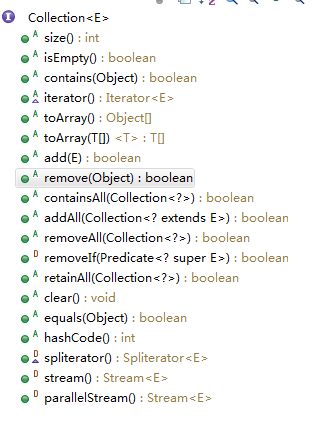
Collection接口中定义的方法如下,所有继承自Collection接口的接口(List,Set)的实现类均实现了这些方法。
List容器是有序、可重复的,常用的实现类:ArrayList,LinkedList,Vector(线程安全的)
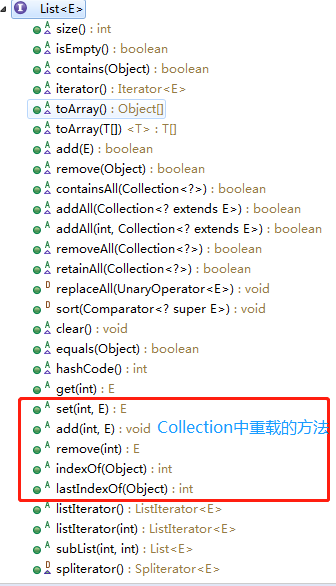
带索引的add,remove操作。
自己实现的MyArrayList:
package test.stringTest; public class MyArrayList<E> { private Object[] elementData; // 元素个数 private int size; // 数组默认长度 private final static int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; public MyArrayList() { elementData = new Object[DEFAULT_CAPACITY]; } public MyArrayList(int length) { if (length <= 0) throw new RuntimeException("容器容量值需为正整数:" + length); elementData = new Object[length]; } public void add(E element) { if (size == elementData.length) grow(); elementData[size++] = element; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public E get(int index) { if (indexInRange(index)) return (E) elementData[index]; else throw new RuntimeException("索引越界:" + index); } public void remove(E element) { int index = -1; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { if (element.equals(elementData[i])) { index = i; break; } } if (index != -1) { remove(index); } } public void remove(int index) { if (!indexInRange(index)) { throw new RuntimeException("索引越界:" + index); } int numMoved = elementData.length - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) { System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, numMoved); } else { elementData[index] = null; } size--; } private boolean indexInRange(int index) { return index < size && index >= 0 ? true : false; } public int size() { return size; } public boolean isEmpty() { return size == 0 ? true : false; } // 数组扩容 private void grow() { Object[] newArray = new Object[elementData.length + (elementData.length >> 1)]; System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, newArray, 0, elementData.length); elementData = newArray; } @Override public String toString() { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append("["); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { sb.append(elementData[i].toString() + ","); } sb.setCharAt(sb.length() - 1, ']'); return sb.toString(); } public static void main(String[] args) { MyArrayList<String> list = new MyArrayList<>(20); int i = 0; while (i <= 50) { list.add("aaa" + i); i++; } System.out.println(list); System.out.println(list.get(31)); System.out.println(list.size()); list.remove(21); list.remove("aaa4"); System.out.println(list); System.out.println(list.size); System.out.println(list.isEmpty()); } }
HashMap底层实现:数组加链表(JDK8以后当元素个数超过8时,会转变为红黑树结构)。首先根据Key计算出hashcode,然后根据hashcode,利用hash算法计算出数组的下标,然后将值放入该下标数组存储的链表中(有重复(equals比较)的key值则覆盖) 两个相同的对象必须具有相同的hashcode。
/** * The table, initialized on first use, and resized as * necessary. When allocated, length is always a power of two. * (We also tolerate length zero in some operations to allow * bootstrapping mechanics that are currently not needed.) */ transient Node<K,V>[] table;
/** * Basic hash bin node, used for most entries. (See below for * TreeNode subclass, and in LinkedHashMap for its Entry subclass.) */ static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { final int hash; final K key; V value; Node<K,V> next; Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { this.hash = hash; this.key = key; this.value = value; this.next = next; }
..........
自己实现的HashMap:

1 package test.stringTest; 2 3 public class MyHashMap<K,V> { 4 Node<K,V>[] table; // 位桶数组 5 int size; 6 7 public MyHashMap() { 8 table = new Node[16]; 9 } 10 11 public void put(K key, V value) { 12 Node<K,V> node = new Node<>(); 13 node.key = key; 14 node.value = value; 15 node.next = null; 16 node.hash = myHash(key, table.length); 17 Node<K,V> temp = table[node.hash]; 18 Node<K,V> lastNode = temp; 19 boolean isOverride = false; // 有没被覆盖 20 if (temp == null) { 21 table[node.hash] = node; 22 size++; 23 } else { 24 while (temp != null) { 25 // key相同 则覆盖 26 if (temp.key.equals(key)) { 27 temp.value = value; 28 isOverride = true; 29 break; 30 } else { 31 // 不同 则继续向下遍历 32 lastNode = temp; 33 temp = temp.next; 34 } 35 } 36 // 没有覆盖发生 则将Node添加到后面 37 if (!isOverride) { 38 lastNode.next = node; 39 size++; 40 } 41 } 42 } 43 44 public Object get(Object key) { 45 int hash = myHash(key, table.length); 46 Node<K,V> temp = table[hash]; 47 if (temp != null) { 48 while (temp != null) { 49 if (temp.key.equals(key)) 50 return temp.value; 51 else 52 temp = temp.next; 53 } 54 } 55 return null; 56 } 57 58 @Override 59 public String toString() { 60 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("{"); 61 for (int i = 0; i < table.length; i++) { 62 Node<K,V> temp = table[i]; 63 while (temp != null) { 64 sb.append(temp.key + ":" + temp.value + ","); 65 temp = temp.next; 66 } 67 } 68 sb.setCharAt(sb.length() - 1, '}'); 69 return sb.toString(); 70 } 71 72 private int myHash(Object key, int length) { 73 return key.hashCode() % length; 74 } 75 76 public static void main(String[] args) { 77 MyHashMap<String,Integer> map = new MyHashMap<>(); 78 map.put("aaa", 111); 79 map.put("bbb", 222); 80 map.put("ccc", 333); 81 map.put("ddd", 444); 82 map.put("aae", 555); 83 map.put("ccc", 666); 84 map.put("rre", 777); 85 map.put("aaa", 321); 86 System.out.println(map.size); 87 System.out.println(map.get("ccc")); 88 } 89 90 } 91 92 class Node<K,V> { 93 int hash; 94 K key; 95 V value; 96 Node<K,V> next; 97 }
