两个配置文件
一:
server {
listen 80; #
# 在本机所有ip上监听80,也可以写为192.168.1.202:80,这样的话,就只监听192.168.1.202上的80口
server_name www.heytool.com; # 域名
root /www/html/www.heytool.com; # 站点根目录(程序目录)
index index.html index.htm; # 索引文件
location / { # 可以有多个location
root /www/html/www.heytool.com; # 站点根目录(程序目录)
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
# 定义错误页面,如果是500错误,则把站点根目录下的50x.html返回给用户
location = /50x.html {
root /www/html/www.heytool.com;
}
}
# 开始配置站点bbs.heytool.com
server {
listen 80;
server_name bbs.heytool.com;
root /www/html/bbs.heytool.com;
index index.html index.htm; # 索引文件
location / {
root /www/html/bbs.heytool.com;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root /www/html/bbs.heytool.com;
}
}
}
一个server配置段一般对应一个域名

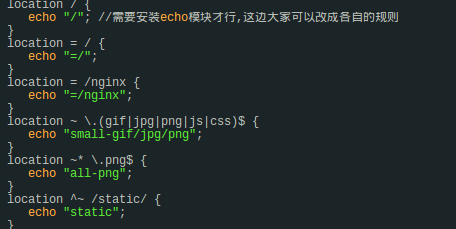
location的语法规则: location [=|~|~*|^~] /uri/ { … }
= 表示精确匹配,这个优先级也是最高的
^~ 表示uri以某个常规字符串开头,理解为匹配 url路径即可。nginx不对url做编码,因此请求为/static/20%/aa,可以被规则^~ /static/ /aa匹配到(注意是空格)。
~ 表示区分大小写的正则匹配
~* 表示不区分大小写的正则匹配(和上面的唯一区别就是大小写)
!~和!~*分别为区分大小写不匹配及不区分大小写不匹配的正则
/ 通用匹配,任何请求都会匹配到,默认匹配.
首先匹配 =,其次匹配^~, 其次是按文件中顺序的正则匹配,最后是交给 / 通用匹配。当有匹配成功时候,停止匹配,按当前匹配规则处理请求。
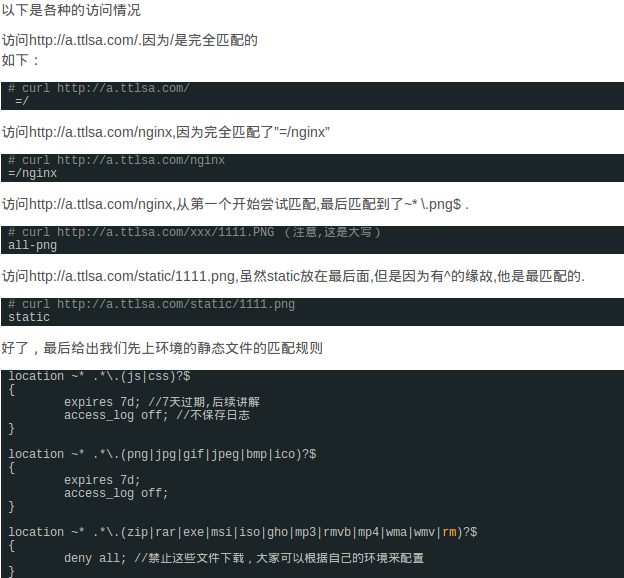
例子: