【参考文章】:Mybatis-Executor解析
1. Executor的继承结构
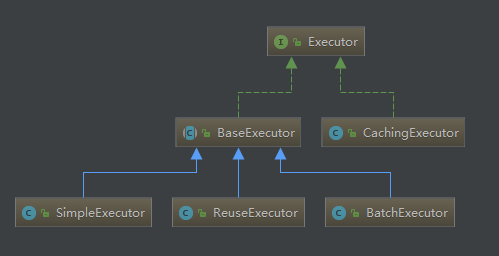
2. Executor(顶层接口)
定义了执行器的一些基本操作;
public interface Executor { ResultHandler NO_RESULT_HANDLER = null; // 更新 int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException; // 查询,先查缓存,再查数据库 <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey cacheKey, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException; // 查询 <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException; <E> Cursor<E> queryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) throws SQLException; List<BatchResult> flushStatements() throws SQLException; // 事务提交 void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException; // 事务回滚 void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException; // 创建缓存的键对象 CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql); // 缓存中是否有这个查询的结果 boolean isCached(MappedStatement ms, CacheKey key); // 清空缓存 void clearLocalCache(); void deferLoad(MappedStatement ms, MetaObject resultObject, String property, CacheKey key, Class<?> targetType); Transaction getTransaction(); void close(boolean forceRollback); boolean isClosed(); void setExecutorWrapper(Executor executor); }
3. BaseExecutor
BaseExecutor是一个抽象类,采用模板方法的设计模式。
它实现了Executor接口,实现了执行器的基本功能。
具体使用哪一个Executor则是可以在 mybatis 的 config.xml 中进行配置的。默认为SimpleExecutor;
配置如下:
<settings> <!--SIMPLE、REUSE、BATCH--> <setting name="defaultExecutorType" value="SIMPLE"/> </settings>
3.1 构造方法
子类的构造方法会调用 BaseExecutor 的构造方法。
默认都支持一级缓存;
public abstract class BaseExecutor implements Executor { protected BaseExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction) { this.transaction = transaction; this.deferredLoads = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<DeferredLoad>(); // 一级缓存 this.localCache = new PerpetualCache("LocalCache"); this.localOutputParameterCache = new PerpetualCache("LocalOutputParameterCache"); this.closed = false; this.configuration = configuration; this.wrapper = this; }
}
3.2 update
insert,update,delete操作都会调用此方法;
调用此方法时会清空一级缓存;
@Override public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException { ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing an update").object(ms.getId()); if (closed) { throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed."); } // 数据变更操作会清空一级缓存 clearLocalCache(); return doUpdate(ms, parameter); }
3.3 query
查询操作会先在缓存中查询,缓存命中失败后再去数据中查询
@Override public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException { BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter); // 创建一级缓存的键对象 CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql); // 调用下面的 query 方法 return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") @Override public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId()); if (closed) { throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed."); } if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) { clearLocalCache(); } List<E> list; try { queryStack++; // 先在缓存中查询,缓存命中失败再去数据库查询 list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null; if (list != null) { handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql); } else { list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); } } finally { queryStack--; } if (queryStack == 0) { for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) { deferredLoad.load(); } // issue #601 deferredLoads.clear(); if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) { // issue #482 clearLocalCache(); } } return list; }
3.4 createCacheKey
一级缓存通过 HashMap 实现,它的键对象根据SQL的ID,参数,SQL本身,分页参数以及JDBC的参数信息构成。
@Override // 创建CacheKey对象 public CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) { if (closed) { throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed."); } CacheKey cacheKey = new CacheKey(); // MappedStatement的id cacheKey.update(ms.getId()); // 分页参数的offset cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getOffset()); // 分页参数的limit cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getLimit()); // SQL语句本身 cacheKey.update(boundSql.getSql()); // 传递给jdbc的参数 List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings(); TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = ms.getConfiguration().getTypeHandlerRegistry(); // mimic DefaultParameterHandler logic for (ParameterMapping parameterMapping : parameterMappings) { if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) { Object value; String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty(); if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) { value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName); } else if (parameterObject == null) { value = null; } else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) { value = parameterObject; } else { MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject); value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName); } cacheKey.update(value); } } if (configuration.getEnvironment() != null) { // issue #176 cacheKey.update(configuration.getEnvironment().getId()); } return cacheKey; }
3.5定义的抽象方法
// 定义的四个抽象方法,在去掉 do 前缀的相应方法中被调用 protected abstract int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException; protected abstract List<BatchResult> doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback) throws SQLException; protected abstract <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException; protected abstract <E> Cursor<E> doQueryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException;
4. SimpleExecutor
最简单的执行器,根据对应的sql直接执行即可,不会做一些额外的操作;
拼接完SQL之后,直接交给 StatementHandler 去执行。

/** * Copyright 2009-2016 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.apache.ibatis.executor; import org.apache.ibatis.cursor.Cursor; import org.apache.ibatis.executor.statement.StatementHandler; import org.apache.ibatis.logging.Log; import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.BoundSql; import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.MappedStatement; import org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration; import org.apache.ibatis.session.ResultHandler; import org.apache.ibatis.session.RowBounds; import org.apache.ibatis.transaction.Transaction; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.sql.Statement; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.List; /** * @author Clinton Begin */ public class SimpleExecutor extends BaseExecutor { public SimpleExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction) { super(configuration, transaction); } @Override public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException { Statement stmt = null; try { Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null); stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); return handler.update(stmt); } finally { closeStatement(stmt); } } @Override public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { Statement stmt = null; try { Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler); } finally { closeStatement(stmt); } } @Override protected <E> Cursor<E> doQueryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, null, boundSql); Statement stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); return handler.<E>queryCursor(stmt); } @Override public List<BatchResult> doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback) throws SQLException { return Collections.emptyList(); } private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException { Statement stmt; Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog); stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout()); handler.parameterize(stmt); return stmt; } }
5. BatchExecutor
通过批量操作来优化性能。通常需要注意的是批量更新操作,由于内部有缓存的实现,使用完成后记得调用flushStatements来清除缓存。
public class BatchExecutor extends BaseExecutor { public static final int BATCH_UPDATE_RETURN_VALUE = Integer.MIN_VALUE + 1002; private final List<Statement> statementList = new ArrayList<Statement>(); private final List<BatchResult> batchResultList = new ArrayList<BatchResult>(); // 上一次的SQL语句 private String currentSql; // 上一次的MappedStatement 对象 private MappedStatement currentStatement; // 因为调用父类的构造方法,所以 BatchExecutor 自己的私有属性 currentSql和currentStatement 开始都为null public BatchExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction) { super(configuration, transaction); } @Override public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject) throws SQLException { final Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); final StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameterObject, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null); final BoundSql boundSql = handler.getBoundSql(); final String sql = boundSql.getSql(); final Statement stmt; // 第一次肯定是false,进入else分支,currentSql和currentStatement被初始化,后面进入false分支则进行更新 if (sql.equals(currentSql) && ms.equals(currentStatement)) { // 取上一次的 Statement 对象 int last = statementList.size() - 1; stmt = statementList.get(last); applyTransactionTimeout(stmt); handler.parameterize(stmt);//fix Issues 322 BatchResult batchResult = batchResultList.get(last); batchResult.addParameterObject(parameterObject); } else { Connection connection = getConnection(ms.getStatementLog()); stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout()); handler.parameterize(stmt); //fix Issues 322 // currentSql和currentStatement 更新为此次的对象 currentSql = sql; currentStatement = ms; statementList.add(stmt); batchResultList.add(new BatchResult(ms, sql, parameterObject)); } // handler.parameterize(stmt); handler.batch(stmt); return BATCH_UPDATE_RETURN_VALUE; } }
6. ReuseExecutor
可重用的执行器,重用的对象是Statement,也就是说该执行器会缓存同一个sql的Statement,省去Statement的重新创建,优化性能。
内部的实现是通过一个HashMap来维护Statement对象的。由于当前Map只在该session中有效,所以使用完成后记得调用
flushStatements来清除Map。 调用实现的四个抽象方法时会调用 prepareStatement()
public class ReuseExecutor extends BaseExecutor { private final Map<String, Statement> statementMap = new HashMap<String, Statement>(); // 调用父类构造器 public ReuseExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction) { super(configuration, transaction); } private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException { Statement stmt; BoundSql boundSql = handler.getBoundSql(); String sql = boundSql.getSql(); if (hasStatementFor(sql)) { // 如果缓存了该SQL,则返回其Statement对象 stmt = getStatement(sql); applyTransactionTimeout(stmt); } else { // 如果没有缓存该SQL,则创建SQL的Statement,并加入缓存 Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog); stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout()); putStatement(sql, stmt); } handler.parameterize(stmt); return stmt; } // 是否缓存了这个 sql private boolean hasStatementFor(String sql) { try { return statementMap.keySet().contains(sql) && !statementMap.get(sql).getConnection().isClosed(); } catch (SQLException e) { return false; } } // 返回指定sql的 Statement private Statement getStatement(String s) { return statementMap.get(s); } // 添加SQL和Statement private void putStatement(String sql, Statement stmt) { statementMap.put(sql, stmt); } }
7. CachingExecutor
采用静态代理;代理一个 Executor 对象。
执行 update 方法前判断是否清空二级缓存;
执行 query 方法前先在二级缓存中查询,命中失败再通过被代理类查询。
public class CachingExecutor implements Executor { // 持有的 Executor,最终的操作都由该对象实现 private final Executor delegate; private final TransactionalCacheManager tcm = new TransactionalCacheManager(); public CachingExecutor(Executor delegate) { this.delegate = delegate; delegate.setExecutorWrapper(this); } public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject) throws SQLException { this.flushCacheIfRequired(ms); return this.delegate.update(ms, parameterObject); } public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { Cache cache = ms.getCache(); if (cache != null) { this.flushCacheIfRequired(ms); if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) { this.ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql); List<E> list = (List)this.tcm.getObject(cache, key); if (list == null) { list = this.delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); this.tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); } return list; } } return this.delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); } // 是否清空二级缓存 private void flushCacheIfRequired(MappedStatement ms) { Cache cache = ms.getCache(); if (cache != null && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) { this.tcm.clear(cache); } } }
