SpringBoot中的starter是一种非常重要的机制,能够抛弃以前繁杂的配置,将其统一集成进 starter,应用者只需要在maven中引入starter依赖,SpringBoot就能自动扫描到要加载的信息并启 动相应的默认配置。starter让我们摆脱了各种依赖库的处理,需要配置各种信息的困扰。 SpringBoot会自动通过classpath路径下的类发现需要的Bean,并注册进IOC容器。SpringBoot提供 了针对日常企业应用研发各种场景的spring-boot-starter依赖模块。所有这些依赖模块都遵循着约定 成俗的默认配置,并允许我们调整这些配置,即遵循“约定大于配置”的理念。
为什么要自定义starter
在日常开发工作中,经常会有一些独立于业务之外的配置模块,我们经常将其放到一个特定的 包下,然后如果另一个工程需要复用这块功能的时候,需要将代码硬拷贝到另一个工程,重新集成一遍,比较麻烦。如果我们将这些可独立于业务代码之外的功配置模块封装成一个个starter,复用的时候只需要将其在pom中引用依赖即可,SpringBoot为我们完成自动装配。
自定义starter的命名规则
SpringBoot提供的starter以spring-boot-starter-xxx的方式命名的。官方建议自定义的starter使用 xxx-spring-boot-starter命名规则。以区分SpringBoot生态提供的starter。
操作步骤
1.新建spring工程
这个应该不用多说,使用idea中Spring Initializr即可构建
工程结构如下
2.pom配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.2.6.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <groupId>demo-spring-boot-starter</groupId> <artifactId>demo</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>demo</name> <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> <properties> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
3.定义一个实体类映射配置信息
package demospringbootstart.demo.properties; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; /** * @Author:VIC * @Date:Created in 15:04 2020/04/09 * @Description:配置信息实体类 */ // 该注解可以把相同前缀的配置信息通过配置项名称映射成实体类,这里我们指定前缀"demo", // 就可以将以"demo"为前缀的配置项信息拿到 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "demo") public class DemoProperties { private String sayWhat; private String toWho; public String getSayWhat() { return sayWhat; } public void setSayWhat(String sayWhat) { this.sayWhat = sayWhat; } public String getToWho() { return toWho; } public void setToWho(String toWho) { this.toWho = toWho; } }
4.定义配置类
package demospringbootstart.demo.config; import demospringbootstart.demo.properties.DemoProperties; import demospringbootstart.demo.service.DemoService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; /** * @Author:VIC * @Date:Created in 15:35 2020/04/09 * @Description:配置类 */ //@Configuration声明为一个配置类,没什么好说的 @Configuration //该注解用来开启上面一步 @ConfigurationProperties 注解配置bean的支持, //就是告诉springboot能够支持@ConfigurationProperties, // 或者你也可以在@ConfigurationProperties注解标识的类上添加@Configuration和@Component,效果一样 @EnableConfigurationProperties(DemoProperties.class) //@ConditionalOnProperty用来控制@Configuration是否生效,简单来说也就是我们可以通过在yml或properties配置文件中控制 @Configuration 注解的配置类是否生效。 @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "demo", name = "isopen", havingValue = "true") public class DemoConfig { @Autowired private DemoProperties properties; @Bean public DemoService demoService() { return new DemoService(properties.getSayWhat(), properties.getToWho()); } }
5.提供一个service类
package demospringbootstart.demo.service; /** * @Author:VIC * @Date:Created in 15:28 2020/04/09 * @Description:随便实现一个service,这里没什么好说的,这个service提供给集成该starter的业务方调用 */ public class DemoService { public String sayWhat; public String toWho; public DemoService(String sayWhat, String toWho) { this.sayWhat = sayWhat; this.toWho = toWho; } public String sayHello() { return this.sayWhat + "!!!" + this.toWho; } }
6.新建spring.factories文件(重要)
将spring.factories放到META-INF文件夹下面,spring.factories文件内容如下
#自动装配,至于为什么配置了这个文件,springboot就会去装配这里配置的Democonfig类,读者可以去看看springboot SPI机制的实现(有时间搞一篇博客)
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=demospringbootstart.demo.config.DemoConfig
7.测试使用
以上步骤完成后,然后只需mvn clean install,一个自定义starter就制作完成了
======================分隔线======================
使用自定义的starter
1.引入starter依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>demo-spring-boot-starter</groupId>
<artifactId>demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
2.填写配置文件内容
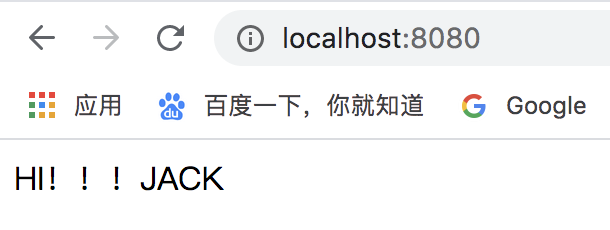
demo.isopen=true demo.to-who=JACK demo.say-what=HI
3.写段代码调用一下看看
package com.zhaowa.course.design.controller; import demospringbootstart.demo.service.DemoService; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import javax.annotation.Resource; /** * @Author:VIC * @Date:Created in 15:53 2020/04/09 * @Description: */ @RestController public class TestController { @Resource private DemoService demoService; @RequestMapping("/") public String test(){ return demoService.sayHello(); } }