本篇文章要分享的是基于MATLAB的腐蚀膨胀算法实现,腐蚀膨胀是形态学图像处理的基础,腐蚀在二值图像的基础上做“收缩”或“细化”操作,膨胀在二值图像的基础上做“加长”或“变粗”的操作。
什么是二值图像呢?把一幅图片看做成一个二维的数组,那么二值图像是一个只有0和1的逻辑数组,我们前面Sobel边缘检测后的图像输出边缘效果,设置个阈值,大于阈值输出为1,小于阈值输出为0,最后输出就是一幅二值图像了。
腐蚀
腐蚀是一种消除边界点,使边界向内部收缩的过程。可以用来消除小且无意义的物体。用3X3的结构元素,扫描图像的每一个像素,用结构元素与其覆盖的二值图像做“与”操作,如果都为1,结果图像的该像素为1。否则为0。结果会使二值图像小一圈。
有一个形象的比喻来可以说明该运算,用0表示蛀虫,1表示大米。蛀虫腐蚀大米的过程便是

腐蚀
如图所示,对于一个像素矩阵而言,只要有蛀虫(0)的存在,大米(1)就会被腐蚀掉了,即使只存在一个蛀虫(0),但是还是会被蛀虫腐蚀完毕,最后一幅图上面由于没有蛀虫(0)所以大米完好无损。
关于算法的实现,可以用下式子来表示,即3x3像素的运算:
P = P11 & P12 & P13 & P21 & P22 & P23 & P31 & P32 & P33
在FPGA中,为了通过面积去换速度,我们将上式改变如下:
P1 = P11 & P12 & P13
P2 = P21 & P22 & P23
P3 = P31 & P32 & P33
P = P1 & P2 & P3
MATLAB中可以直接写一个按位或运算。
膨胀
膨胀是将与物体接触的所有背景点合并到该物体中,使边界向外部扩张的过程。可以用来填补物体中的空洞。用3X3的结构元素,扫描图像的每一个像素,用结构元素与其覆盖的二值图像做“与”操作,如果都为0,结果图像的该像素为0,。否则为1。结果使二值图像扩大一圈。
先腐蚀后膨胀的过程称为开运算。用来消除小物体、在纤细点处分离物体、平滑较大物体的边界的同时并不明显的改变其面积。先膨胀后腐蚀的过程称为比运算,用来填充物体内细小空间、连接邻近物体、平滑其边界的同时并不明显改变其面积。
膨胀算法用最简单的比喻来描述:0表示害虫,1表示青蛙,青蛙吃了害虫表示膨胀运算,我们用3*3像素阵列来解释:
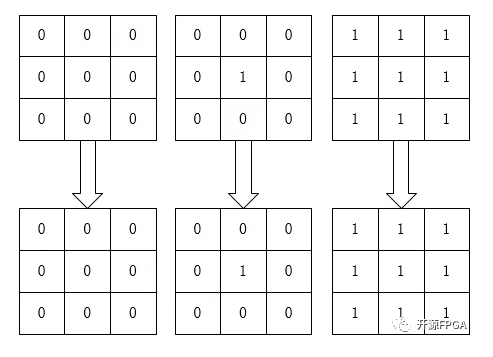
膨胀
如图所示,图左只有害虫(0),所以害虫都活着,中间那个图,虽然只有一个害虫,但是还是会被青蛙全部吃掉,最右边的那幅图,都是青蛙,所以青蛙始终是青蛙。
关于算法的实现,可以用下式子来表示,即3x3像素的运算:
P = P11 | P12 | P13 | P21 | P22 | P23 | P31 | P32 | P33
在HDL中,为了通过面积去换速度,我们将上式改变如下:
P1 = P11 | P12 | P13
P2 = P21 | P22 | P23
P3 = P31 | P32 | P33
P = P1 | P2 | P3
MATLAB中可以直接写一个按位与运算。
开运算闭运算
先腐蚀后膨胀叫开运算,开运算的作用是清除图像边缘周围非边缘的细小的点。先膨胀后腐蚀为闭运算,闭运算的作用是清除图像内部的空洞,
如果我们的目标物体外面有很多无关的小区域,就用开运算去除掉;如果物体内部有很多小黑洞,就用闭运算填充掉。
MATLAB逻辑运算函数
bitand(), 对十进制数进行逐位逻辑与运算:先将十进制数转换成二进制数,然后逐位与运算,其运算结果转换为十进制。
bitor(), 对十进制数进行逐位逻辑或运算:先将十进制数转换成二进制数,然后逐位与运算,其运算结果转换为十进制。
MATLAB代码实现
%%%imopen Erosion_Dilation clc,clear,close all,clear all img = imread('1.png'); img_gray = rgb2gray(img); figure; subplot(2,2,1),imshow(img),title('灰度图像') subplot(2,2,2),imshow(img_gray),title('灰度图像') hold on; %%中值滤波 %Median Filter imgn = imnoise(img_gray,'salt & pepper',0.02); subplot(2,2,3),imshow(imgn),title('椒盐噪声图像'); Median_Img = img_gray; [ROW,COL] = size(Median_Img); for r = 2:ROW-1 for c = 2:COL-1 median3x3 =[imgn(r-1,c-1) imgn(r-1,c) imgn(r-1,c+1) imgn(r,c-1) imgn(r,c) imgn(r,c+1) imgn(r+1,c-1) imgn(r+1,c) imgn(r+1,c+1)]; sort1 = sort(median3x3, 2, 'descend'); sort2 = sort([sort1(1), sort1(4), sort1(7)], 'descend'); sort3 = sort([sort1(2), sort1(5), sort1(8)], 'descend'); sort4 = sort([sort1(3), sort1(6), sort1(9)], 'descend'); mid_num = sort([sort2(3), sort3(2), sort4(1)], 'descend'); Median_Img(r,c) = mid_num(2); end end subplot(2,2,4),imshow(Median_Img),title('中值滤波图像') %%Sobel算子边缘检测 Median_Img = double(Median_Img); Sobel_Img = zeros(ROW,COL); Sobel_Threshold = 80; for r = 2:ROW-1 for c = 2:COL-1 Sobel_x = Median_Img(r-1,c+1) + 2*Median_Img(r,c+1) + Median_Img(r+1,c+1) - Median_Img(r-1,c-1) - 2*Median_Img(r,c-1) - Median_Img(r+1,c-1); Sobel_y = Median_Img(r-1,c-1) + 2*Median_Img(r-1,c) + Median_Img(r-1,c+1) - Median_Img(r+1,c-1) - 2*Median_Img(r+1,c) - Median_Img(r+1,c+1); %Sobel_Num = abs(Sobel_x) + abs(Sobel_y); Sobel_Num = sqrt(Sobel_x^2 + Sobel_y^2); if(Sobel_Num > Sobel_Threshold) Sobel_Img(r,c)=1; else Sobel_Img(r,c)=0; end end end figure subplot(2,2,1),imshow(Sobel_Img),title('Sobel算子图像') BW1=edge(img_gray,'sobel'); %用Sobel算子进行边缘检测 subplot(2,2,2),imshow(BW1),title('Sobel算子图像') %%腐蚀算法 Erosion_img = zeros(ROW,COL); for r = 2:ROW-1 for c = 2:COL-1 %and1 = bitand(Sobel_Img(r-1,c-1) + bitand(Sobel_Img(r-1,c) + Sobel_Img(r-1,c+1))); %and2 = bitand(Sobel_Img(r ,c-1) + bitand(Sobel_Img(r ,c) + Sobel_Img(r ,c+1))); %and3 = bitand(Sobel_Img(r+1,c-1) + bitand(Sobel_Img(r+1,c) + Sobel_Img(r+1,c+1))); %Erosion_img(r,c) = bitand(and1,bitand(and2,and3)); and1 = Sobel_Img(r-1,c-1) & Sobel_Img(r-1,c) & Sobel_Img(r-1,c+1); and2 = Sobel_Img(r ,c-1) & Sobel_Img(r ,c) & Sobel_Img(r ,c+1); and3 = Sobel_Img(r+1,c-1) & Sobel_Img(r+1,c) & Sobel_Img(r+1,c+1); Erosion_img(r,c) = and1 & and2 & and3; end end subplot(2,2,3),imshow(Erosion_img),title('腐蚀图像') %%膨胀算法 Dilation_img = zeros(ROW,COL); for r = 2:ROW-1 for c = 2:COL-1 %and1 = bitand(Sobel_Img(r-1,c-1) + bitand(Sobel_Img(r-1,c) + Sobel_Img(r-1,c+1))); %and2 = bitand(Sobel_Img(r ,c-1) + bitand(Sobel_Img(r ,c) + Sobel_Img(r ,c+1))); %and3 = bitand(Sobel_Img(r+1,c-1) + bitand(Sobel_Img(r+1,c) + Sobel_Img(r+1,c+1))); %Erosion_img(r,c) = bitand(and1,bitand(and2,and3)); and1 = Sobel_Img(r-1,c-1) | Sobel_Img(r-1,c) | Sobel_Img(r-1,c+1); and2 = Sobel_Img(r ,c-1) | Sobel_Img(r ,c) | Sobel_Img(r ,c+1); and3 = Sobel_Img(r+1,c-1) | Sobel_Img(r+1,c) | Sobel_Img(r+1,c+1); Dilation_img(r,c) = and1 | and2 | and3; end end subplot(2,2,4),imshow(Dilation_img),title('膨胀图像') %%开运算-先腐蚀后膨胀算法 Erosion_Dilation_img = zeros(ROW,COL); for r = 2:ROW-1 for c = 2:COL-1 %and1 = bitand(Sobel_Img(r-1,c-1) + bitand(Sobel_Img(r-1,c) + Sobel_Img(r-1,c+1))); %and2 = bitand(Sobel_Img(r ,c-1) + bitand(Sobel_Img(r ,c) + Sobel_Img(r ,c+1))); %and3 = bitand(Sobel_Img(r+1,c-1) + bitand(Sobel_Img(r+1,c) + Sobel_Img(r+1,c+1))); %Erosion_img(r,c) = bitand(and1,bitand(and2,and3)); and1 = Erosion_img(r-1,c-1) | Erosion_img(r-1,c) | Erosion_img(r-1,c+1); and2 = Erosion_img(r ,c-1) | Erosion_img(r ,c) | Erosion_img(r ,c+1); and3 = Erosion_img(r+1,c-1) | Erosion_img(r+1,c) | Erosion_img(r+1,c+1); Erosion_Dilation_img(r,c) = and1 | and2 | and3; end end figure subplot(1,2,1),imshow(Erosion_Dilation_img),title('先腐蚀在膨胀图像') %%闭运算-先膨胀后腐蚀算法 Dilation_Erosion_img = zeros(ROW,COL); for r = 2:ROW-1 for c = 2:COL-1 %and1 = bitand(Sobel_Img(r-1,c-1) + bitand(Sobel_Img(r-1,c) + Sobel_Img(r-1,c+1))); %and2 = bitand(Sobel_Img(r ,c-1) + bitand(Sobel_Img(r ,c) + Sobel_Img(r ,c+1))); %and3 = bitand(Sobel_Img(r+1,c-1) + bitand(Sobel_Img(r+1,c) + Sobel_Img(r+1,c+1))); %Erosion_img(r,c) = bitand(and1,bitand(and2,and3)); and1 = Dilation_img(r-1,c-1) & Dilation_img(r-1,c) & Dilation_img(r-1,c+1); and2 = Dilation_img(r ,c-1) & Dilation_img(r ,c) & Dilation_img(r ,c+1); and3 = Dilation_img(r+1,c-1) & Dilation_img(r+1,c) & Dilation_img(r+1,c+1); Dilation_Erosion_img(r,c) = and1 & and2 & and3; end end subplot(1,2,2),imshow(Dilation_Erosion_img),title('先膨胀在腐蚀图像')