1.__str__和__repe__
class Person(object): def __init__(self,name,age): self.name = name self.age = age def __str__(self): return 'stf:我叫{},今年{}岁'.format(self.name,self.age) def __repr__(self): return 'repr:我叫{},今年{}岁'.format(self.name, self.age) p = Person('wdc',22) print(repr(p)) print(str(p)) print(p)

str函数或者print函数调用时 = obj.__srt__()
repr函数或者交互式解释器中调用时 = obj.__repr__()
这两个方法的返回值必须是字符串,否则会抛出异常
class Person(object): def __init__(self,name,age): self.name = name self.age = age # def __str__(self): # return 'stf:我叫{},今年{}岁'.format(self.name,self.age) def __repr__(self): return 'repr:我叫{},今年{}岁'.format(self.name, self.age) p = Person('wdc',22) print(repr(p)) print(str(p)) print(p)

如果__str__没有被定义,那么就会使用__repr__来代替输出。
2.__del__析构方法
class Person(object): def __init__(self,name,age): self.name = name self.age = age def __del__(self): print('析构方法') p = Person('wdc',22) print('11111111111') print('11111111111') del p #删除对象p print('11111111111') print('11111111111')
 当对象再内存中被释放时,自动触发执行。
当对象再内存中被释放时,自动触发执行。
3.__new__方法
class Person(object): def __init__(self,name,age): self.name = name self.age = age print(self.name) def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs): # 负责执行__init__,进行一些初始化前的工作 print(cls,args,kwargs) return object.__new__(cls) p = Person('wdc',22)

当有__new__方法时,不执行__init__方法,直接执行__new__方法,如果要想知道__init__方法,就要在__new__中返回:object.__new__(cls)
__new__方法实现单例模式:
class Person(object): tasks = [] instance = None def __init__(self,name): self.name = name def add_task(self,job): self.tasks.append(job) print('{}添加任务{},共{}个任务'.format(self.name,job,len(self.tasks))) def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs): # 只有第一次实例化的时候,正常精选,后面每次实例化,并不正在创建一个新实例 if cls.instance == None: # 进行正常的实例化,并把实例化后的对象,村再cls.instance中 obj = object.__new__(cls) #实例化过程 cls.instance = obj #把实例化好的对象存下来 return cls.instance #以后的每次实例化,直接返回第一次村的实例对象 p1 = Person('wdc') p2 = Person('yhf') p3 = Person('qqq') p1.add_task('w') p2.add_task('d') p3.add_task('c')

4.__call__方法
:在对象后加括号执行
class Per(object): def __init__(self,name): self.name = name def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs): print(self,args,kwargs) p = Per('wdc') p.__call__() p()

5.__dict__
:获取对象的全部属性
class Wdc(object): def qqq(): print('wdc+++++') one = Wdc() one.age = 18 one.name = 'wdc' print(one.__dict__)
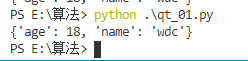
6.__class__
:用来找到对象所对应的类
class Wdc(object): def qqq(): print('wdc+++++') one = Wdc() print(one.__class__)
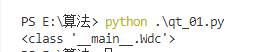
7.__slots__
:限制对象的属性名。
class Person(object): # 基于Person类的对象添加属性只能添加下面列表中存在的字段 __slots__ = ['age', 'name'] pass p = Person() p.age = 18 p.qqq = 456
