1、路由控制简单配置
from django.conf.urls import url from . import views urlpatterns = [ url(r'^articles/2003/$', views.special_case_2003), ]
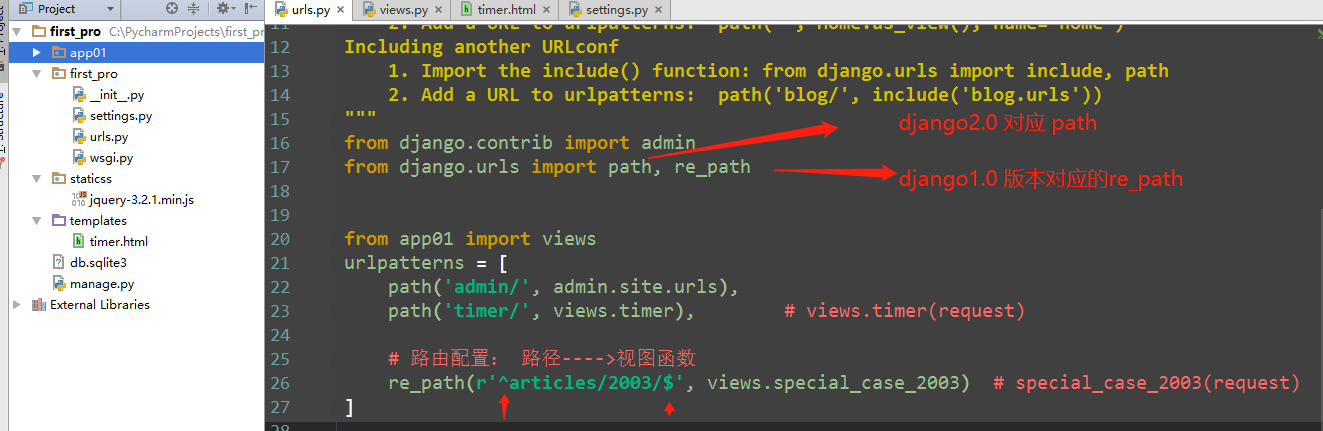

import re
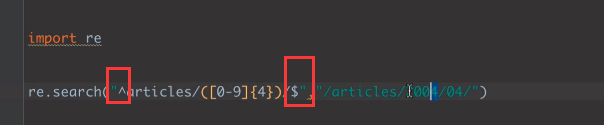
re.search('^articles/2003/$', 'article/2003') # 可以匹配到 匹配开头结尾
re.search('^articles/2003/$', 'article/2003/yun/1992') # 匹配不到
re.search('^articles/2003/', 'article/2003/yun/1991') # 可以匹配到 只匹配开头
2.有名分组

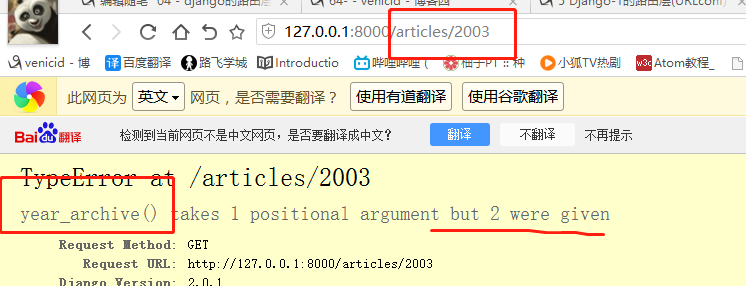
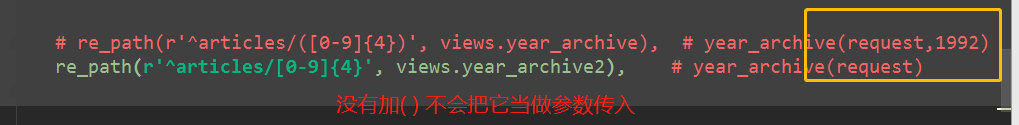
re_path(r'^articles/([0-9]{4})', views.year_archive), # year_archive(request,1992)
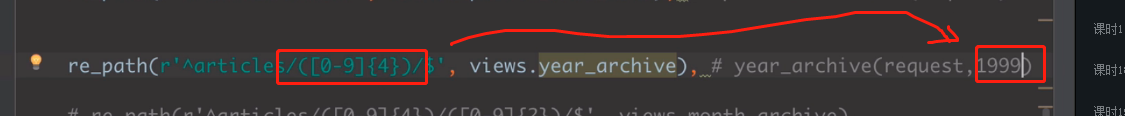
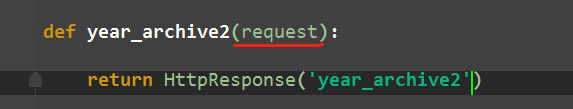
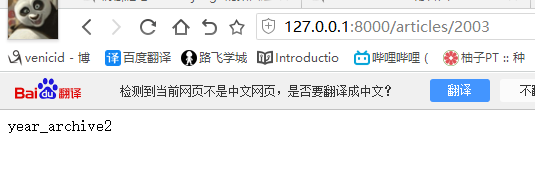
re_path(r'^articles/([0-9]{4})', views.year_archive), # year_archive(request,1992) re_path(r'^articles/[0-9]{4}', views.year_archive2), # year_archive(request)
3
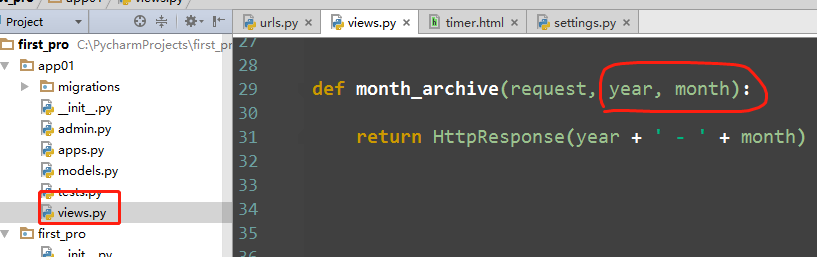
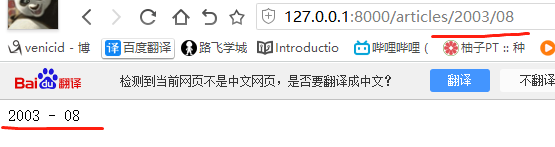
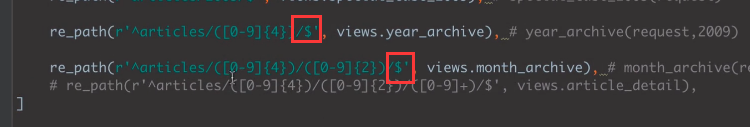
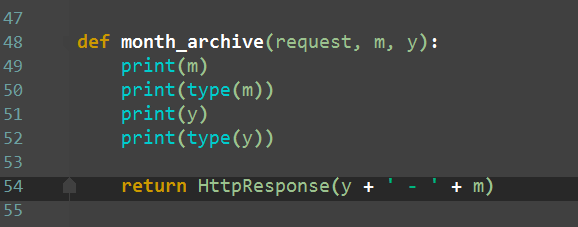
re_path(r'^articles/([0-9]{4})/([0-9]{2})', views.month_archive), # year_archive(request,1992,08)
re_path(r'^articles/([0-9]{4})/([0-9]{2})/([0-9]{2})/$', views.month_archive), # year_archive(request,1992,08)

注意:
- 若要从URL 中捕获一个值,只需要在它周围放置一对圆括号。
- 不需要添加一个前导的反斜杠,因为每个URL 都有。例如,应该是
^articles而不是^/articles。 - 每个正则表达式前面的'r' 是可选的但是建议加上。它告诉Python 这个字符串是“原始的” —— 字符串中任何字符都不应该转义
规范写法
from django.conf.urls import url from . import views urlpatterns = [ url(r'^articles/2003/$', views.special_case_2003), url(r'^articles/([0-9]{4})/$', views.year_archive), url(r'^articles/([0-9]{4})/([0-9]{2})/$', views.month_archive), url(r'^articles/([0-9]{4})/([0-9]{2})/([0-9]+)/$', views.article_detail), ]
4
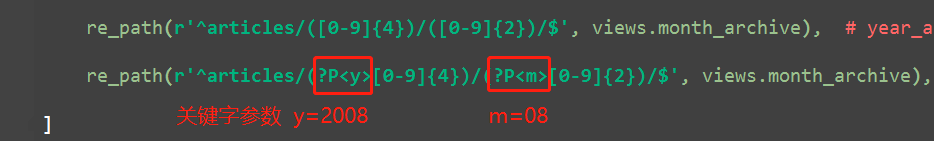
2.有名分组:关键字参数
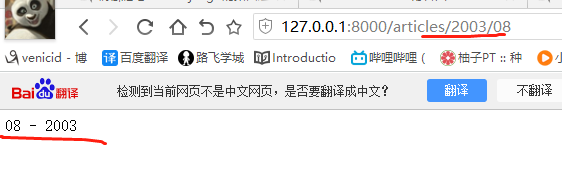
re_path(r'^articles/([0-9]{4})/([0-9]{2})/$', views.month_archive), # year_archive(request,1992,08) re_path(r'^articles/(?P<y>[0-9]{4})/(?P<m>[0-9]{2})/$', views.month_archive), # year_archive(request,y=2009,m=08)
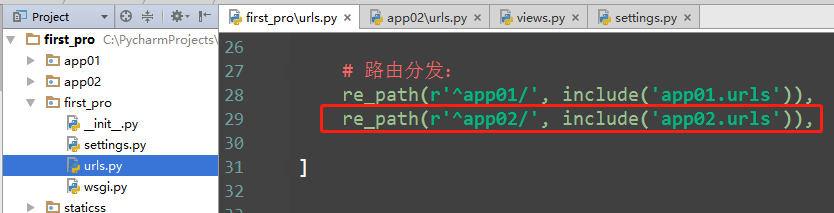
3、分发
主url
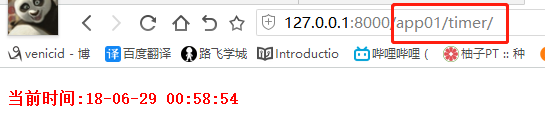
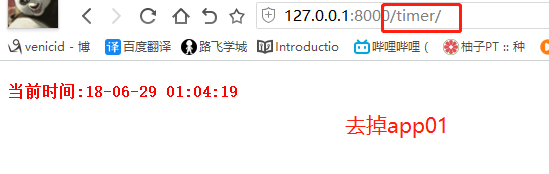
from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path, re_path, include urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), # 路由分发: re_path(r'^app01/', include('app01.urls')), # http://127.0.0.1:8000/app01/timer/ re_path(r'^', include('app01.urls')), # http://127.0.0.1:8000/timer/ # 多个url对应一个view ]
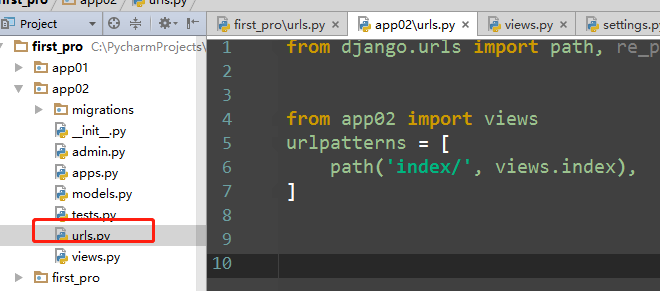
app01的urls.py
from django.urls import path, re_path from app01 import views urlpatterns = [ path('timer/', views.timer), # views.timer(request) # 路由配置: 路径---->视图函数 re_path(r'^articles/([0-9]{4})/$', views.year_archive), # year_archive(request,1992) re_path(r'^articles/([0-9]{4})/([0-9]{2})/$', views.month_archive), # year_archive(request,1992,08) re_path(r'^articles/(?P<y>[0-9]{4})/(?P<m>[0-9]{2})/$', views.month_archive), # year_archive(request,y=2009,m=08) ]

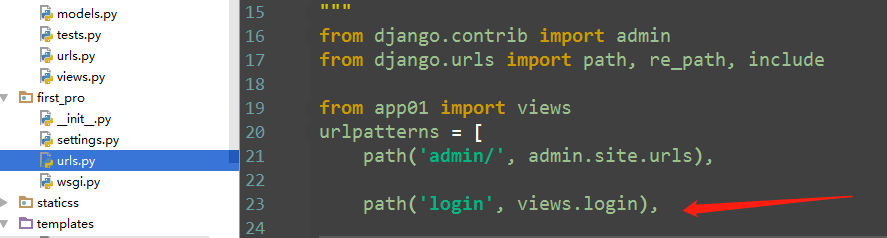
3.路由控制之登录验证
1) urls.py
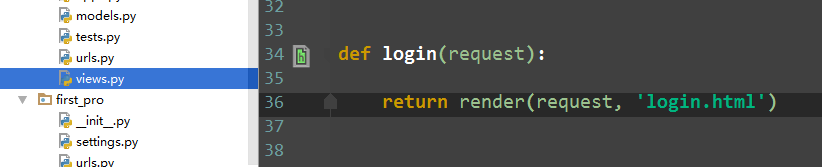
2)view.py
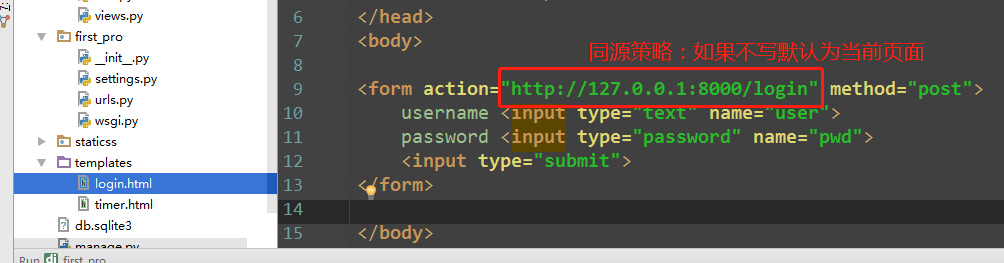
3)templates
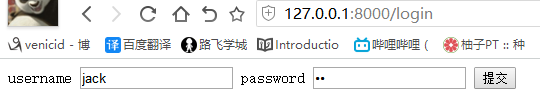
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> {#<form action="" method="post"> 如果不写默认为当前页面,同源策略#} <form action="http://127.0.0.1:8000/login" method="post"> username <input type="text" name="user"> password <input type="password" name="pwd"> <input type="submit"> </form> </body> </html>
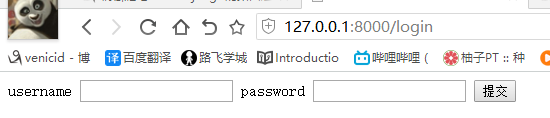
4) runserver 启动,访问
5)提交 CSRF错误
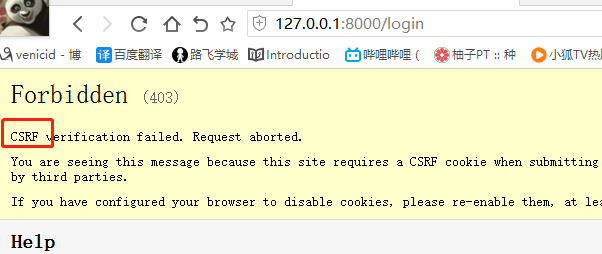
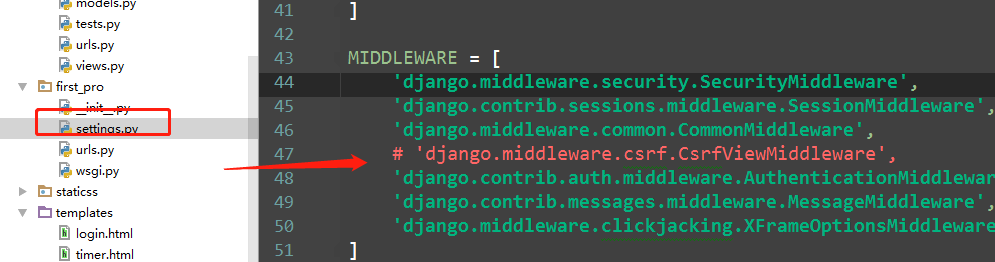
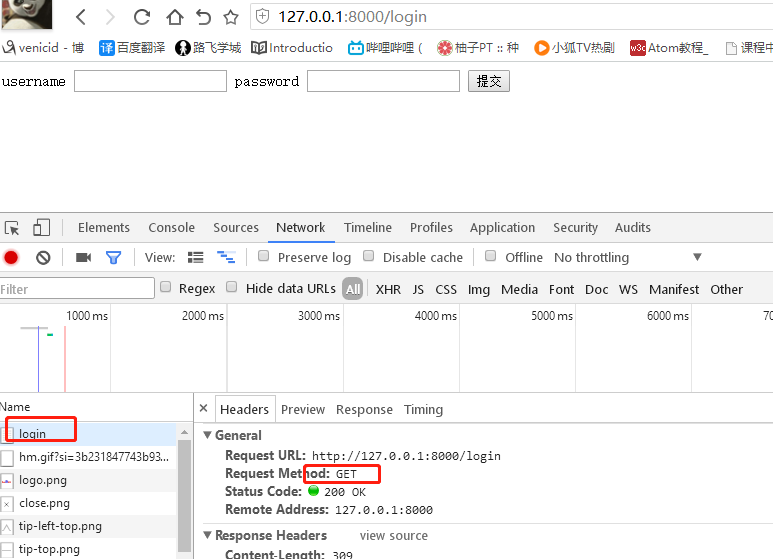

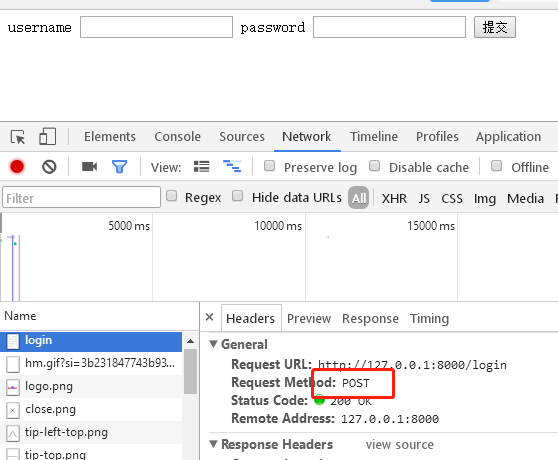
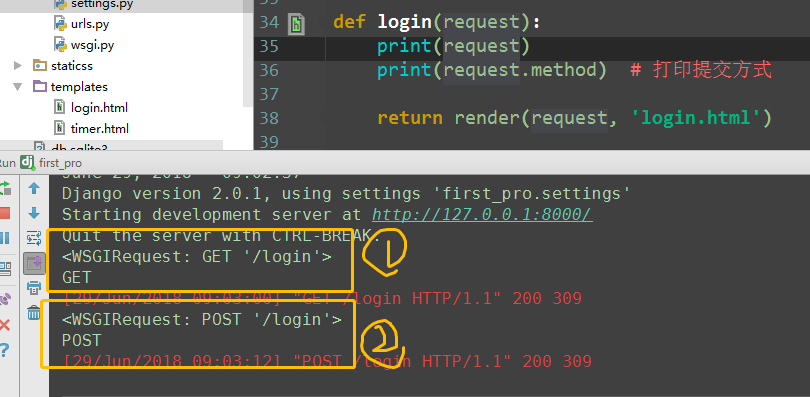
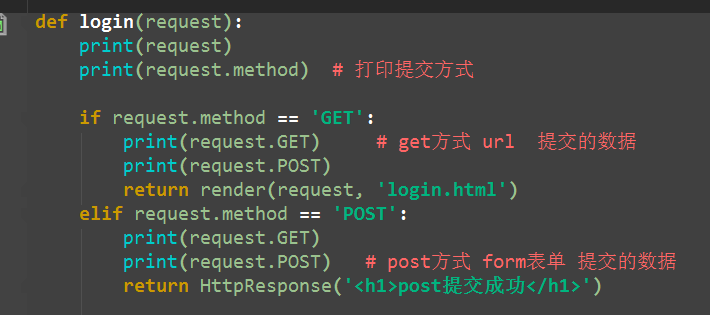

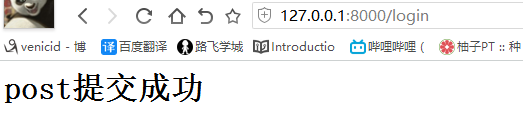
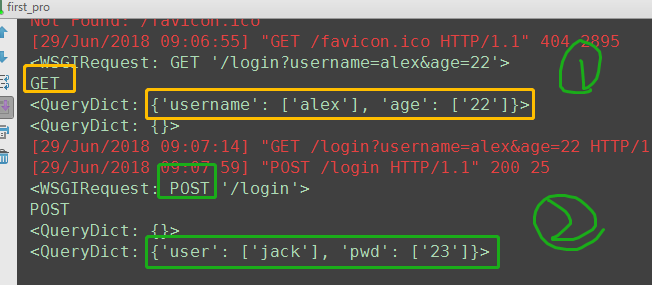
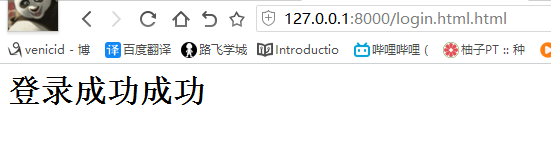
def login(request): print(request) print(request.method) # 打印提交方式 if request.method == 'GET': print(request.GET) # get方式 url 提交的数据 print(request.POST) return render(request, 'login.html') elif request.method == 'POST': print(request.GET) print(request.POST) # post方式 form表单 提交的数据 # <QueryDict: {'user': ['jack'], 'pwd': ['23']}> user = request.POST.get('user') # dict的get方法 pwd = request.POST.get('pwd') if user == 'jack' and pwd == '123': return HttpResponse('<h1>登录成功成功</h1>') else: return HttpResponse('<h1>error username or password</h1>')

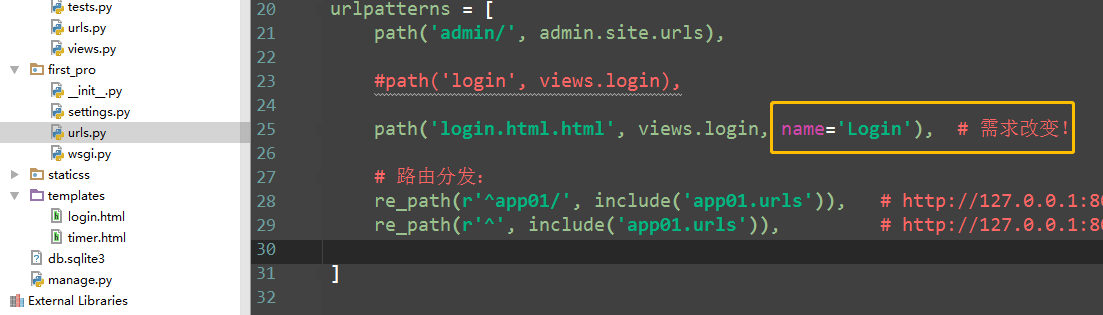
4)路由控制之反向解析
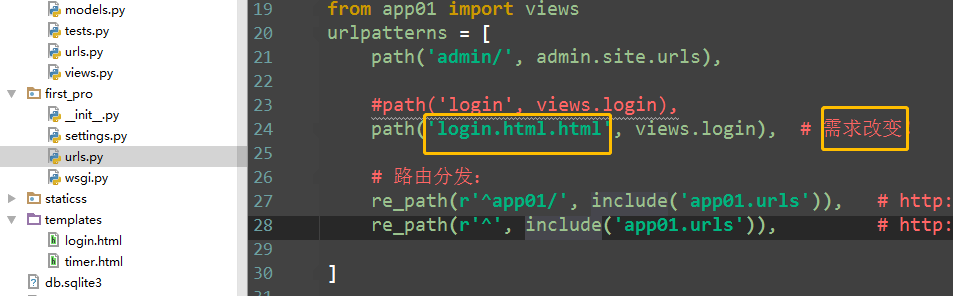
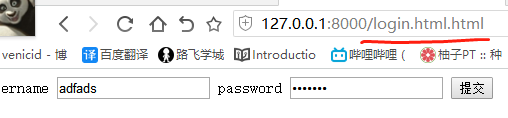
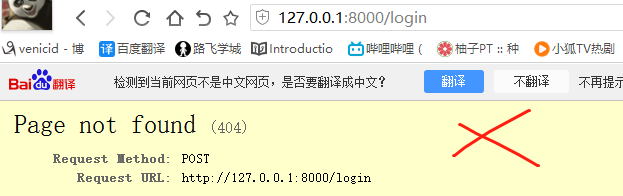
方式1:增加别名name='Login'
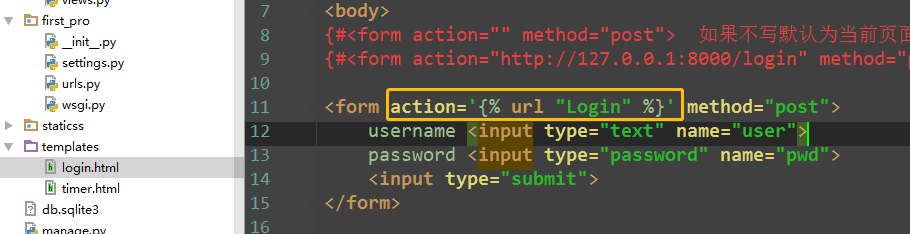

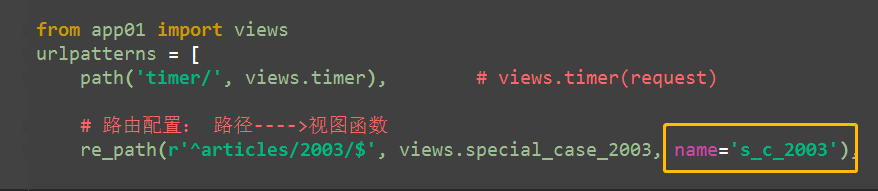
方式2:view函数内,反向解析
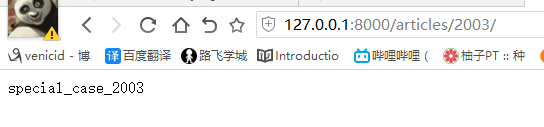
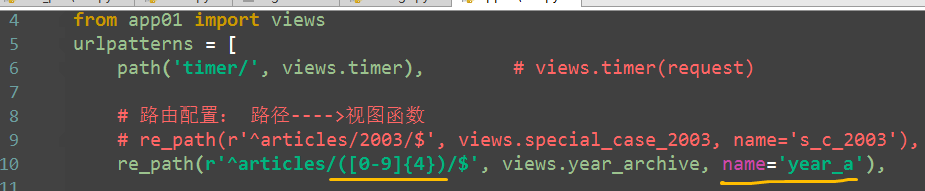
# 路由配置: 路径---->视图函数 re_path(r'^articles/2003/$', views.special_case_2003, name='s_c_2003'), # special_case_2003(request) re_path(r'^articles/([0-9]{4})/$', views.year_archive, name='year_a'),
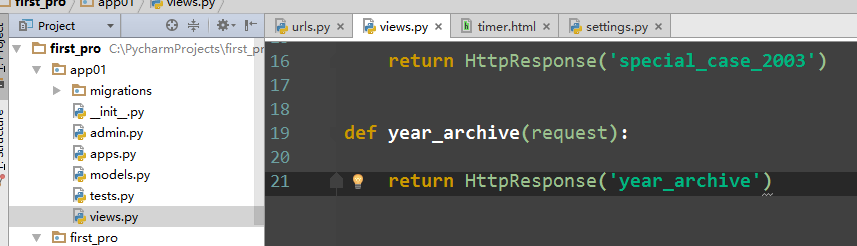
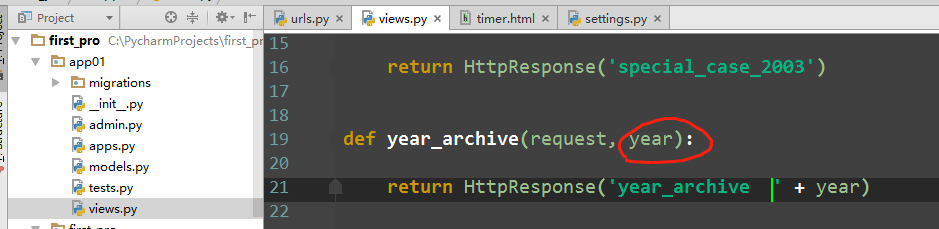
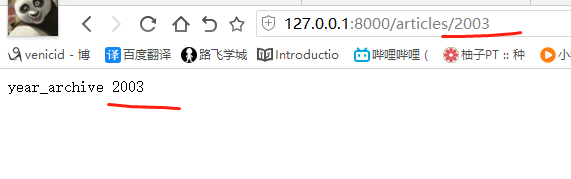
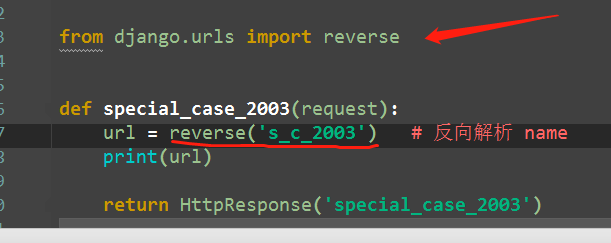
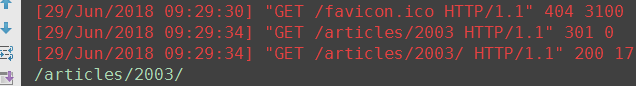
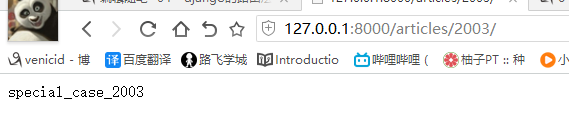
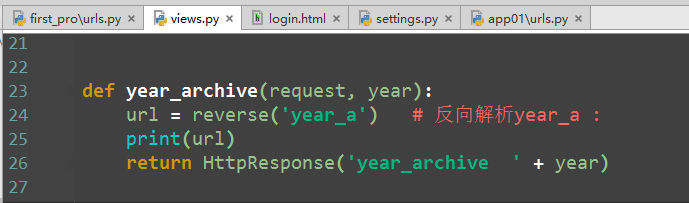
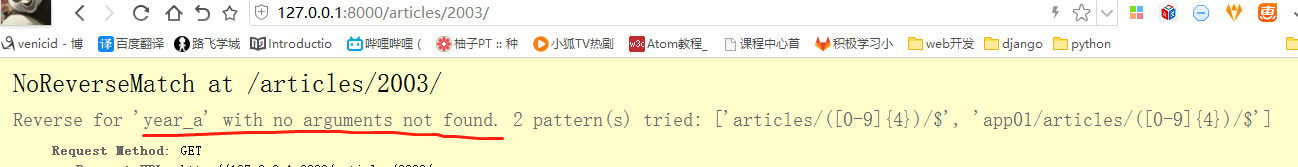
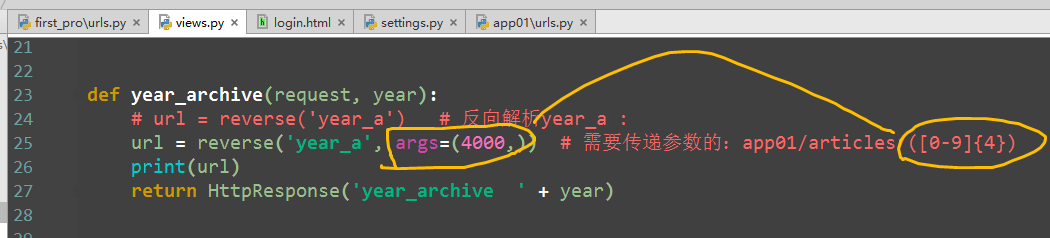
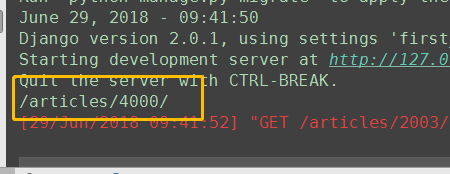
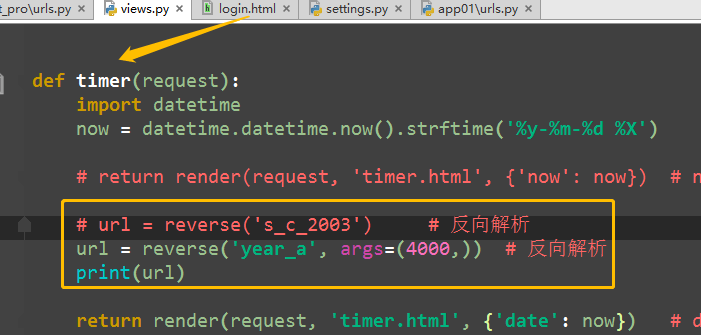
def special_case_2003(request): url = reverse('s_c_2003') # 反向解析 name: /articles/2003/ print(url) return HttpResponse('special_case_2003') def year_archive(request, year): # url = reverse('year_a') # 反向解析year_a : url = reverse('year_a', args=(4000,)) # 需要传递参数的:app01/articles/([0-9]{4}) print(url) return HttpResponse('year_archive ' + year)
2.
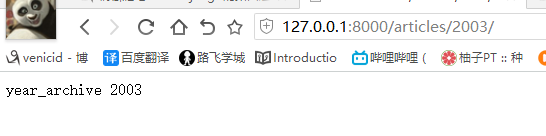
view中的反向解析,可以在任何地方解析

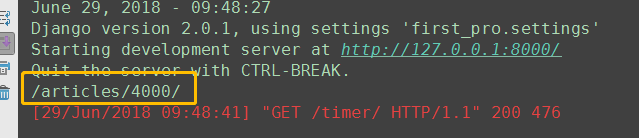
4.名称空间
1.why
python manage.py startapp app02 # 创建一个新的app app02
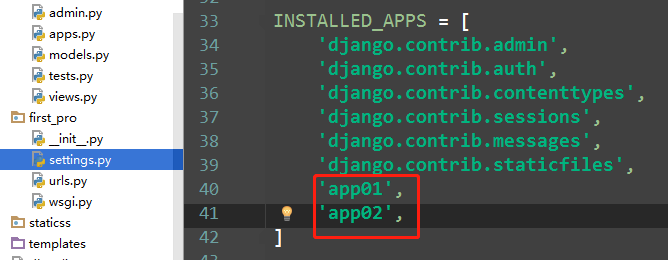
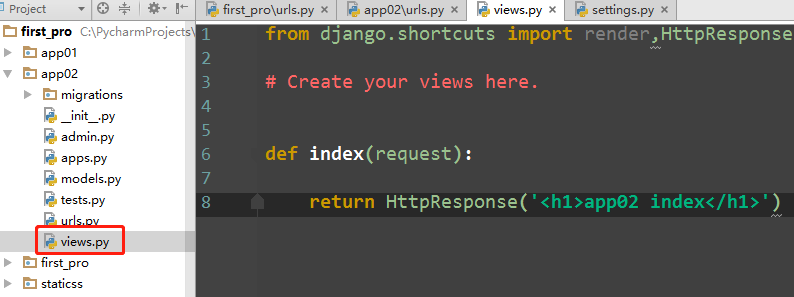
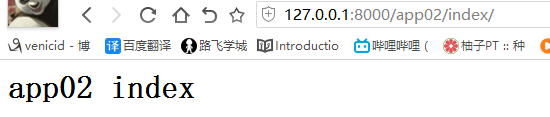
如果此时app01 也存在个index
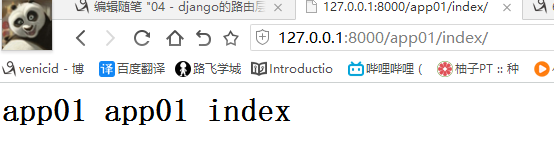
如果两个index都有name
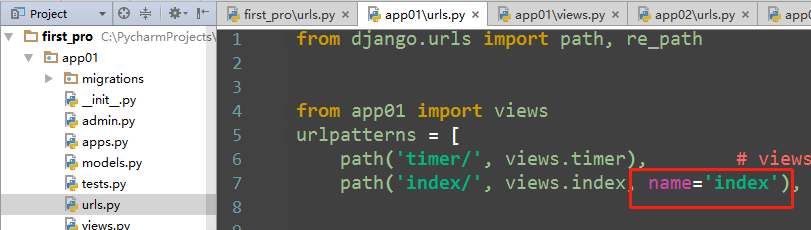
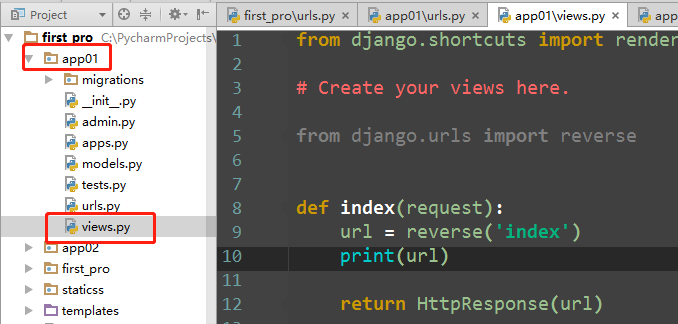
因为存在url的先后问题,后面的会覆盖前面的,所以访问到的是app02的 url

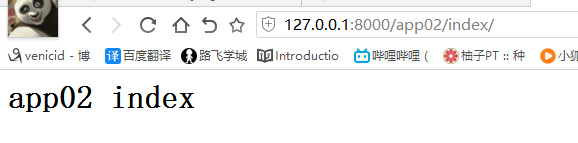
2、how
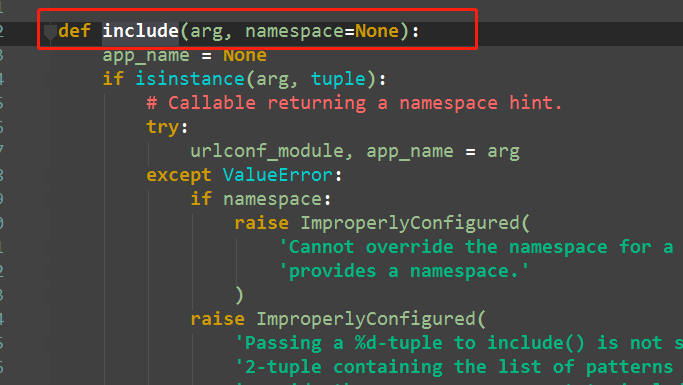
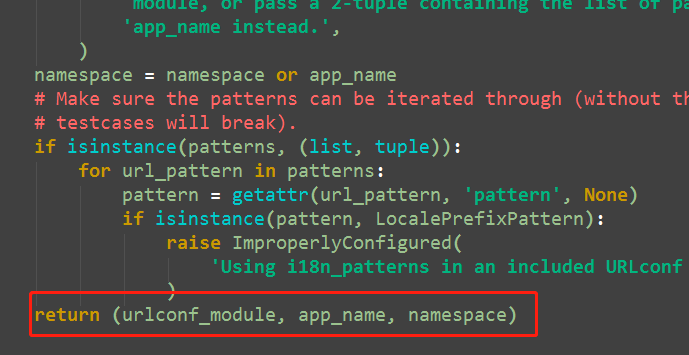
include函数源码

urls代码
re_path(r'^app01/', include(('app01.urls', 'app01'))), # 元组 re_path(r'^app02/', include(('app02.urls', 'app02'))),
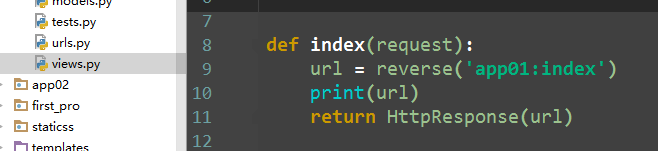
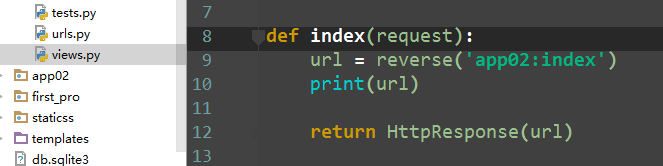
views视图
def index(request): url = reverse('app02:index') return HttpResponse(url)
5、url控制器之path方法 django2.0版
1.why
3.path方法:给输入的url限定数据类型格式
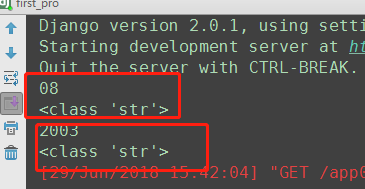
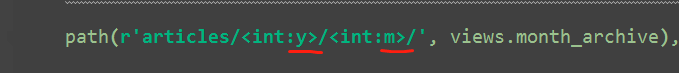
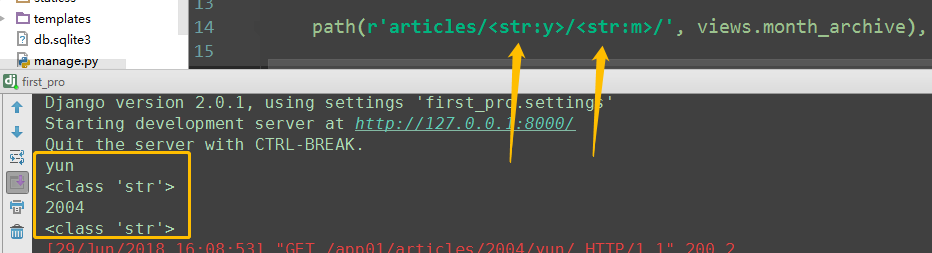
#re_path(r'^articles/(?P<y>[0-9]{4})/(?P<m>[0-9]{2})/$', views.month_archive), # year_archive(request,y=2009,m=08) path(r'articles/<int:y>/<int:m>/', views.month_archive), # year_archive(request,y=2009,m=08) # path方法 无^ $匹配

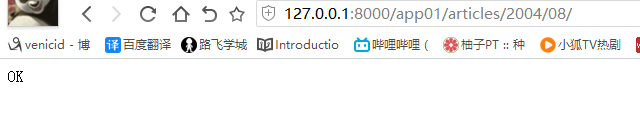
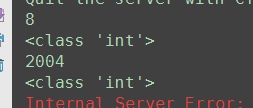
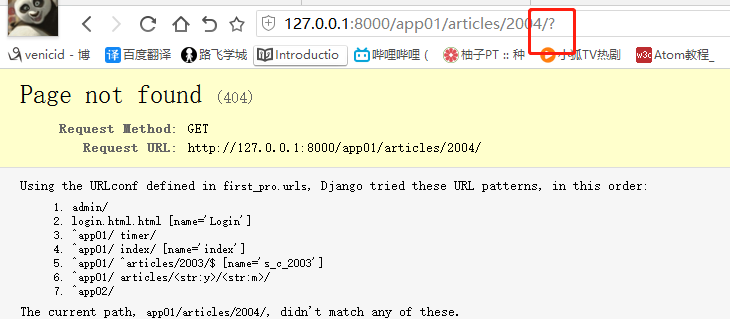
如果path方法写上 ^ $ ,或者 输入的是字符串的话


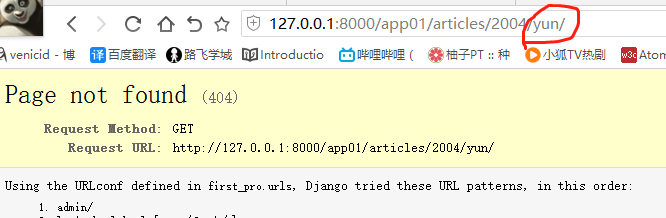
限定为str格式
特殊字符

?是get方法的标志
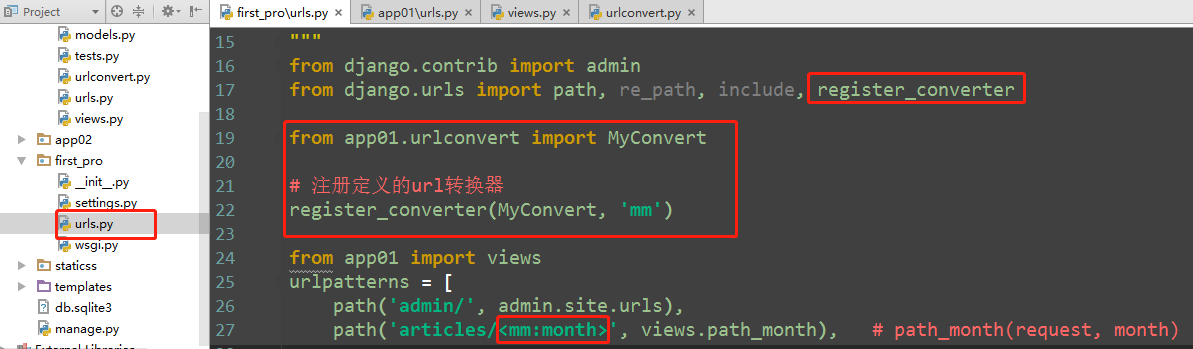
6、path自定义转化器
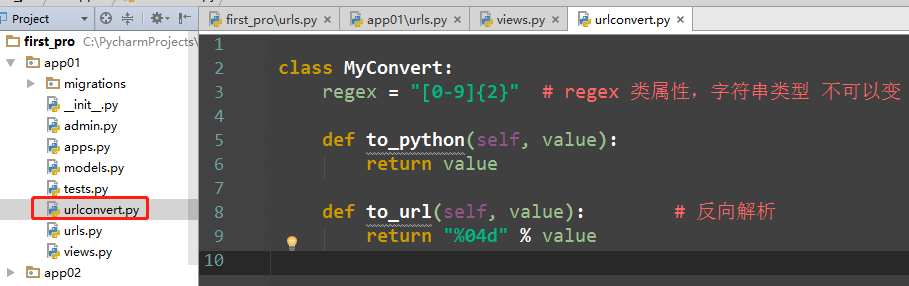
自定义:新建一个urlconvert文件
class MyConvert: regex = "[0-9]{2}" # regex 类属性,字符串类型 不可以变 def to_python(self, value): return value def to_url(self, value): # 反向解析 return "%04d" % value
使用register_converter 将其注册到URL配置中:
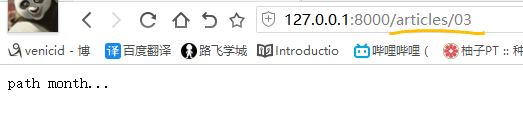
from django.urls import path, re_path, include, register_converter from app01.urlconvert import MyConvert # 注册定义的url转换器 register_converter(MyConvert, 'mm') from app01 import views urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), path('articles/<mm:month>', views.path_month), # path_month(request, month), ]

10. URL控制总结
1、路由分发
主url文件
from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path, re_path, include urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), # path(r'^app01/$', include(('app01.urls', 'app01'))) 错误 re_path(r'^app01/', include(('app01.urls', 'app01'))) # path 是2.0用法 # re_path 是1.0 用法,# include可以起作用 # 路由分发, r'^app01/' $不可以添加 ]
app01的url
from django.urls import path, re_path, include from app01 import views urlpatterns = [ # path(r'index/', views.index, name='index') # 不可用 re_path(r'^index/$', views.index, name='index') # r'^index/$' 必须加入^ $ 开头 结尾符号 ]

2
3
4
5