介绍:
Flume由Cloudera公司开发,是一个分布式、高可靠、高可用的海量日志采集、聚 合、传输的系统。
简单的说,Flume是实时采集日志的数据采集引擎。
重要组件:Source、Channel、Sink
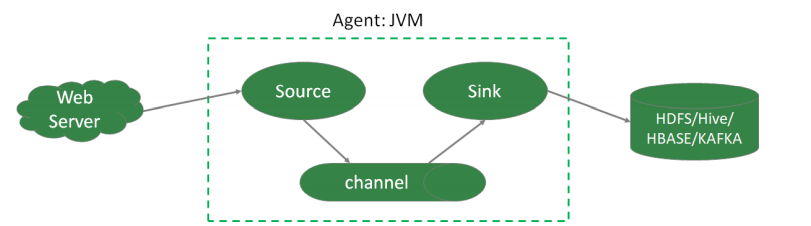
- Agent本质上是一个 JVM 进程,该JVM进程控制Event数据流从外部日志生产者 那里传输到目的地(或者是下一个Agent)。一个完整的Agent中包含了三个组 件Source、Channel和Sink,Source是指数据的来源和方式,Channel是一个数 据的缓冲池,Sink定义了数据输出的方式和目的地。
- Source是负责接收数据到Flume Agent的组件。Source组件可以处理各种类 型、各种格式的日志数据,包括avro、exec、spooldir、netcat等。
- Channel是位于Source和Sink之间的缓冲区。Channel允许Source和Sink运作 在不同的速率上。Channel是线程安全的,可以同时处理多个Source的写入操作 及多个Sink的读取操作。
- Memory Channel是内存中的队列。Memory Channel在允许数据丢失的情 景下适用。如果不允许数据丢失,应该避免使用Memory Channel,因为程 序死亡、机器宕机或者重启都可能会导致数据丢失;
- File Channel将所有事件写到磁盘。因此在程序关闭或机器宕机的情况下不 会丢失数据;
- Sink不断地轮询Channel中的事件且批量地移除它们,并将这些事件批量写入到 存储或索引系统、或者被发送到另一个Flume Agent。
- Sink是完全事务性的。在从Channel批量删除数据之前,每个Sink用Channel启 动一个事务。批量事件一旦成功写出到存储系统或下一个Flume Agent,Sink就 利用Channel提交事务。事务一旦被提交,该Channel从自己的内部缓冲区删除 事件。
- Event是Flume定义的一个数据流传输的最小单位。
flume 流程:
- 1. Source接收事件,交给其Channel处理器处理事件
- 2. 处理器通过拦截器Interceptor,对事件一些处理,比如压缩解码,正则拦截,时 间戳拦截,分类等
- 3. 经过拦截器处理过的事件再传给Channel选择器,将事件写入相应的Channel。 Channel Selector有两种:
- Replicating Channel Selector(默认),会将source过来的Event发往所有 Channel(比较常用的场景是,用多个Channel实现冗余副本,保证可用性)
- Multiplexing Channel Selector,根据配置分发event。此selector会根据 event中某个header对应的value来将event发往不同的channel,一般配合拦截器使用
- 4. 最后由Sink处理器处理各个Channel的事件
常用source:
- avro source:监听 Avro 端口来接收外部 avro 客户端的事件流。avro-source 接收到的是经过avro序列化后的数据,然后反序列化数据继续传输。如果是avro source的话,源数据必须是经过avro序列化后的数据。利用 Avro source可以实现多 级流动、扇出流、扇入流等效果。接收通过flume提供的avro客户端发送的日 志信 息。
- Taildir Source(1.7):监控指定的多个文件,一旦文件内有新写入的数据, 就会将其写入到指定的sink内,本来源可靠性高,不会丢失数据。其不会对于跟踪的 文件有任何处理,不会重命名也不会删除,不会做任何修改。目前不支持Windows 系统,不支持读取二进制文件,支持一行一行的读取文本文件。
- netcat source:一个NetCat Source用来监听一个指定端口,并接收监听到的 数据。
常用channel:
- (1)memory channel:缓存到内存中(最常用)
- (2)file channel:缓存到文件中
- (3)JDBC channel:通过JDBC缓存到关系型数据库中
- (4)kafka channel:缓存到kafka中
常用sink:
- (1)logger sink:将信息显示在标准输出上,主要用于测试
- (2)avro sink:Flume events发送到sink,转换为Avro events,并发送到配置好 的hostname/port。从配置好的channel按照配置好的批量大小批量获取events
- (3)null sink:将接收到events全部丢弃
- (4)HDFS sink:将 events 写进HDFS。支持创建文本和序列文件,支持两种文件 类型压缩。文件可以基于数据的经过时间、大小、事件的数量周期性地滚动
- (5)Hive sink:该sink streams 将包含分割文本或者JSON数据的events直接传送 到Hive表或分区中。使用Hive 事务写events。当一系列events提交到Hive时,它们 马上可以被Hive查询到
- (6)HBase sink:保存到HBase中
- (7)kafka sink:保存到kafka中
flume 文档链接: Flume 1.9用户手册中文版 — 可能是目前翻译最完整的版本了 (liyifeng.org)
案例:netcat source,memory,logger sink
# a1是agent的名称。source、channel、sink的名称分别为:r1 c1 k1 a1.sources = r1 a1.channels = c1 a1.sinks = k1 # source a1.sources.r1.type = netcat a1.sources.r1.bind = linux123 a1.sources.r1.port = 8888 # channel a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 10000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # sink a1.sinks.k1.type = logger # source、channel、sink之间的关系 a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
启动:
$FLUME_HOME/bin/flume-ng agent --name a1 --conf-file $FLUME_HOME/conf/flume-netcat-logger.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
- name。定义agent的名字,要与参数文件一致
- conf-file。指定参数文件位置
- -D表示flume运行时动态修改 flume.root.logger 参数属性值,并将控制台日志 打印级别设置为INFO级别。日志级别包括:log、info、warn、error
案例:taildir,memory,hdfs/file_roll
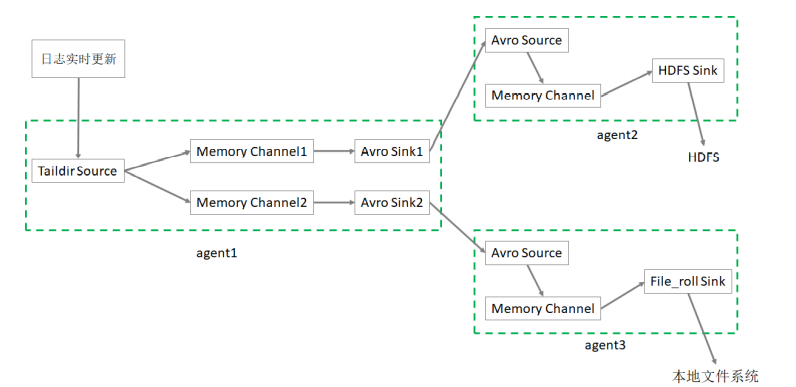
# Name the components on this agent a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 k2 a1.channels = c1 c2 # 将数据流复制给所有channel a1.sources.r1.selector.type = replicating # source a1.sources.r1.type = taildir # 记录每个文件最新消费位置 a1.sources.r1.positionFile = /root/flume/taildir_position.json a1.sources.r1.filegroups = f1 # 备注:.*log 是正则表达式;这里写成 *.log 是错误的 a1.sources.r1.filegroups.f1 = /tmp/root/.*log # sink a1.sinks.k1.type = avro a1.sinks.k1.hostname = linux123 a1.sinks.k1.port = 9091 a1.sinks.k2.type = avro a1.sinks.k2.hostname = linux123 a1.sinks.k2.port = 9092 # channel a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 10000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 500 a1.channels.c2.type = memory a1.channels.c2.capacity = 10000 a1.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 500 # Bind the source and sink to the channel a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 a1.sinks.k2.channel = c2
# Name the components on this agent a2.sources = r1 a2.sinks = k1 a2.channels = c1 # Describe/configure the source a2.sources.r1.type = avro a2.sources.r1.bind = linux123 a2.sources.r1.port = 9091 # Describe the channel a2.channels.c1.type = memory a2.channels.c1.capacity = 10000 a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 500
# Describe the sink a2.sinks.k1.type = hdfs a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = hdfs://linux121:8020/flume2/%Y%m%d/%H
# 上传文件的前缀
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = flume2-
# 是否使用本地时间戳
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true
# 500个Event才flush到HDFS一次
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.batchSize = 500
# 设置文件类型,可支持压缩
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream
# 60秒生成一个新的文件
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval = 60
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize = 0
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount = 0
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.minBlockReplicas = 1
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a2.sources.r1.channels = c1
a2.sinks.k1.channel = c1
# Name the components on this agent a3.sources = r1 a3.sinks = k1 a3.channels = c2 # Describe/configure the source a3.sources.r1.type = avro a3.sources.r1.bind = linux123 a3.sources.r1.port = 9092 # Describe the sink a3.sinks.k1.type = file_roll # 目录需要提前创建好 a3.sinks.k1.sink.directory = /root/flume/output # Describe the channel a3.channels.c2.type = memory a3.channels.c2.capacity = 10000 a3.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 500 # Bind the source and sink to the channel a3.sources.r1.channels = c2 a3.sinks.k1.channel = c2
分别启动:
$FLUME_HOME/bin/flume-ng agent --name a3 --conf-file ~/conf/flume-avro-file.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console & $FLUME_HOME/bin/flume-ng agent --name a2 --conf-file ~/conf/flume-avro-hdfs.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console & $FLUME_HOME/bin/flume-ng agent --name a1 --conf-file ~/conf/flume-taildir-avro.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console &
hdfs sink 参数说明:
一般使用 HDFS Sink 都会采用滚动生成文件的方式,滚动生成文件的策略有:
- 基于时间
- hdfs.rollInterval
- 缺省值:30,单位秒
- 0禁用
- 基于文件大小
- hdfs.rollSize
- 缺省值:1024字节
- 0禁用
- 基于event数量
- hdfs.rollCount
- 10
- 0禁用
- 基于文件空闲时间
- hdfs.idleTimeout
- 缺省值:0。禁用
- 基于HDFS文件副本数
- hdfs.minBlockReplicas
- 默认:与HDFS的副本数一致
- 要将该参数设置为1;否则HFDS文件所在块的复制会引起文件滚动
其他重要配置:
- hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp
- 使用本地时间,而不是event header的时间戳
- 默认值:false
- hdfs.round
- 时间戳是否四舍五入
- 默认值false
- 如果为true,会影响所有的时间,除了t%
- hdfs.roundValue
- 四舍五入的最高倍数(单位配置在hdfs.roundUnit),但是要小于当前时间
- 默认值:1
- hdfs.roundUnit
- 可选值为:second、minute、hour
- 默认值:second
如果要避免hdfs sink产生小文件,参数配置参考如下:
a1.sinks.k1.type=hdfs a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp=true a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path=hdfs://linux121:9000/flume/events/%Y/%m/ %d/%H/%M a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.minBlockReplicas=1 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval=3600 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize=0 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount=0 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.idleTimeout=0
拦截器:
时间戳拦截器:具体参考官方文档
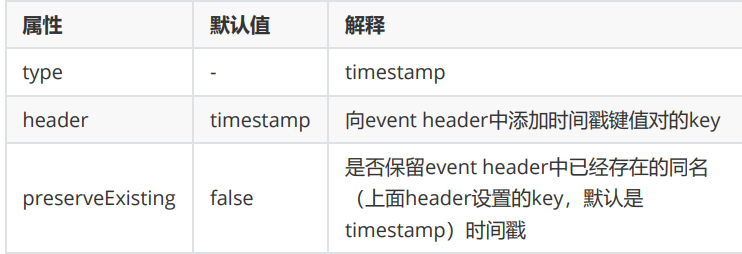
# Name the components on this agent a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 a1.channels = c1 # configure the source a1.sources.r1.type = netcat a1.sources.r1.bind = linux123 a1.sources.r1.port = 8888 # 这部分是新增 时间拦截器的 内容 a1.sources.r1.interceptors = i1 a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.type = timestamp # 是否保留Event header中已经存在的同名时间戳,缺省值false a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.preserveExisting= false # 这部分是新增 时间拦截器的 内容 # Describe the sink a1.sinks.k1.type = logger # Use a channel which buffers events in memory a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 10000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 500 # Bind the source and sink to the channel a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
host 拦截器:
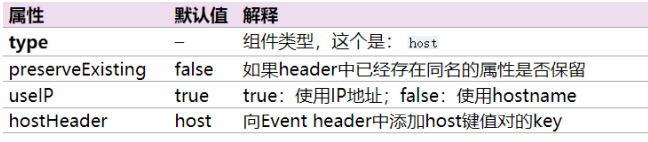
# Name the components on this agent a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 a1.channels = c1 # configure the source a1.sources.r1.type = netcat a1.sources.r1.bind = linux123 a1.sources.r1.port = 8888 # 这部分是新增 时间拦截器 的内容 a1.sources.r1.interceptors = i1 i2 a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.type = timestamp a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.preserveExisting= false # 这部分是新增 主机名拦截器 的内容 a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i2.type = host # 如果header中已经存在同名的属性是否保留 a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i2.preserveExisting= false # true:使用IP地址;false:使用hostname a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i2.useIP = false # 这部分是新增 主机名拦截器 的内容 # Describe the sink a1.sinks.k1.type = logger # Use a channel which buffers events in memory a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 10000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 500 # Bind the source and sink to the channel a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
channel 选择器 :
replication:
a1.sources = r1 a1.channels = c1 c2 c3 a1.sources.r1.selector.type = replicating a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2 c3 a1.sources.r1.selector.optional = c3
multiplexing:
a1.sources = r1 a1.channels = c1 c2 c3 c4 a1.sources.r1.selector.type = multiplexing a1.sources.r1.selector.header = state #以每个Event的 header中的state这个属性的值作为选择channel的依据 a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.CZ = c1 #如果state=CZ,则选 择c1这个channel a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.US = c2 c3 #如果state=US,则选 择c2 和 c3 这两个channel a1.sources.r1.selector.default = c4 #默认使用c4这个channel
Sink组逻辑处理器:
负载均衡:
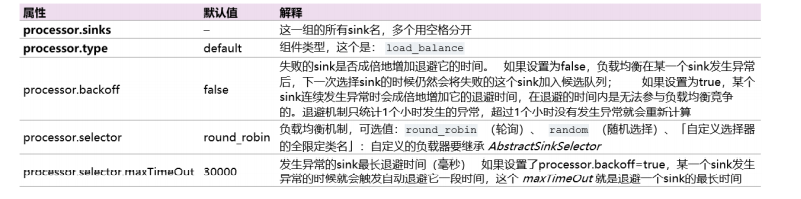
a1.sinkgroups = g1 a1.sinkgroups.g1.sinks = k1 k2 a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.type = load_balance
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.backoff = true
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.selector = random
故障转移:
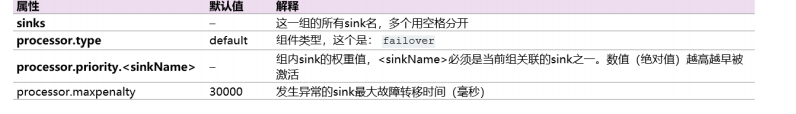
a1.sinkgroups = g1 a1.sinkgroups.g1.sinks = k1 k2 a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.type = failover a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.priority.k1 = 5 a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.priority.k2 = 10 a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.maxpenalty = 1000
flume 事务:
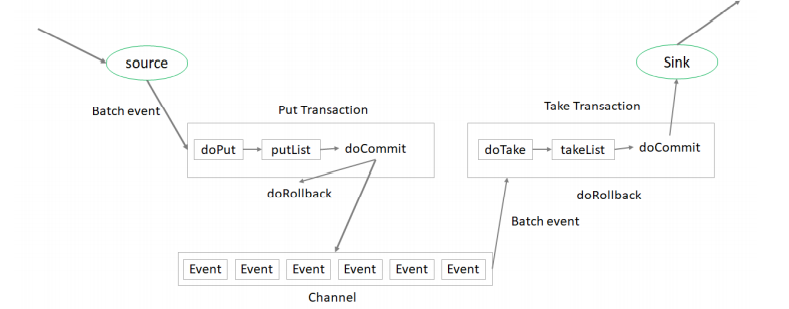
put 事务流程:
- 把一批event写入putList(临时缓冲区)
- 检查channel 是否有足够的空间保存putList的所有event
- 如果可以保存,doCommit,如果不能保存 doRollback
take事务流程:
- 把一批event写入takeList
- 把takeList的所有event 发送给下一级flume 或者其他存储系统
- 如果全部发送成功,doCommit ,如果发送失败, doRollback
flume 是否丢数据:
- source: tailDir source 不丢数据,其他可能丢
- channel: file channel 不丢数据,memory channel 可能丢数据
- sink :不会丢数据,但可能重复(take事务失败重新发送)