Mybatis源码分析-解析器模块
原创-转载请说明出处
1. 解析器模块的作用
- 对XPath进行封装,为mybatis-config.xml配置文件以及映射文件提供支持
- 为处理动态 SQL 语句中的占位符提供支持
2. 解析器模块parsing包
3. 解析器模块parsing包
- GenericTokenParser
- package-info.java
- ParsingException
- PropertyParser
- TokenHandler
- XNode
- XPathParser
mybati-config.xml文件
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!-- autoMappingBehavior should be set in each test case -->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC">
<property name="" value=""/>
</transactionManager>
<dataSource type="UNPOOLED">
<property name="driver" value="org.hsqldb.jdbcDriver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:hsqldb:mem:automapping"/>
<property name="username" value="sa"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="org/apache/ibatis/autoconstructor/AutoConstructorMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
4. mybatis 解析mybatis-config.xml过程
4.1 分析步骤
- 打开mybatis源码项目;
- 进入单元测试目录下:org.apache.ibatis.autoconstructor.AutoConstructorTest,方法:fullyPopulatedSubject();
- 调试模式下运行测试方法fullyPopulatedSubject(),断点观察,mybatis是如何对mybatis-config.xml配置文件进行解析的。
4.2 代码过程解析
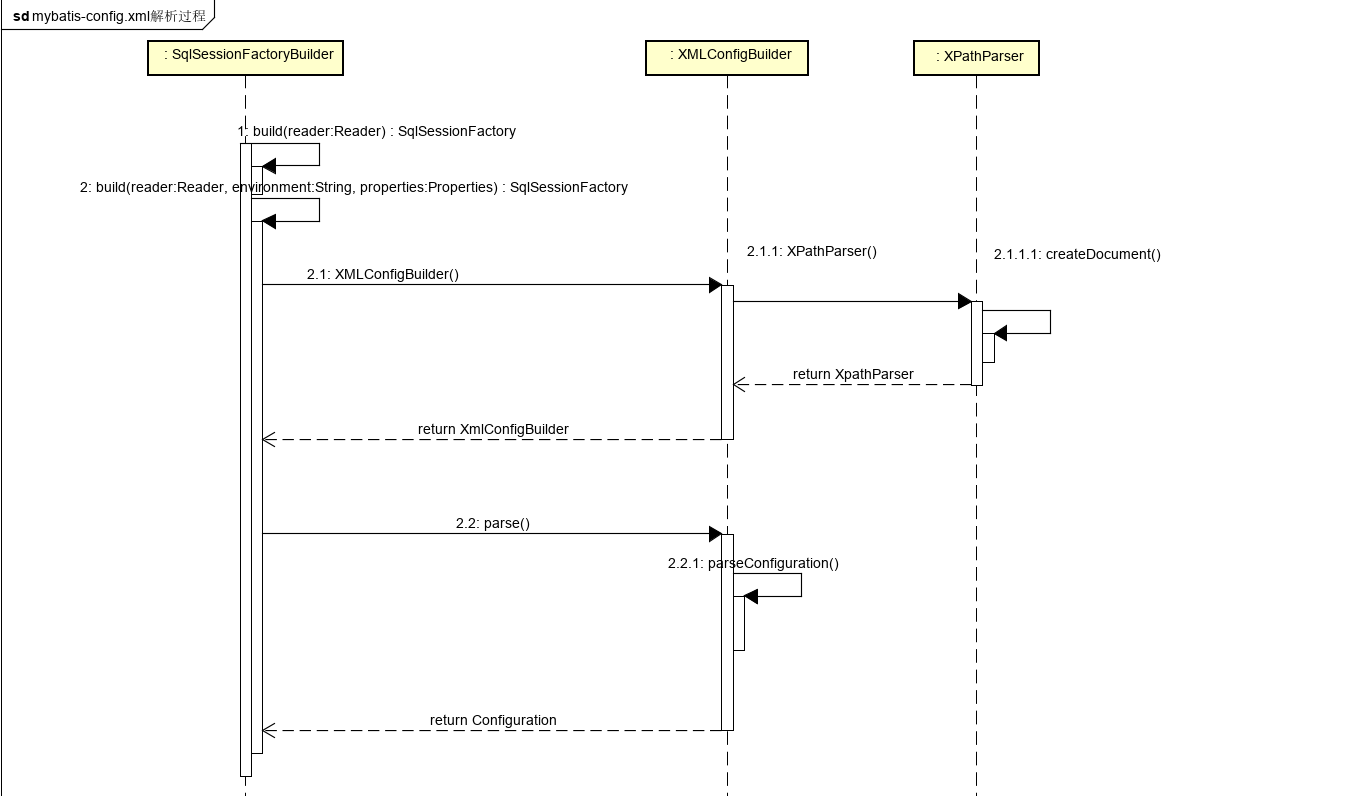
第一步:创建SqlSessionFactory的整体过程
try (Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("org/apache/ibatis/autoconstructor/mybatis-config.xml")) {
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
}
上面代码中,mybatis通过提供一个Resources的工具类来加载配置文件,获取输入流。然后再通过SqlSessionFactoryBuilder的builder方法来构建SqlSessionFactory对象,其中builder方法里的实现就是对mybatis-config.xml配置文件进行解析的入口。下面的代码就是builder方法的具体实现:
1.调用builder方法
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader) {
return build(reader, null, null);
}
2.调用builder重载方法
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
//2.1> 创建配置文件解析器
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(reader, environment, properties);
//2.2> 调用parse方法解析配置文件,将对应的属性存入并生成Configuration对象
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
3.通过Configuration创建SqlSessionFactory
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
//创建DefaultSqlSessionFactory对象
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
上面代码中展示了创建SqlSessionFactory 的整体流程,其中最重要的是2.1:创建配置文件解析器和2.2:调用parse方法解析配置文件,将对应的属性存入并生成Configuration对象
第二步:创建配置文件解析器XMLConfigBuilder
XMLConfigBuilder.class
/**
* 构造XMLConfigBuilder
* @param inputStream 输入流
* @param environment environment环境
* @param props Properties properties对象
*/
public XMLConfigBuilder(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties props) {
this(new XPathParser(inputStream, true, props, new XMLMapperEntityResolver()), environment, props);
}
/**
* 构造XMLConfigBuilder
* @param parser XPathParser
* @param environment environment环境
* @param props properties对象
*/
private XMLConfigBuilder(XPathParser parser, String environment, Properties props) {
//调用父类(BaseBuilder)构造函数,创建Configuration:会进行别名注册
super(new Configuration());
ErrorContext.instance().resource("SQL Mapper Configuration");
//Configuration设置properties
this.configuration.setVariables(props);
this.parsed = false;
this.environment = environment;
this.parser = parser;
}
上面的代码就是构建XMLConfigBuilder的整体过程,该过程会构建XPathParser,XPathParser主要用来解析XML封装了Document、EntityResolver 和XPath等对象,提供了一系列的解析XML的方法。
下面的代码是XPathParser构建的代码,使用到了工程模式去创建XPath对象。
XPathParser.class
/**
* 构造 XPathParser 对象
*
* @param inputStream inputStream 输入流
* @param validation 是否校验 XML
* @param variables 变量 Properties 对象
* @param entityResolver XML 实体解析器
*/
public XPathParser(InputStream inputStream, boolean validation, Properties variables, EntityResolver entityResolver) {
commonConstructor(validation, variables, entityResolver);
this.document = createDocument(new InputSource(inputStream));
}
private void commonConstructor(boolean validation, Properties variables, EntityResolver entityResolver) {
this.validation = validation;
this.entityResolver = entityResolver;
this.variables = variables;
XPathFactory factory = XPathFactory.newInstance();
this.xpath = factory.newXPath();
}
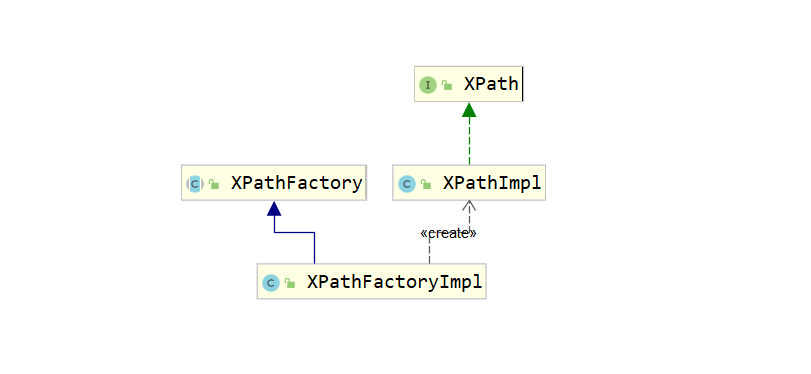
- 创建 Document 对象,Document 对象代表整个 XML 文档。这里会解析XML输入源得到Document对象。
/**
* 创建 Document 对象
*
* @param inputSource XML 的 InputSource 对象
* @return Document 对象
*/
private Document createDocument(InputSource inputSource) {
// important: this must only be called AFTER common constructor
try {
// 1> 创建DocumentBuilderFactory对象
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
factory.setValidating(validation);// 设置是否检验XML
factory.setNamespaceAware(false);
factory.setIgnoringComments(true);
factory.setIgnoringElementContentWhitespace(false);
factory.setCoalescing(false);
factory.setExpandEntityReferences(true);
//2> 创建DocumentBuilder对象
DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();
builder.setEntityResolver(entityResolver);// 设置实体解析器
builder.setErrorHandler(new ErrorHandler() {// 实现都是空的
@Override
public void error(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException {
throw exception;
}
@Override
public void fatalError(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException {
throw exception;
}
@Override
public void warning(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException {
}
});
//3> 解析XML文件 返回Document对象
return builder.parse(inputSource);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error creating document instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
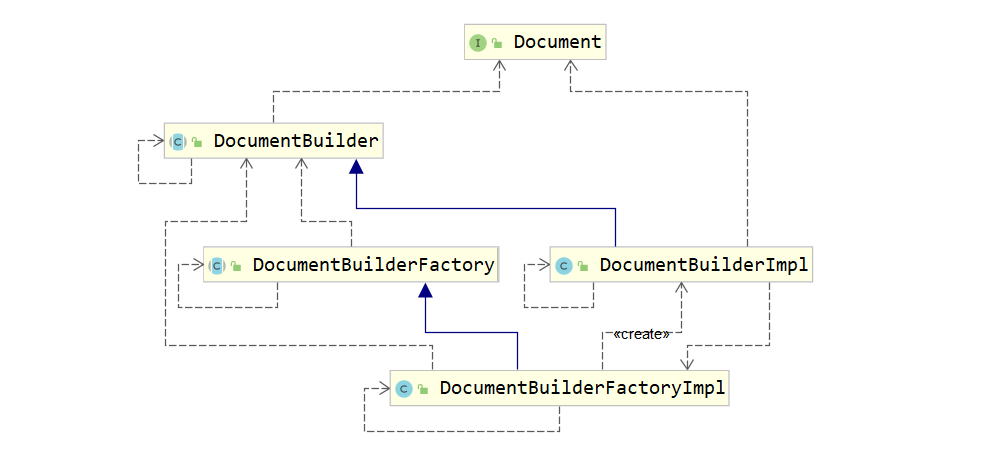
第三步:创建配置文件解析器XMLConfigBuilder
通过XMLConfigBuilder的parse()去解析mybatis-config.xml配置文件并返回Configuration对象。
XMLConfigBuilder.class
//1> 创建配置文件解析器
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(reader, environment, properties);
//2> 调用parse方法解析配置文件,将对应的属性存入并生成Configuration对象
return build(parser.parse());
/**
* 解析mybatis-config.xml
* @return configuration
*/
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
//解析configuration节点<configuration></configuration>
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
XPathParser是解析xml的核心
XPathParser.class
/**
* 获取Document中符合xpath表达式:expression的XNODE对象
* @param expression xpath表达式
* @return XNode
*/
public XNode evalNode(String expression) {
return evalNode(document, expression);
}
/**
* 获取XNode对象
* @param root Document xml 对象
* @param expression xpath表达式
* @return XNode
*/
public XNode evalNode(Object root, String expression) {
//1> 获得Node对象
Node node = (Node) evaluate(expression, root, XPathConstants.NODE);
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
//2> 封装成XNode对象
return new XNode(this, node, variables);
}
/**
* 获得指定元素或节点的值
* 并返回指定类型的结果
*
* @param expression 表达式
* @param root 指定节点
* @param returnType 返回类型
* @return 值
*/
private Object evaluate(String expression, Object root, QName returnType) {
try {
// 获取指定上下文中的 XPath 表达式并返回指定类型的结果。
return xpath.evaluate(expression, root, returnType);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error evaluating XPath. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
第四步:解析mybatis-config.xml中configuration节点下配置信息
主要代码:parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
XMLConfigBuilder.class
/**
* 解析mybatis-config.xml
* @return configuration
*/
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
//解析configuration节点<configuration></configuration>
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
/**
* 解析configuration下子节点的属性
* @param root configuration节点
*/
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
//issue #117 read properties first
// 1> 解析properties节点信息
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
//2> 解析settings节点信息
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
//2.1> 指定 VFS 的实现
loadCustomVfs(settings);
//2.2> 加载setting logImpl配置, 指定MyBatis 所用日志的具体实现
loadCustomLogImpl(settings);
//2.3> 解析并注册别名
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
//2.4 解析并加载插件到拦截器
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
//2.5 解析并加载对象工厂objectFactory
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
//2.6 解析并加载objectWrapperFactory
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
//2.7 解析并加载reflectorFactory
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
//2.8设置settings属性值
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
//2.9解析environments节点信息,并设置environment属性
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
//2.10解析databaseIdProvider节点(数据库厂商信息)
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
//2.11解析typeHandlers节点
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
//2.12 解析mappers节点
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
4.3 代码过程解析
4.3.1 解析properties节点信息
<properties resource="config.properties">
<property name="username" value="cmj"/>
</properties>
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
解析<properties>的整体步骤如下:
- 解析各个子节点
获取name和value属性值,存入Properties对象中 - 获取
节点的resource和url属性值,不能两个同时有值,否则报错 - 从resource或url的输入流中读取配置信息,存入Properties对象中
- 获取configuration对象中的Properties属性,存入Properties对象中
- XPathParser对象和configuration对象设置最新的Properties属性
- 注:由于解析
<properties>的时候是先解析其子节点<property>中的属性,然后再读取resource或者url中的属性,所以这回导致同名属性覆盖的问题,resource或url中的属性会覆<property>中的属性。
/**
* 解析properties节点
* Properties 是一个Hashtable
* @param context propertise节点xnode
*/
private void propertiesElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
//1.获取propertises下propertise属性
Properties defaults = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
//2> 获取resource属性
String resource = context.getStringAttribute("resource");
//3> 获取url属性,远程文件
String url = context.getStringAttribute("url");
if (resource != null && url != null) {
throw new BuilderException("The properties element cannot specify both a URL and a resource based property file reference. Please specify one or the other.");
}
if (resource != null) {
//4> resource存在,则读取resource文件中的配置
defaults.putAll(Resources.getResourceAsProperties(resource));
} else if (url != null) {
//5> url存在,则获取url文件中的配置
defaults.putAll(Resources.getUrlAsProperties(url));
}
//6> 获取configuration中的Properties
Properties vars = configuration.getVariables();
if (vars != null) {
//6.1> Properties的defaults加入从configuration获取的properties
defaults.putAll(vars);
}
//7> XPathParser 设置Properties属性
parser.setVariables(defaults);
//8> configuration设置Properties属性
configuration.setVariables(defaults);
}
}
1.1获取<properties>子节点的属性值
/**
* 获取子节点的属性值 name 和 value
*/
public Properties getChildrenAsProperties() {
Properties properties = new Properties();
for (XNode child : getChildren()) {
String name = child.getStringAttribute("name");
String value = child.getStringAttribute("value");
if (name != null && value != null) {
properties.setProperty(name, value);
}
}
return properties;
}
2.1获取resource或url属性值: context.getStringAttribute("resource");
/**
* 获取指定属性的值
* @param name 属性名称
* @return 属性值
*/
public String getStringAttribute(String name) {
return getStringAttribute(name, null);
}
/**
* 获取指定属性的值
* @param name 属性名称
* @param def 默认值
* @return 属性值
*/
public String getStringAttribute(String name, String def) {
String value = attributes.getProperty(name);
if (value == null) {
return def;
} else {
return value;
}
}
4.1读取resource文件中的配置信息:Resources.getResourceAsProperties(resource)
/**
* Returns a resource on the classpath as a Properties object
*
* @param resource The resource to find
* @return The resource
* @throws java.io.IOException If the resource cannot be found or read
*/
public static Properties getResourceAsProperties(String resource) throws IOException {
Properties props = new Properties();
//1> 获取resource输入流
try (InputStream in = getResourceAsStream(resource)) {
//2> 加载输入流中的配置
props.load(in);
}
return props;
}
5.1读取url文件的配置信息:Resources.getUrlAsProperties(url)
/**
* Gets a URL as a Properties object
*
* @param urlString - the URL to get
* @return A Properties object with the data from the URL
* @throws java.io.IOException If the resource cannot be found or read
*/
public static Properties getUrlAsProperties(String urlString) throws IOException {
Properties props = new Properties();
//1> 通过URLConnection,获取url输入流
try (InputStream in = getUrlAsStream(urlString)) {
//2> 加载输入流中的配置
props.load(in);
}
return props;
}
4.3.2 解析settings节点信息
settings中的配置比较多,具体可以看官网。

<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="multipleResultSetsEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="useColumnLabel" value="true"/>
<setting name="useGeneratedKeys" value="false"/>
<setting name="autoMappingBehavior" value="PARTIAL"/>
<setting name="autoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior" value="WARNING"/>
<setting name="defaultExecutorType" value="SIMPLE"/>
<setting name="defaultStatementTimeout" value="25"/>
<setting name="defaultFetchSize" value="100"/>
<setting name="safeRowBoundsEnabled" value="false"/>
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
<setting name="localCacheScope" value="SESSION"/>
<setting name="jdbcTypeForNull" value="OTHER"/>
<setting name="lazyLoadTriggerMethods" value="equals,clone,hashCode,toString"/>
</settings>
settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
解析settings的步骤分为如下几步:
- 1.将settings下的所有子节点获取属性值,并存入Properties对象中
- 2.
loadCustomVfs(settings);获取vfsImpl配置,加载指定的vfs类 - 3.
loadCustomLogImpl(settings);获取logImpl配置,指定MyBatis 所用日志的具体实现 - 4.根据Properties配置信息,设置configuration对应的setting对应的属性值
第一步:获取settings下的所有子节点属性值,这一步比较复杂,获取<settrings>各个子节点的属性,然后接下来通过反射去校验Configuration类中是否有相应的配置属性。
/**
* 读取settings的子节点属性
* @param context settings节点
* @return Properties
*/
private Properties settingsAsProperties(XNode context) {
if (context == null) {
return new Properties();
}
//1> 获取<settings>下子节点<setting>的属性值
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
//2> 获取Configuration的元信息
MetaClass metaConfig = MetaClass.forClass(Configuration.class, localReflectorFactory);
// Check that all settings are known to the configuration class
//3> 检查<setting>属性配置在Configuration中是否存在相应的setter方法
for (Object key : props.keySet()) {
if (!metaConfig.hasSetter(String.valueOf(key))) {
throw new BuilderException("The setting " + key + " is not known. Make sure you spelled it correctly (case sensitive).");
}
}
return props;
}
1.获取子节点下的属性信息context.getChildrenAsProperties()
/**
* 获取子节点的Properties属性 name 和 value
*/
public Properties getChildrenAsProperties() {
Properties properties = new Properties();
for (XNode child : getChildren()) {
String name = child.getStringAttribute("name");
String value = child.getStringAttribute("value");
if (name != null && value != null) {
properties.setProperty(name, value);
}
}
return properties;
}
1.获取Configuration的元信息: MetaClass.forClass(Configuration.class, localReflectorFactory)
MetaClass类中含有ReflectorFactory和Reflector,这是mybatis的反射核心类,用于获取目标类的各种属性,ReflectorFactory的实现类是DefaultReflectorFactory,这里也涉及到工厂模式。MetaClass类的构造函数是私有的,所以不能通过构造函数创建,需要通过forClass方法去创建。
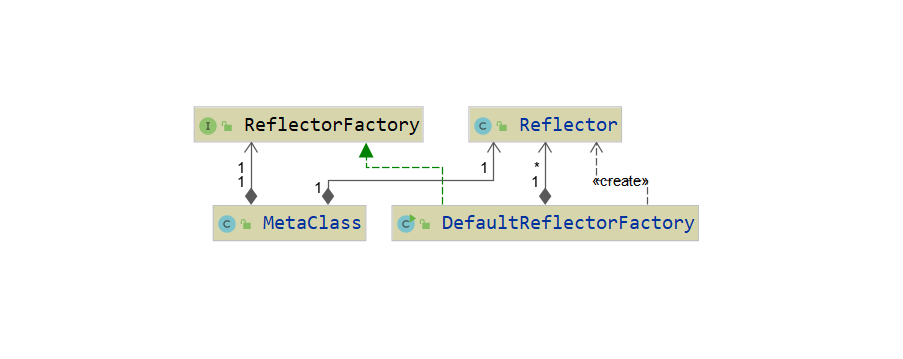
MetaClass.class
public static MetaClass forClass(Class<?> type, ReflectorFactory reflectorFactory) {
return new MetaClass(type, reflectorFactory);
}
private MetaClass(Class<?> type, ReflectorFactory reflectorFactory) {
this.reflectorFactory = reflectorFactory;
//根据类型创建 Reflector
this.reflector = reflectorFactory.findForClass(type);
}
DefaultReflectorFactory.class
@Override
public Reflector findForClass(Class<?> type) {
if (classCacheEnabled) {
// synchronized (type) removed see issue #461
return reflectorMap.computeIfAbsent(type, Reflector::new);
} else {
return new Reflector(type);
}
}
上述代码创建了Reflector 实体类。
在源码上Reflector的注释是这样的,很清晰知道它有什么用了
This class represents a cached set of class definition information that(这个类用于存放类定义的信息)
allows for easy mapping between property names and getter/setter methods.(能够方便映射属性名称和getter和setter方法)
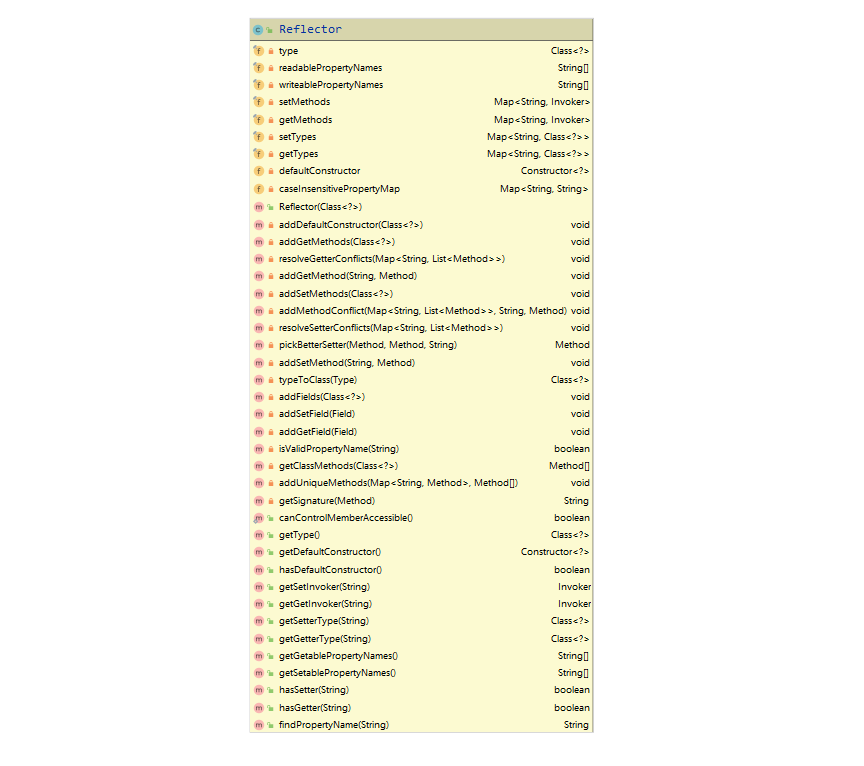
Reflector.class
Reflector 类创建解析,创建Reflector 对象时会对目标类的各个变量和gettersetter方法进行解析,并分为以下几个步骤:
- 解析目标类的无参构造函数,并赋值到defaultConstructor成员变量中
- 解析getter方法,并将解析结果存入getMethods和getTypes中
- 解析setter方法,并将解析结果存入setMethods和setTypes中
- 解析字段属性
/**
* 初始化Reflector
* 获取目标类的信息
* @param clazz 目标类
*/
public Reflector(Class<?> clazz) {
type = clazz;
//1> 获取类的构造函数并赋值给defaultConstructor
addDefaultConstructor(clazz);
//2> 解析getter方法,并将解析结果存入getMethods和getTypes中
addGetMethods(clazz);
//3> 解析setter方法,并将解析结果存入setMethods和setTypes中
addSetMethods(clazz);
//4> 解析字段属性,将字段属性信息存入getMethods,setMethods,getTypes,setTypes中
addFields(clazz);
//getMethods中key集合(可读属性名称集合)
readablePropertyNames = getMethods.keySet().toArray(new String[getMethods.keySet().size()]);
//setMethods中key集合(可写属性名称集合)
writeablePropertyNames = setMethods.keySet().toArray(new String[setMethods.keySet().size()]);
for (String propName : readablePropertyNames) {
caseInsensitivePropertyMap.put(propName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH), propName);
}
for (String propName : writeablePropertyNames) {
caseInsensitivePropertyMap.put(propName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH), propName);
}
}
Reflector:构造函数解析,解析目标类的无参构造函数
private void addDefaultConstructor(Class<?> clazz) {
Constructor<?>[] consts = clazz.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor<?> constructor : consts) {
if (constructor.getParameterTypes().length == 0) {
this.defaultConstructor = constructor;
}
}
}
Reflector:getter方法解析
getter方法解析主要分为三步
- 获取get / is 开头的无参方法
- 根据规则解决getter方法冲突(具体看下面代码解析)
/**
* 添加目标类的getter方法
* @param cls 目标类
*/
private void addGetMethods(Class<?> cls) {
Map<String, List<Method>> conflictingGetters = new HashMap<>();
Method[] methods = getClassMethods(cls);
for (Method method : methods) {
//排除有参数的方法
if (method.getParameterTypes().length > 0) {
continue;
}
String name = method.getName();
//isXXX()和getXXX()方法都获取
if ((name.startsWith("get") && name.length() > 3)
|| (name.startsWith("is") && name.length() > 2)) {
//获取方法名称,并首位转成小写字母。如getAge()或isAge()会获取得到age
name = PropertyNamer.methodToProperty(name);
//将方法存入Map<String, List<Method>> conflictingGetters,以待用于解决冲突
addMethodConflict(conflictingGetters, name, method);
}
}
//解决冲突的方法,并给setMethods和setTypes赋值
resolveGetterConflicts(conflictingGetters);
}
解决getter方法冲突: resolveGetterConflicts(conflictingGetters),有下面的规则:
1.如果两个getter方法返回类型一样且不是boolean返回类型,则抛出异常
2.如果两个getter方法返回类型一样且是返回类型未boolean的isXXX()方法,则选取该方法
3.如果两个返回类型不一样,选取返回类型是子类的getter方法
/**
* 解决Getter冲突,如:isAge()和getAge()便是冲突方法
* 只有List<Method> > 1 时才需要解决冲突
* @param conflictingGetters 方法集合
*/
private void resolveGetterConflicts(Map<String, List<Method>> conflictingGetters) {
for (Entry<String, List<Method>> entry : conflictingGetters.entrySet()) {
Method winner = null;
String propName = entry.getKey();
for (Method candidate : entry.getValue()) {
if (winner == null) {
winner = candidate;
continue;
}
Class<?> winnerType = winner.getReturnType();
Class<?> candidateType = candidate.getReturnType();
//如果两个方法返回类型一致
if (candidateType.equals(winnerType)) {
//如果两个方法返回类型一致,且返回类型都不是boolean类型则抛出异常
if (!boolean.class.equals(candidateType)) {
throw new ReflectionException(
"Illegal overloaded getter method with ambiguous type for property "
+ propName + " in class " + winner.getDeclaringClass()
+ ". This breaks the JavaBeans specification and can cause unpredictable results.");
//如果返回类型为boolean且是isXXX的方法则candidate胜出
} else if (candidate.getName().startsWith("is")) {
winner = candidate;
}
//如果winnerType是candidateType,则选取winner
} else if (candidateType.isAssignableFrom(winnerType)) {
//如果candidateType是winnerType的子类,则选取candidate
} else if (winnerType.isAssignableFrom(candidateType)) {
winner = candidate;
} else {
throw new ReflectionException(
"Illegal overloaded getter method with ambiguous type for property "
+ propName + " in class " + winner.getDeclaringClass()
+ ". This breaks the JavaBeans specification and can cause unpredictable results.");
}
}
//将筛选出的方法添加到getMethods并将其返回值添加到getTypes
addGetMethod(propName, winner);
}
}
Reflector:setter方法解析
setter方法解析主要分为三步
- 获取set 开头且只有一个入参的方法
- 根据规则解决setter方法冲突(具体看下面代码解析)
/**
* 添加setter方法到setMethods变量中
* @param cls 目标类
*/
private void addSetMethods(Class<?> cls) {
Map<String, List<Method>> conflictingSetters = new HashMap<>();
Method[] methods = getClassMethods(cls);
for (Method method : methods) {
String name = method.getName();
//1> 获取只有一个参数的setXXX()方法,等到方法名XXX
if (name.startsWith("set") && name.length() > 3) {
if (method.getParameterTypes().length == 1) {
name = PropertyNamer.methodToProperty(name);
//2> 添加放到到冲突列表:conflictingSetters,待进行冲突处理
addMethodConflict(conflictingSetters, name, method);
}
}
}
//3> 解决setter方法冲突
resolveSetterConflicts(conflictingSetters);
}
解决setter方法冲突:resolveSetterConflicts(conflictingSetters);
1.如果setter方法入参类型与对应的getter方法返回类型一致,则选取
2.如果存在两个setter方法,判断参数类型,取参数类型是子类的方法,若参数类型不是父子类关系,则抛出异常
/**
* setter方法冲突筛选,将最终筛选出来的存入setMethods和setTypes变量中
* @param conflictingSetters setter方法集合
*/
private void resolveSetterConflicts(Map<String, List<Method>> conflictingSetters) {
for (String propName : conflictingSetters.keySet()) {
List<Method> setters = conflictingSetters.get(propName);
Class<?> getterType = getTypes.get(propName);
Method match = null;
ReflectionException exception = null;
for (Method setter : setters) {
//1> setter方法的参数类型与getter返回值类型一致,则当前setter方法为目标方法
Class<?> paramType = setter.getParameterTypes()[0];
if (paramType.equals(getterType)) {
// should be the best match
match = setter;
break;
}
//2> 如果存在两个setter方法,判断参数类型,取参数类型是子类的方法,若参数类型不是父子类关系,则抛出异常
if (exception == null) {
try {
match = pickBetterSetter(match, setter, propName);
} catch (ReflectionException e) {
// there could still be the 'best match'
match = null;
exception = e;
}
}
}
if (match == null) {
throw exception;
} else {
//3> 排除冲突后的setter方法存入setMethods
addSetMethod(propName, match);
}
}
}
pickBetterSetter(match, setter, propName) 方法用于比较两个setter方法,筛选入参是子类的setter方法
/**
* 参数类型比较,返回子类
* 如果类型不是父子类关系,直接报错
* @param setter1 方法1
* @param setter2 方法2
* @param property property
* @return 返回是子类的方法
*/
private Method pickBetterSetter(Method setter1, Method setter2, String property) {
if (setter1 == null) {
return setter2;
}
Class<?> paramType1 = setter1.getParameterTypes()[0];
Class<?> paramType2 = setter2.getParameterTypes()[0];
//paramType2是paramType1的子类
if (paramType1.isAssignableFrom(paramType2)) {
return setter2;
//paramType1是paramType2的子类
} else if (paramType2.isAssignableFrom(paramType1)) {
return setter1;
}
throw new ReflectionException("Ambiguous setters defined for property '" + property + "' in class '"
+ setter2.getDeclaringClass() + "' with types '" + paramType1.getName() + "' and '"
+ paramType2.getName() + "'.");
}
4.3.3 解析typeAliases节点信息
用于定义类的别名,可以在xml中的resultType中直接使用别名。
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.chen.mybatis.demo2.pojo"/>
<typeAlias type="com.chen.mybatis.demo2.pojo.BlogTypealiase" alias="blogTypealiase"/>
</typeAliases>
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
解析别名,并对别名进行注册的步骤如下
1.解析package节点,将包下所有的类注册别名。
2.解析typeAlias节点,根据type和alias信息注册别名。
方法typeAliasesElement(XNode parent)解析,对package和typeAlias节点信息分别进行解析并注册别名,别名若存在则抛出异常
别名的规则:
1.获取package节点的包下的所有类进行注册
2.获取typeAlias节点type和alias信息注册别名
/**
* 解析别名typeAliases
*/
private void typeAliasesElement(XNode parent) {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
//1> 如果是package节点,则将包下的所有类注册到别名中
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String typeAliasPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAliases(typeAliasPackage);
} else {
//2> 如果是typeAlias节点,则将每一个typeAlias节点的信息注册到别名中
String alias = child.getStringAttribute("alias");
String type = child.getStringAttribute("type");
try {
//2.1> 根据typeAlias节点的type和alias信息注册别名
Class<?> clazz = Resources.classForName(type);
if (alias == null) {
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias(clazz);
} else {
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias(alias, clazz);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error registering typeAlias for '" + alias + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
}
}
- 4.3.3.1 注册package节点下的包下的所有类的别名
configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAliases(typeAliasPackage)
public void registerAliases(String packageName){
registerAliases(packageName, Object.class);
}
/**
* 注册包下类的别名
* @param packageName 报名
* @param superType 父类
*/
public void registerAliases(String packageName, Class<?> superType){
//获取包下是Object.class的子类的类
ResolverUtil<Class<?>> resolverUtil = new ResolverUtil<>();
resolverUtil.find(new ResolverUtil.IsA(superType), packageName);
Set<Class<? extends Class<?>>> typeSet = resolverUtil.getClasses();
for(Class<?> type : typeSet){
// Ignore inner classes and interfaces (including package-info.java)
// Skip also inner classes. See issue #6
//如果不是匿名内部类,接口类,称员类
if (!type.isAnonymousClass() && !type.isInterface() && !type.isMemberClass()) {
registerAlias(type);
}
}
}
registerAlias(Class type)和registerAlias(String alias, Class value)是注册别名的主要方法。
第一步获取类名作为别名
第二步如果类中存在注解@Alias则获取注解的value作为别名
第三步将别名转换为小写后再对该类进行别名注册
/**
* 注册别名
* 获取类中@Alias注解作为别名,如果不存在则获取类名
* @param type 目标类
*/
public void registerAlias(Class<?> type) {
//1.获取类名
String alias = type.getSimpleName();
//2.获取目标类中的@Alias注解信息,value值
Alias aliasAnnotation = type.getAnnotation(Alias.class);
if (aliasAnnotation != null) {
alias = aliasAnnotation.value();
}
//3.注册别名
registerAlias(alias, type);
}
/**
* 注册别名
* @param alias 别名
* @param value 目标类
*/
public void registerAlias(String alias, Class<?> value) {
if (alias == null) {
throw new TypeException("The parameter alias cannot be null");
}
// issue #748
//别名转成小写
String key = alias.toLowerCase(Locale.ENGLISH);
//判断别名是否已经存在,存在则不予以注册
if (TYPE_ALIASES.containsKey(key) && TYPE_ALIASES.get(key) != null && !TYPE_ALIASES.get(key).equals(value)) {
throw new TypeException("The alias '" + alias + "' is already mapped to the value '" + TYPE_ALIASES.get(key).getName() + "'.");
}
TYPE_ALIASES.put(key, value);
}
- 4.3.3.2 根据typeAlias节点下type和alias信息注册别名
这部分代码跟包别名注册差不多,,主要还是通过registerAlias(Class type)和registerAlias(String alias, Class value)这两个方法进行别名注册。
String alias = child.getStringAttribute("alias");
String type = child.getStringAttribute("type");
try {
//2.1> 根据typeAlias节点的type和alias信息注册别名
Class<?> clazz = Resources.classForName(type);
if (alias == null) {
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias(clazz);
} else {
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias(alias, clazz);
}
- 4.3 解析并加载plugins插件到拦截器中
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="com.chen.mybatis.demo2.plugins.ExamplePlugin">
<property name="someProperty" value="101"/>
</plugin>
</plugins>
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"))加载插件,其中代码比较清晰就直接放代码了
/**
*加载plugins插件到拦截器中
*/
private void pluginElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
//1> 获取拦截器的类全路径
String interceptor = child.getStringAttribute("interceptor");
//2> 获取plugin节点下property节点的信息
Properties properties = child.getChildrenAsProperties();
//3> 创建拦截器实例
Interceptor interceptorInstance = (Interceptor) resolveClass(interceptor).newInstance();
//4> 拦截器设置properties熟悉
interceptorInstance.setProperties(properties);
//5> configuration添加拦截器
configuration.addInterceptor(interceptorInstance);
}
}
}
4.3.4 解析并加载对象工厂objectFactory
<objectFactory type="com.chen.mybatis.demo2.objectFactory.ExampleObjectFactory">
<property name="someProperty" value="100"/>
</objectFactory>
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));设置objectFactory对象。
/**
* 解析并加载对象工厂objectFactory
*/
private void objectFactoryElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
//1> 获取type属性的值(类的全路径)
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type");
//2> 获取property节点信息name和value值
Properties properties = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
//3> 构建ObjectFactory对象
ObjectFactory factory = (ObjectFactory) resolveClass(type).newInstance();
//4> ObjectFactory设置property属性
factory.setProperties(properties);
//5> configuration设置ObjectFactory
configuration.setObjectFactory(factory);
}
}
4.3.5 解析并加载对象加工工厂ObjectWrapperFactory
<objectWrapperFactory type="com.chen.mybatis.demo2.objectFactory.ExampleObjectWrapperFactory"/>
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));代码就如下了,比较简单
/**
* 解析并加载objectWrapperFactory
*/
private void objectWrapperFactoryElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
//1> 获取type属性的值(类的全路径)
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type");
//2> 构建ObjectWrapperFactory对象
ObjectWrapperFactory factory = (ObjectWrapperFactory) resolveClass(type).newInstance();
//3> configuration设置ObjectWrapperFactory
configuration.setObjectWrapperFactory(factory);
}
}
4.3.6 解析并加载反射工厂ReflectorFactory
<reflectorFactory type="com.chen.mybatis.demo2.objectFactory.ExampleReflectorFactory"/>
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
/**
* 解析并加载reflectorFactory
*/
private void reflectorFactoryElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
//1> 获取type属性的值(类的全路径)
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type");
//2> 构建ReflectorFactory对象
ReflectorFactory factory = (ReflectorFactory) resolveClass(type).newInstance();
//3> configuration设置ReflectorFactory
configuration.setReflectorFactory(factory);
}
}
4.3.7 设置settings属性值
将之前解析得到的setting属性信息设置到configuration中,其中有一些是会有自己的默认值的。
settingsElement(settings);
/**
* 设置setting属性值
* @param props Properties对象
*/
private void settingsElement(Properties props) {
configuration.setAutoMappingBehavior(AutoMappingBehavior.valueOf(props.getProperty("autoMappingBehavior", "PARTIAL")));
configuration.setAutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior(AutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior.valueOf(props.getProperty("autoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior", "NONE")));
configuration.setCacheEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("cacheEnabled"), true));
configuration.setProxyFactory((ProxyFactory) createInstance(props.getProperty("proxyFactory")));
configuration.setLazyLoadingEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("lazyLoadingEnabled"), false));
configuration.setAggressiveLazyLoading(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("aggressiveLazyLoading"), false));
configuration.setMultipleResultSetsEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("multipleResultSetsEnabled"), true));
configuration.setUseColumnLabel(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("useColumnLabel"), true));
configuration.setUseGeneratedKeys(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("useGeneratedKeys"), false));
configuration.setDefaultExecutorType(ExecutorType.valueOf(props.getProperty("defaultExecutorType", "SIMPLE")));
configuration.setDefaultStatementTimeout(integerValueOf(props.getProperty("defaultStatementTimeout"), null));
configuration.setDefaultFetchSize(integerValueOf(props.getProperty("defaultFetchSize"), null));
configuration.setMapUnderscoreToCamelCase(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("mapUnderscoreToCamelCase"), false));
configuration.setSafeRowBoundsEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("safeRowBoundsEnabled"), false));
configuration.setLocalCacheScope(LocalCacheScope.valueOf(props.getProperty("localCacheScope", "SESSION")));
configuration.setJdbcTypeForNull(JdbcType.valueOf(props.getProperty("jdbcTypeForNull", "OTHER")));
configuration.setLazyLoadTriggerMethods(stringSetValueOf(props.getProperty("lazyLoadTriggerMethods"), "equals,clone,hashCode,toString"));
configuration.setSafeResultHandlerEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("safeResultHandlerEnabled"), true));
configuration.setDefaultScriptingLanguage(resolveClass(props.getProperty("defaultScriptingLanguage")));
configuration.setDefaultEnumTypeHandler(resolveClass(props.getProperty("defaultEnumTypeHandler")));
configuration.setCallSettersOnNulls(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("callSettersOnNulls"), false));
configuration.setUseActualParamName(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("useActualParamName"), true));
configuration.setReturnInstanceForEmptyRow(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("returnInstanceForEmptyRow"), false));
configuration.setLogPrefix(props.getProperty("logPrefix"));
configuration.setConfigurationFactory(resolveClass(props.getProperty("configurationFactory")));
}
4.3.8 解析environments节点信息,并设置environment属性
事务管理器和数据源都在environments节点下进行配置。transactionManager节点是事务管理器,dataSource节点是数据源。
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
/**
* 解析environments节点信息
*/
private void environmentsElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
if (environment == null) {
//1>获取environments节点default属性值
environment = context.getStringAttribute("default");
}
for (XNode child : context.getChildren()) {
//2>获取environment节点id值
String id = child.getStringAttribute("id");
//3> 判断id是否为environments节点的default值
if (isSpecifiedEnvironment(id)) {
//4>解析transactionManager节点,创建TransactionFactory对象
TransactionFactory txFactory = transactionManagerElement(child.evalNode("transactionManager"));
//5>解析dataSource节点,创建DataSourceFactory对象
DataSourceFactory dsFactory = dataSourceElement(child.evalNode("dataSource"));
DataSource dataSource = dsFactory.getDataSource();
//6.创建Environment.Builder对象,并设置transactionFactory和dataSource
Environment.Builder environmentBuilder = new Environment.Builder(id)
.transactionFactory(txFactory)
.dataSource(dataSource);
//7.configuration设置environment属性
configuration.setEnvironment(environmentBuilder.build());
}
}
}
}
4.3.9 解析databaseIdProvider节点(数据库厂商信息)
databaseIdProvider的配置一般如下
<databaseIdProvider type="DB_VENDOR">
<property name="MySQL" value="mysql"/>
<property name="Oracle" value="oracle"/>
</databaseIdProvider>
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
配置数据库厂商信息,也就是设置DatabaseId值。mybatis会通过数据源获取到数据源中数据库名称,再根据该名称跟所配置的信息进行对比,拿去与数据源名称一致的property 的value值作为DatabaseId,设置到configuration中。
/**
* 解析databaseIdProvider节点
*/
private void databaseIdProviderElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
DatabaseIdProvider databaseIdProvider = null;
if (context != null) {
//1> 获取type属性值
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type");
// awful patch to keep backward compatibility
if ("VENDOR".equals(type)) {
type = "DB_VENDOR";
}
//2> 获取databaseIdProvider节点下的property节点信息,并创建DatabaseIdProvider对象
Properties properties = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
databaseIdProvider = (DatabaseIdProvider) resolveClass(type).newInstance();
databaseIdProvider.setProperties(properties);
}
//3> 获取databaseId,并设置configuration的databaseId
Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
if (environment != null && databaseIdProvider != null) {
String databaseId = databaseIdProvider.getDatabaseId(environment.getDataSource());
configuration.setDatabaseId(databaseId);
}
}
先看看第二步:DatabaseIdProvider databaseIdProvider = (DatabaseIdProvider) resolveClass(type).newInstance();
- 当type = “DB_VENDOR” 时,创建的DatabaseIdProvider类实现类实际上是:VendorDatabaseIdProvider类
- 为什么?因为Configuration创建的时候一样注册了别名。
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("DB_VENDOR", VendorDatabaseIdProvider.class);
再来看第三步,获取databaseId,并设置configuration的databaseId的代码实现。主要是这段代码
String databaseId = databaseIdProvider.getDatabaseId(environment.getDataSource());
会先通过数据源获取数据的产品名称信息,再跟property的name属性相比较,如果是当前数据库的产品名称则拿去其value值作为DatabaseId。
/**
* 获取数据库名称
* @param dataSource 数据源
*/
@Override
public String getDatabaseId(DataSource dataSource) {
if (dataSource == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("dataSource cannot be null");
}
try {
return getDatabaseName(dataSource);
} catch (Exception e) {
LogHolder.log.error("Could not get a databaseId from dataSource", e);
}
return null;
}
/**
* 获取数据库名称
* @param dataSource 数据源
* @return 数据库名称
*/
private String getDatabaseName(DataSource dataSource) throws SQLException {
//1> 获取数据库产品名称如oracle、mysql
String productName = getDatabaseProductName(dataSource);
//2> 如果数据源中数据库产品名称包含databaseIdProvider节点下的property节点name属性值,则返回对应的value值作为数据库名称
if (this.properties != null) {
for (Map.Entry<Object, Object> property : properties.entrySet()) {
if (productName.contains((String) property.getKey())) {
return (String) property.getValue();
}
}
// no match, return null
return null;
}
return productName;
}
/**
* 获取数据库产品名称如oracle、mysql
*/
private String getDatabaseProductName(DataSource dataSource) throws SQLException {
Connection con = null;
try {
con = dataSource.getConnection();
DatabaseMetaData metaData = con.getMetaData();
return metaData.getDatabaseProductName();
} finally {
if (con != null) {
try {
con.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// ignored
}
}
}
}
4.3.10 解析typeHandlers节点
typeHandlers中关于TypeHandlerRegistry类走register()各种重载方法互相调用,一时间有点头晕。
从入口方法中有两种处理,一种是自动映射package下的typehandler,另一种是解析单个节点的typeHandler。
/**
* 解析typeHandlers节点,并对typehandler进行注册
*/
private void typeHandlerElement(XNode parent) {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
//1> 从指定包中注册TypeHandler
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String typeHandlerPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
typeHandlerRegistry.register(typeHandlerPackage);
} else {
//2>解析typeHandler节点,获取javaType,jdbcType,handler属性值
String javaTypeName = child.getStringAttribute("javaType");
String jdbcTypeName = child.getStringAttribute("jdbcType");
String handlerTypeName = child.getStringAttribute("handler");
//3> 获取javaTypeName为别名对应的类,如不存在,则返回javaTypeName指定的类
Class<?> javaTypeClass = resolveClass(javaTypeName);
//4> 获取jdbcTypeName对应的JdbcType
JdbcType jdbcType = resolveJdbcType(jdbcTypeName);
//5> 获取handlerTypeName为别名对应的类,如不存在,则返回handlerTypeName指定的类
Class<?> typeHandlerClass = resolveClass(handlerTypeName);
//6> 注册TypeHandler
if (javaTypeClass != null) {
if (jdbcType == null) {
typeHandlerRegistry.register(javaTypeClass, typeHandlerClass);
} else {
typeHandlerRegistry.register(javaTypeClass, jdbcType, typeHandlerClass);
}
} else {
typeHandlerRegistry.register(typeHandlerClass);
}
}
}
}
}
TypeHandlerRegistry类中register重载方法的调用关系图,比较清晰的看到register重载方法的调用
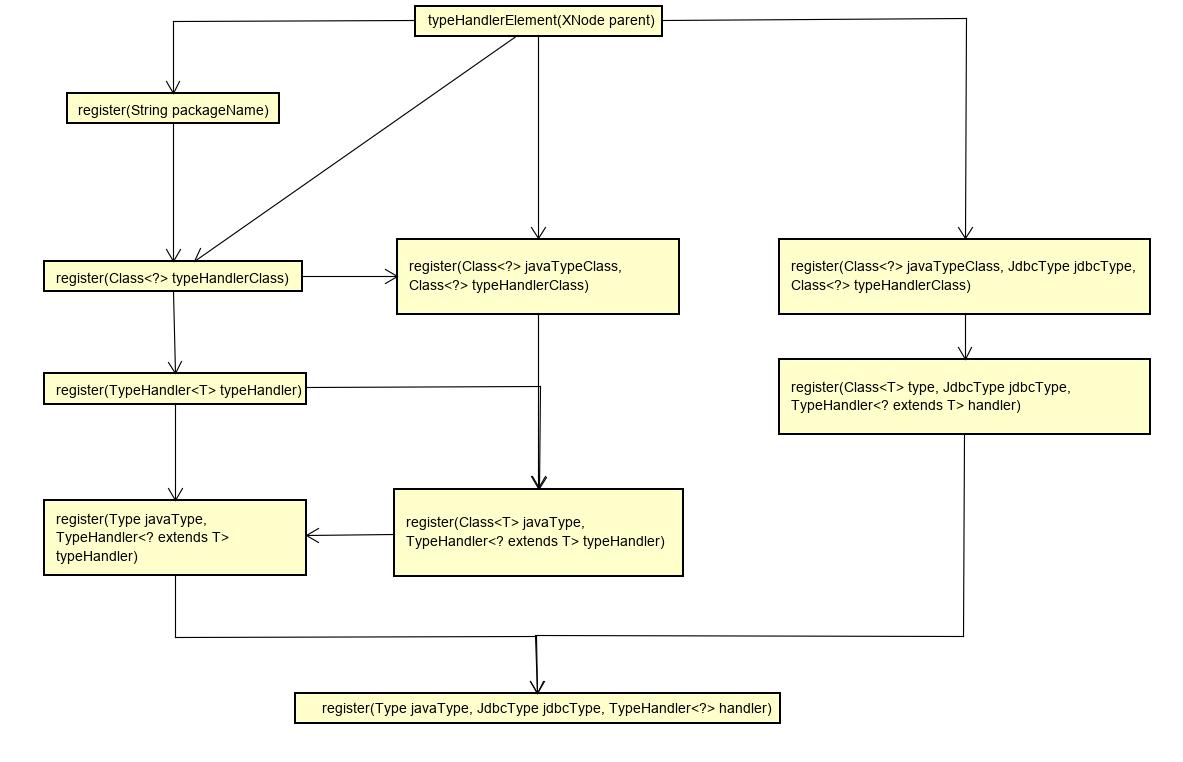
register(String packageName)方法
该方法用于自动扫描包中的typehandler,并进行注册
/**
* 注册TypeHandler,自动扫描类型处理器
* @param packageName 包路径
*/
public void register(String packageName) {
//1> 获取包下的类
ResolverUtil<Class<?>> resolverUtil = new ResolverUtil<>();
resolverUtil.find(new ResolverUtil.IsA(TypeHandler.class), packageName);
Set<Class<? extends Class<?>>> handlerSet = resolverUtil.getClasses();
//2> 注册TypeHandler,非内部类,接口,抽象类才能注册
for (Class<?> type : handlerSet) {
//Ignore inner classes and interfaces (including package-info.java) and abstract classes
if (!type.isAnonymousClass() && !type.isInterface() && !Modifier.isAbstract(type.getModifiers())) {
register(type);
}
}
}
register(Class<?> typeHandlerClass)方法
该方法主要用于判断typehandler中javaType是否存在,从而调用不同的重载方法
/**
* 存在@MappedTypes,且有值,则存在javaType,调用register(Class<?> javaTypeClass, Class<?> typeHandlerClass)重载方法
* 不存在@MappedTypes或者没有值,则调用register(TypeHandler<T> typeHandler)重载方法
*/
public void register(Class<?> typeHandlerClass) {
boolean mappedTypeFound = false;
//1> 获取@MappedTypes注解
MappedTypes mappedTypes = typeHandlerClass.getAnnotation(MappedTypes.class);
if (mappedTypes != null) {
//2> 遍历@MappedTypes注解中value值
for (Class<?> javaTypeClass : mappedTypes.value()) {
//3> 调用register重载方法进行注册
register(javaTypeClass, typeHandlerClass);
mappedTypeFound = true;
}
}
if (!mappedTypeFound) {
register(getInstance(null, typeHandlerClass));
}
}
register(TypeHandler<T> typeHandler)方法
/**
* 只有typeHandler参数的register重载方法
*
*/
public <T> void register(TypeHandler<T> typeHandler) {
boolean mappedTypeFound = false;
//1> 获取@MappedTypes注解,存在javaType值,则调用register(Type javaType, TypeHandler<? extends T> typeHandler)方法注册typehandler
MappedTypes mappedTypes = typeHandler.getClass().getAnnotation(MappedTypes.class);
if (mappedTypes != null) {
for (Class<?> handledType : mappedTypes.value()) {
//调用重载方法register(Type javaType, TypeHandler<? extends T> typeHandler)
register(handledType, typeHandler);
mappedTypeFound = true;
}
}
// @since 3.1.0 - try to auto-discover the mapped type
//自动发现映射类型
if (!mappedTypeFound && typeHandler instanceof TypeReference) {
try {
TypeReference<T> typeReference = (TypeReference<T>) typeHandler;
//调用重载方法register(Type javaType, TypeHandler<? extends T> typeHandler)
register(typeReference.getRawType(), typeHandler);
mappedTypeFound = true;
} catch (Throwable t) {
// maybe users define the TypeReference with a different type and are not assignable, so just ignore it
}
}
if (!mappedTypeFound) {
register((Class<T>) null, typeHandler);
}
}
register(Type javaType, TypeHandler<? extends T> typeHandler)方法
判断是否存在注解@MappedJdbcTypes(JdbcType)是否存在,再将jdbcType作为入参,调用register重载方法
private <T> void register(Type javaType, TypeHandler<? extends T> typeHandler) {
//1> 获取typahandler类中@MappedJdbcTypes注解value值
MappedJdbcTypes mappedJdbcTypes = typeHandler.getClass().getAnnotation(MappedJdbcTypes.class);
if (mappedJdbcTypes != null) {
//2> 遍历MappedJdbcTypes的value值,进行遍历注册TypeHandler
for (JdbcType handledJdbcType : mappedJdbcTypes.value()) {
register(javaType, handledJdbcType, typeHandler);
}
//3> 如果MappedJdbcTypes注解中includeNullJdbcType=true,则注册jdbcType=null的TypeHandler
if (mappedJdbcTypes.includeNullJdbcType()) {
register(javaType, null, typeHandler);
}
} else {
register(javaType, null, typeHandler);
}
}
register(Type javaType, JdbcType jdbcType, TypeHandler<?> handler)最终调用的方法
实现将typehandler存储到对应的称员变量中(map)
/**
* 注册TypeHandler
* @param javaType
* @param jdbcType
* @param handler
*/
private void register(Type javaType, JdbcType jdbcType, TypeHandler<?> handler) {
if (javaType != null) {
//1> 存储以javaType为key的 Map<JdbcType, TypeHandler<?>>到TYPE_HANDLER_MAP变量中
Map<JdbcType, TypeHandler<?>> map = TYPE_HANDLER_MAP.get(javaType);
if (map == null || map == NULL_TYPE_HANDLER_MAP) {
map = new HashMap<>();
TYPE_HANDLER_MAP.put(javaType, map);
}
map.put(jdbcType, handler);
}
//2> 添加TypeHandler到ALL_TYPE_HANDLERS_MAP
ALL_TYPE_HANDLERS_MAP.put(handler.getClass(), handler);
}
4.3.11 解析mappers节点
解析mappers节点这个放到之后的章节再进行描述。