加到local中 ''' _request_ctx_stack.push(self) # Open the session at the moment that the request context is # available. This allows a custom open_session method to use the # request context (e.g. code that access database information # stored on `g` instead of the appcontext). self.session = self.app.open_session(self.request) if self.session is None: self.session = self.app.make_null_session()
3._implicit_app_ctx_stack 调用
--app_ctx(app,g) --> self._implicit_app_ctx_stack.append(app_ctx)堆栈
top = _request_ctx_stack.top
_request_ctx_stack = LocalStack()
class LocalStack(object):
def __init__(self):
self._local = Local()
def __release_local__(self):
self._local.__release_local__()
def _get__ident_func__(self):
return self._local.__ident_func__
def _set__ident_func__(self, value):
object.__setattr__(self._local, '__ident_func__', value)
__ident_func__ = property(_get__ident_func__, _set__ident_func__)
del _get__ident_func__, _set__ident_func__
def __call__(self):
def _lookup():
rv = self.top
if rv is None:
raise RuntimeError('object unbound')
return rv
return LocalProxy(_lookup)
def push(self, obj):
"""Pushes a new item to the stack"""
rv = getattr(self._local, 'stack', None)
if rv is None:
self._local.stack = rv = []
rv.append(obj)
return rv
def pop(self):
"""Removes the topmost item from the stack, will return the
old value or `None` if the stack was already empty.
"""
stack = getattr(self._local, 'stack', None)
if stack is None:
return None
elif len(stack) == 1:
release_local(self._local)
return stack[-1]
else:
return stack.pop()
@property
def top(self):
"""The topmost item on the stack. If the stack is empty,
`None` is returned.
"""
try:
return self._local.stack[-1]
except (AttributeError, IndexError):
return None
app_ctx = self.app.app_context()
# Flask类
def app_context(self):
return AppContext(self)
AppContext(self)
# AppContext类,初始化
def __init__(self, app):
self.app = app # 等于Flask对象
self.url_adapter = app.create_url_adapter(None)
self.g = app.app_ctx_globals_class() # Flask系统全局变量
# Like request context, app contexts can be pushed multiple times
# but there a basic "refcount" is enough to track them.
self._refcnt = 0
4._request_ctx_stack调用
--_request_ctx_stack.push(self) (请求相关)(堆栈)
def push(self, obj): """Pushes a new item to the stack""" rv = getattr(self._local, 'stack', None) if rv is None: self._local.stack = rv = [] rv.append(obj) return rv
self._local
class Local(object): __slots__ = ('__storage__', '__ident_func__') def __init__(self): object.__setattr__(self, '__storage__', {}) object.__setattr__(self, '__ident_func__', get_ident) def __iter__(self): return iter(self.__storage__.items()) def __call__(self, proxy): """Create a proxy for a name.""" return LocalProxy(self, proxy) def __release_local__(self): self.__storage__.pop(self.__ident_func__(), None) def __getattr__(self, name): try: return self.__storage__[self.__ident_func__()][name] except KeyError: raise AttributeError(name) def __setattr__(self, name, value): ident = self.__ident_func__() storage = self.__storage__ try: storage[ident][name] = value except KeyError: storage[ident] = {name: value} def __delattr__(self, name): try: del self.__storage__[self.__ident_func__()][name] except KeyError: raise AttributeError(name)
3、从栈中将请求对象调取出来
--request --->_lookup_req_object
--session --->_lookup_req_object
--current_app--->_find_app
--g--->_lookup_app_object
current_app = LocalProxy(_find_app) request = LocalProxy(partial(_lookup_req_object, 'request')) session = LocalProxy(partial(_lookup_req_object, 'session')) g = LocalProxy(partial(_lookup_app_object, 'g'))
LocalProxy
@implements_bool class LocalProxy(object): __slots__ = ('__local', '__dict__', '__name__', '__wrapped__') def __init__(self, local, name=None): object.__setattr__(self, '_LocalProxy__local', local) object.__setattr__(self, '__name__', name) if callable(local) and not hasattr(local, '__release_local__'): # "local" is a callable that is not an instance of Local or # LocalManager: mark it as a wrapped function. object.__setattr__(self, '__wrapped__', local) def _get_current_object(self): if not hasattr(self.__local, '__release_local__'): return self.__local() try: return getattr(self.__local, self.__name__) except AttributeError: raise RuntimeError('no object bound to %s' % self.__name__)
2.以上四个对象通过localProxy(采用threading.local),调用
--_lookup_app_object
def _lookup_req_object(name): top = _request_ctx_stack.top if top is None: raise RuntimeError(_request_ctx_err_msg) return getattr(top, name)
--_find_app
def _find_app(): top = _app_ctx_stack.top if top is None: raise RuntimeError(_app_ctx_err_msg) return top.app
--_lookup_app
def _lookup_app_object(name): top = _app_ctx_stack.top if top is None: raise RuntimeError(_app_ctx_err_msg) return getattr(top, name)
3.以上三个方法调用
_lookup_req_object ----> _implicit_app_ctx_stack
_find_app和_lookup_app ----> _request_ctx_stack
4.上下文出栈流程
session的保存方式:
wsgi_app()-->full_dispatch_request-->self.dispatch_request()
wsgi_app()
def wsgi_app(self, environ, start_response): try: try: # 4 执行视图函数 response = self.full_dispatch_request() except Exception as e: # 异常处理试图报错,包含信号2345报错执行,got_request_exception信号 error = e response = self.handle_exception(e) except: error = sys.exc_info()[1] raise # 将处理的内容,返回给用户浏览器 return response(environ, start_response) finally: if self.should_ignore_error(error): error = None # 9、结束 ctx.auto_pop(error)
full_dispatch_request
# Flask类
def full_dispatch_request(self): """Dispatches the request and on top of that performs request pre and postprocessing as well as HTTP exception catching and error handling. .. versionadded:: 0.7 """ self.try_trigger_before_first_request_functions() try: request_started.send(self) rv = self.preprocess_request() if rv is None: # 触发执行视图函数,使用session rv = self.dispatch_request() except Exception as e: rv = self.handle_user_exception(e) return self.finalize_request(rv)
finalize_request(self, rv, from_error_handler=False):
# Flask类 def finalize_request(self, rv, from_error_handler=False): response = self.make_response(rv) try: '''8、''' response = self.process_response(response) request_finished.send(self, response=response) except Exception: if not from_error_handler: raise self.logger.exception('Request finalizing failed with an ' 'error while handling an error') return response
self.process_response(response)
# Flask类
def process_response(self, response): ctx = _request_ctx_stack.top bp = ctx.request.blueprint funcs = ctx._after_request_functions if bp is not None and bp in self.after_request_funcs: funcs = chain(funcs, reversed(self.after_request_funcs[bp])) if None in self.after_request_funcs: funcs = chain(funcs, reversed(self.after_request_funcs[None])) # 执行 after_request装饰器 for handler in funcs: response = handler(response) # 将内存中的session持久化到:数据库、.... if not self.session_interface.is_null_session(ctx.session): self.save_session(ctx.session, response) return response
self.save_session(ctx.session, response)
# Flask类
def save_session(self, session, response): return self.session_interface.save_session(self, session, response)
上下文的出栈方式:
wsgi_app()-->ctx.auto_pop(error)-->
auto_pop
# RequestContext类 def auto_pop(self, exc): if self.request.environ.get('flask._preserve_context') or (exc is not None and self.app.preserve_context_on_exception): self.preserved = True self._preserved_exc = exc else: self.pop(exc)
self.pop(exc)
#RequestContext类 def pop(self, exc=_sentinel): app_ctx = self._implicit_app_ctx_stack.pop() try: clear_request = False if not self._implicit_app_ctx_stack: self.preserved = False self._preserved_exc = None if exc is _sentinel: exc = sys.exc_info()[1] self.app.do_teardown_request(exc) # If this interpreter supports clearing the exception information # we do that now. This will only go into effect on Python 2.x, # on 3.x it disappears automatically at the end of the exception # stack. if hasattr(sys, 'exc_clear'): sys.exc_clear() request_close = getattr(self.request, 'close', None) if request_close is not None: request_close() clear_request = True finally: rv = _request_ctx_stack.pop() # get rid of circular dependencies at the end of the request # so that we don't require the GC to be active. if clear_request: rv.request.environ['werkzeug.request'] = None # Get rid of the app as well if necessary. if app_ctx is not None: app_ctx.pop(exc) assert rv is self, 'Popped wrong request context. ' '(%r instead of %r)' % (rv, self)
rv = _request_ctx_stack.pop()
# LocalStack类 def pop(self): stack = getattr(self._local, 'stack', None) if stack is None: return None elif len(stack) == 1: release_local(self._local) return stack[-1] else: return stack.pop()
app_ctx.pop(exc)
#AppContext类
def pop(self, exc=_sentinel):
try:
self._refcnt -= 1
if self._refcnt <= 0:
if exc is _sentinel:
exc = sys.exc_info()[1]
self.app.do_teardown_appcontext(exc)
finally:
rv = _app_ctx_stack.pop()
assert rv is self, 'Popped wrong app context. (%r instead of %r)'
% (rv, self)
# 信号执行8 appcontext_popped
appcontext_popped.send(self.app)
完成