keras介绍
Keras是一个简约,高度模块化的神经网络库。采用Python / Theano开发。
使用Keras如果你需要一个深度学习库:
可以很容易和快速实现原型(通过总模块化,极简主义,和可扩展性)
同时支持卷积网络(vision)和复发性的网络(序列数据)。以及两者的组合。
无缝地运行在CPU和GPU上。
keras的资源库网址为https://github.com/fchollet/keras
olivettifaces人脸数据库介绍
Olivetti Faces是纽约大学的一个比较小的人脸库,由 40个人的400张图片构成,即每个人的人脸图片为10张。每张图片的灰度级为8位,每个像素的灰度大小位于0-255之间,每张图片大小为64×64。 如下图,这个图片大小是1140942,一共有2020张人脸,故每张人脸大小是(1140/20)(942/20)即5747=2679:

预处理模块
使用了PIL(Python Imaging Library)模块,是Python平台事实上的图像处理标准库。
预处理流程是:打开文件-》归一化-》将图片转为数据集-》生成label-》使用pickle序列化数据集
numpy.ndarray.flatten函数的功能是将一个矩阵平铺为向量
from PIL import Image
import numpy
import cPickle
img = Image.open('G:dataolivettifaces.gif')
# numpy supports conversion from image to ndarray and normalization by dividing 255
# 1140 * 942 ndarray
img_ndarray = numpy.asarray(img, dtype='float64') / 255
# create numpy array of 400*2679
img_rows, img_cols = 57, 47
face_data = numpy.empty((400, img_rows*img_cols))
# convert 1140*942 ndarray to 400*2679 matrix
for row in range(20):
for col in range(20):
face_data[row*20+col] = numpy.ndarray.flatten(img_ndarray[row*img_rows:(row+1)*img_rows, col*img_cols:(col+1)*img_cols])
# create label
face_label = numpy.empty(400, dtype=int)
for i in range(400):
face_label[i] = i / 10
# pickling file
f = open('G:dataolivettifaces.pkl','wb')
# store data and label as a tuple
cPickle.dump((face_data,face_label), f)
f.close()
分类模型
程序参考了官方示例:https://github.com/fchollet/keras/blob/master/examples/mnist_cnn.py
一共有40个类,每个类10个样本,共400个样本。其中320个样本用于训练,40个用于验证,剩下40个测试
注意给第一层指定input_shape,如果是MLP,代码为:
model = Sequential()
# Dense(64) is a fully-connected layer with 64 hidden units.# in the first layer, you must specify the expected input data shape:# here, 20-dimensional vectors.
model.add(Dense(64, input_dim=20, init='uniform'))
后面可以不指定Dense的input shape
from __future__ import print_function
import numpy as np
import cPickle
np.random.seed(1337) # for reproducibililty
from keras.datasets import mnist
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers.core import Dense, Dropout, Activation, Flatten
from keras.layers.convolutional import Convolution2D, MaxPooling2D
from keras.utils import np_utils
# split data into train,vavlid and test
# train:320
# valid:40
# test:40
def split_data(fname):
f = open(fname, 'rb')
face_data,face_label = cPickle.load(f)
X_train = np.empty((320, img_rows * img_cols))
Y_train = np.empty(320, dtype=int)
X_valid = np.empty((40, img_rows* img_cols))
Y_valid = np.empty(40, dtype=int)
X_test = np.empty((40, img_rows* img_cols))
Y_test = np.empty(40, dtype=int)
for i in range(40):
X_train[i*8:(i+1)*8,:] = face_data[i*10:i*10+8,:]
Y_train[i*8:(i+1)*8] = face_label[i*10:i*10+8]
X_valid[i] = face_data[i*10+8,:]
Y_valid[i] = face_label[i*10+8]
X_test[i] = face_data[i*10+9,:]
Y_test[i] = face_label[i*10+9]
return (X_train, Y_train, X_valid, Y_valid, X_test, Y_test)
if __name__=='__main__':
batch_size = 10
nb_classes = 40
nb_epoch = 12
# input image dimensions
img_rows, img_cols = 57, 47
# number of convolutional filters to use
nb_filters = 32
# size of pooling area for max pooling
nb_pool = 2
# convolution kernel size
nb_conv = 3
(X_train, Y_train, X_valid, Y_valid, X_test, Y_test) = split_data('G:dataolivettifaces.pkl')
X_train = X_train.reshape(X_train.shape[0], 1, img_rows, img_cols)
X_test = X_test.reshape(X_test.shape[0], 1, img_rows, img_cols)
print('X_train shape:', X_train.shape)
print(X_train.shape[0], 'train samples')
print(X_test.shape[0], 'test samples')
# convert label to binary class matrix
Y_train = np_utils.to_categorical(Y_train, nb_classes)
Y_test = np_utils.to_categorical(Y_test, nb_classes)
model = Sequential()
# 32 convolution filters , the size of convolution kernel is 3 * 3
# border_mode can be 'valid' or 'full'
#‘valid’only apply filter to complete patches of the image.
# 'full' zero-pads image to multiple of filter shape to generate output of shape: image_shape + filter_shape - 1
# when used as the first layer, you should specify the shape of inputs
# the first number means the channel of an input image, 1 stands for grayscale imgs, 3 for RGB imgs
model.add(Convolution2D(nb_filters, nb_conv, nb_conv,
border_mode='valid',
input_shape=(1, img_rows, img_cols)))
# use rectifier linear units : max(0.0, x)
model.add(Activation('relu'))
# second convolution layer with 32 filters of size 3*3
model.add(Convolution2D(nb_filters, nb_conv, nb_conv))
model.add(Activation('relu'))
# max pooling layer, pool size is 2 * 2
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(nb_pool, nb_pool)))
# drop out of max-pooling layer , drop out rate is 0.25
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
# flatten inputs from 2d to 1d
model.add(Flatten())
# add fully connected layer with 128 hidden units
model.add(Dense(128))
model.add(Activation('relu'))
model.add(Dropout(0.5))
# output layer with softmax
model.add(Dense(nb_classes))
model.add(Activation('softmax'))
# use cross-entropy cost and adadelta to optimize params
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adadelta')
# train model with bath_size =10, epoch=12
# set verbose=1 to show train info
model.fit(X_train, Y_train, batch_size=batch_size, nb_epoch=nb_epoch,
show_accuracy=True, verbose=1, validation_data=(X_test, Y_test))
# evaluate on test set
score = model.evaluate(X_test, Y_test, show_accuracy=True, verbose=0)
print('Test score:', score[0])
print('Test accuracy:', score[1])
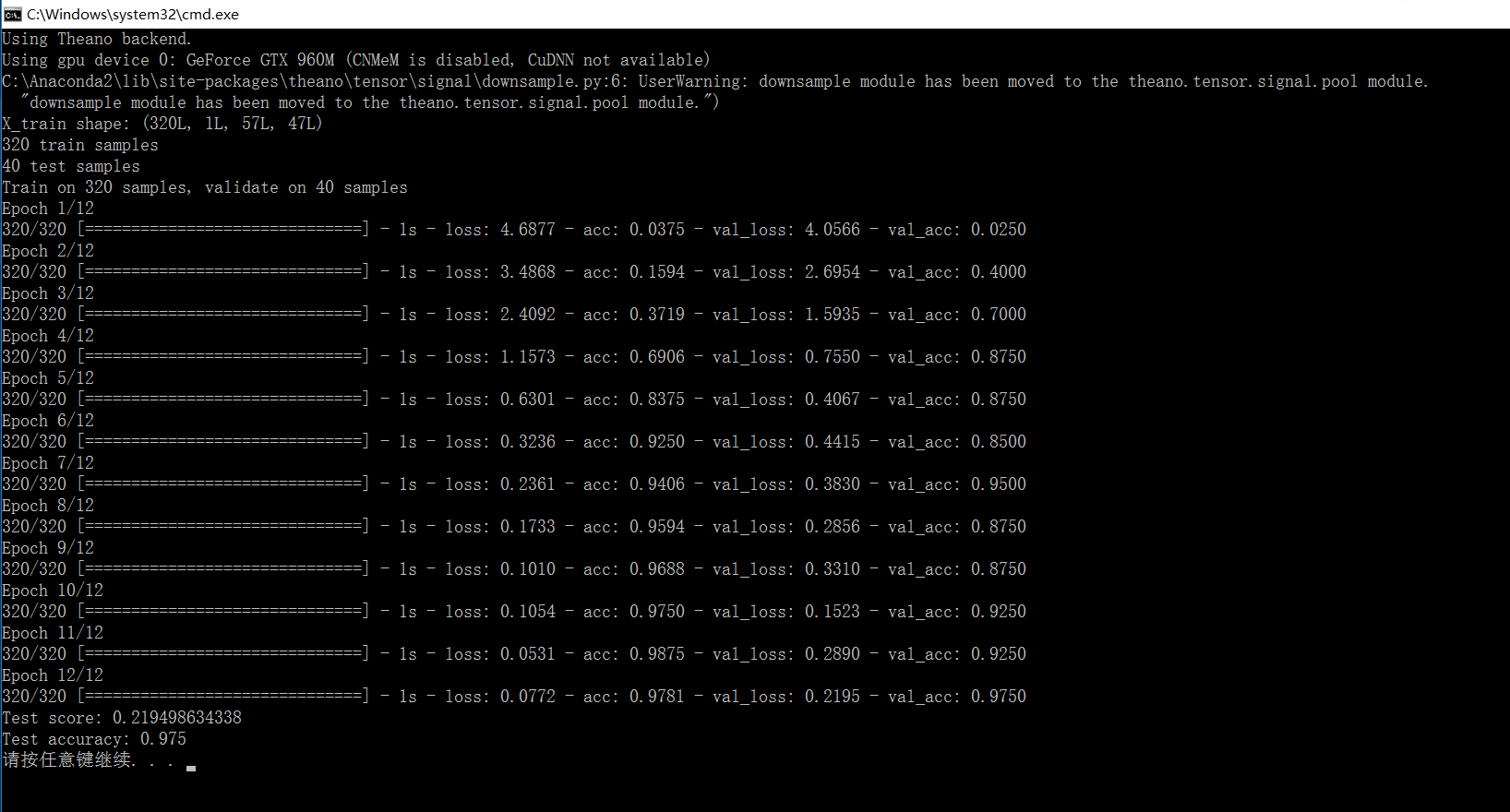
结果:
准确率有97%