一、ThreadLocal回顾
ThreadLocal对象用于在同一个线程中传递数据,避免显式的在方法中传参。
每个线程中保存了ThreadLocalMap对象,ThreadLocalMap对象的key就是ThreadLocal对象本身,value就是当前线程的值。
看下ThreadLocal的get方法

public T get() { //当前线程 Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); //获取当前线程的ThreadLocalMap对象 ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); if (map != null) { //获取该ThreadLocal对象的value ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this); if (e != null) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") T result = (T)e.value; return result; } } //设置初始值 return setInitialValue(); } //获取当前线程的ThreadLocalMap对象 ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) { return t.threadLocals; }
该方法首先从当前线程中获取ThreadLocalMap对象,接着从ThreadLocalMap获取该ThreadLocal锁对应的值;如果未获取到,调用setInitialValue方法,设置初始值,并返回初始值。再看下ThreadLocal的set方法

public void set(T value) { //获取当前线程 Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); //获取当前线程的ThreadLocalMap对象 ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); //如果ThreadLocalMap对象存在,则直接设置key(ThreadLocal对象),value;否则创建ThreadLocalMap对象,并设置key,value if (map != null) map.set(this, value); else createMap(t, value); } void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) { t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue); }
该方法同样获取当前线程的ThreadLocalMap对象,如果该对象不为空,那么设置key(ThreadLocal对象),value;否则创建ThreadLocalMap对象,并设置key,value
二、父线程与子线程传值问题
ThreadLocal无法将父线程中的值传递到子线程
下面的代码在主线程中设置threadLocal的值为"dhytest",在子线程中调用get方法,聪明的你一定知道返回的是null. 因为在子线程中调用get方法,获取的是子线程中的ThreadLocalMap对象,而子线程中的ThreadLocalMap对象并未对key (threadLocal)设置相应的value

static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>(); public static void main(String[] args) { threadLocal.set("dhytest"); new Thread(()->{ System.out.println("子线程获取到的值:" + threadLocal.get()); }).start(); System.out.println("父线程获取到的值:" + threadLocal.get()); }
运行结果:

父线程获取到的值:dhytest 子线程获取到的值:null
如何将父线程的值传递给子线程?
方法一:
在执行start方法前获取到父线程的值,因为在thread对象执行start方法前,当前线程还是父线程,因此可以通过threadLocal.get方法获取父线程的值

static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>(); private void test() throws InterruptedException { Thread.currentThread().setName("main-thread"); //主线程设置一个值 threadLocal.set(new Value("dhyTest")); //运行子线程 Thread childThread = new Thread(new ParentChildTransferValue2.ChildThread(), "child-thread"); childThread.start(); //主线成等待子线程运行完,以便观察主线中设置的值是否被子线程成功修改 childThread.join(); System.out.println("父线程获取到的最终的值:" + threadLocal.get()); } class ChildThread implements Runnable { //获取主线程中设置的值 Value value = threadLocal.get(); @Override public void run() { //打印主线程的值 System.out.println("原父线程的值: " + value); //如果启用了线程(调用start方法),调用get方法是获取不到值的 Value nullValue = threadLocal.get(); System.out.println("子线程中直接调用get方法获取父线程的值,value:" + nullValue); //获取到父线程的值,并进行更改 value.setData(value.getData() + "---子线程对父线程的值做了修改" ); } }
运行结果:
原父线程的值: dhyTest 子线程中直接调用get方法获取父线程的值,value:null 父线程获取到的最终的值:dhyTest---子线程对父线程的值做了修改
方法二:
使用 InheritableThreadLocal

static InheritableThreadLocal<Value> threadLocal = new InheritableThreadLocal<>(); private void test() throws InterruptedException { Thread.currentThread().setName("main-thread"); //主线程设置一个值 threadLocal.set(new Value("dhyTest")); //运行子线程 Thread childThread = new Thread(new ChildThread(), "child-thread"); childThread.start(); //主线成等待子线程运行完,以便观察主线中设置的值是否被子线程成功修改 childThread.join(); System.out.println("父线程获取到的最终的值:" + threadLocal.get()); } class ChildThread implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { Value value = threadLocal.get(); System.out.println("子线程中直接调用get方法获取父线程的值,value:" + value); value.setData(value.getData() + "---子线程对父线程的值做了修改"); } }
运行结果:

子线程中直接调用get方法获取父线程的值,value:dhyTest
父线程获取到的最终的值:dhyTest---子线程对父线程的值做了修改
InheritableThreadLocal分析
为什么使用InheritableThreadLocal,子线程就可以获取到父线程的值
看下InheritableThreadLocal类,InheritableThreadLocal继承了ThreadLocal类,重写了childValue,getMap,createMap方法
对于getMap方法,InheritableThreadLocal中返回的是线程中的inheritableThreadLocals变量,而ThreadLocal返回的是线程中的threadLocals变量;setMap同理

public class InheritableThreadLocal<T> extends ThreadLocal<T> { protected T childValue(T parentValue) { return parentValue; } ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) { return t.inheritableThreadLocals; } void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) { t.inheritableThreadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue); } }
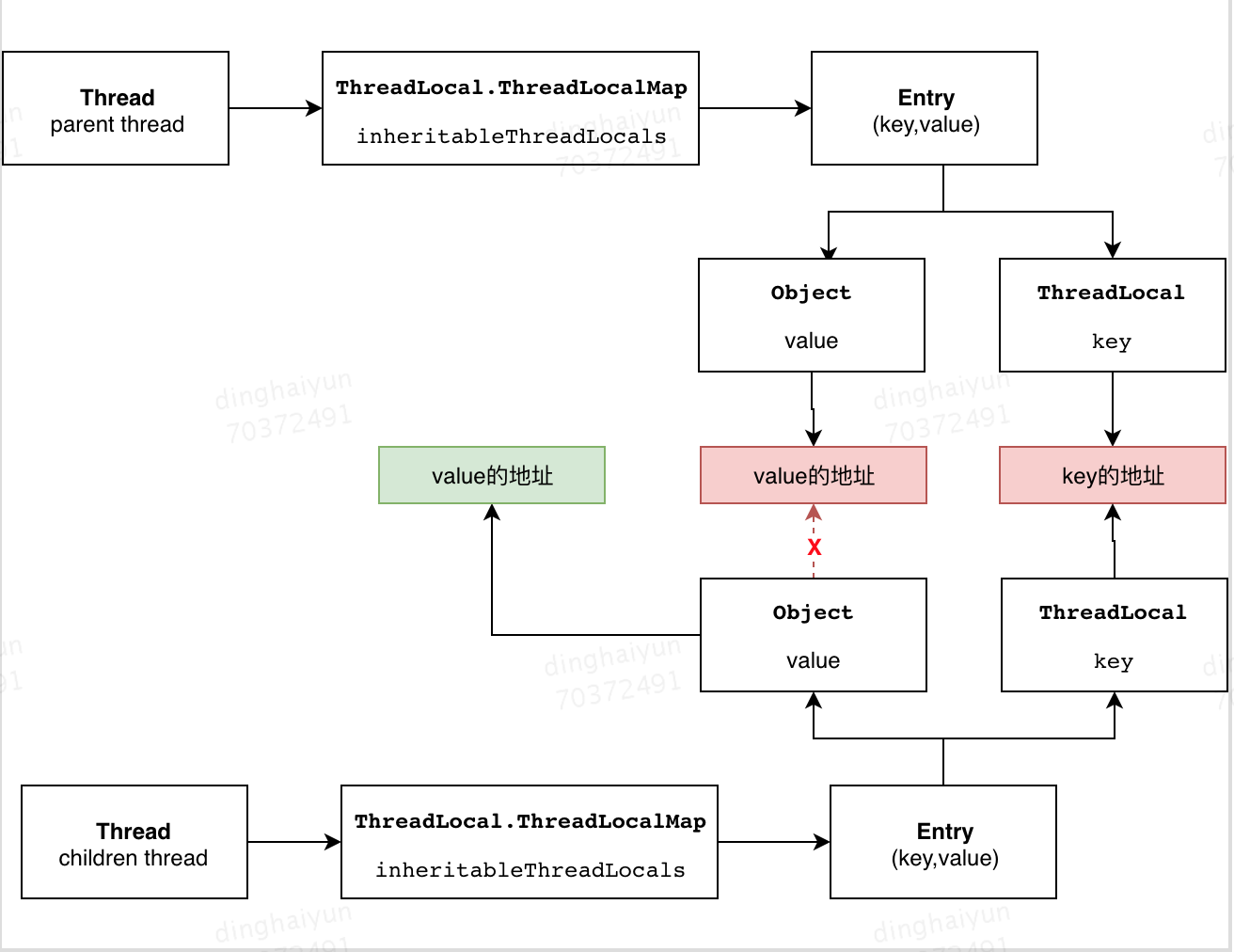
再看下Thread实例化的代码,从构造函数跟进init方法,inheritThreadLocals变量是true。在init方法中,获取父线程,将父线程的inheritableThreadLocals变量赋值给子线程的inheritableThreadLocals变量,从而实现了父线程与子线程的传值

public Thread(Runnable target) { init(null, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0); } private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name, long stackSize) { init(g, target, name, stackSize, null, true); } private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name, long stackSize, AccessControlContext acc, boolean inheritThreadLocals) { if (name == null) { throw new NullPointerException("name cannot be null"); } this.name = name; //这里获取了父线程 Thread parent = currentThread(); SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager(); //中间省略了一些代码 //inheritThreadLocals 是true并且父线程的inheritableThreadLocals不为空,那么将父线程的inheritableThreadLocals拷贝给子线程 if (inheritThreadLocals && parent.inheritableThreadLocals != null) this.inheritableThreadLocals = ThreadLocal.createInheritedMap(parent.inheritableThreadLocals); /* Stash the specified stack size in case the VM cares */ this.stackSize = stackSize; /* Set thread ID */ tid = nextThreadID(); }
具体看下是子线程是如何拷贝父线程的值的:

static ThreadLocalMap createInheritedMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap) { return new ThreadLocalMap(parentMap); } private ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap) { Entry[] parentTable = parentMap.table; int len = parentTable.length; setThreshold(len); table = new Entry[len]; for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) { Entry e = parentTable[j]; if (e != null) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") ThreadLocal<Object> key = (ThreadLocal<Object>) e.get(); if (key != null) { Object value = key.childValue(e.value); Entry c = new Entry(key, value); int h = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1); //如果发生hash碰撞,那么槽位后移 while (table[h] != null) h = nextIndex(h, len); table[h] = c; size++; } } } }
InheritableThreadLocal存在的问题
虽然InheritableThreadLocal可以解决在子线程中获取父线程的值的问题,但是在使用线程池的情况下,由于不同的任务有可能是同一个线程处理,因此这些任务取到的值有可能并不是父线程设置的值
case1:模拟使用线程池情况下(为了便于测试不同任务有同一个线程处理的场景,使用单线程),两个任务由同一个线程处理。
第一个任务中获取到父线程的值,并且重新设置了值;第二个任务中获取到的并不是父线程的值了,而是第一个任务设置的值。

static InheritableThreadLocal<Value> threadLocal = new InheritableThreadLocal<>(); static ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); private void test() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { threadLocal.set(new Value("dhytest")); Future<?> task1 = executorService.submit((new ChildThread("task1"))); task1.get(); Future<?> task2 = executorService.submit(new ChildThread("task2")); task2.get(); System.out.println("父线程的值:" + threadLocal.get()); } class ChildThread implements Runnable { private String taskName; ChildThread(String taskName) { this.taskName = taskName; } @Override public void run() { Value value = threadLocal.get(); System.out.println("任务【" + taskName + "】获取到父线程的值为:" + value); threadLocal.set(new Value("值被任务【" + taskName + "】修改啦")); //如果使用下面的代码,那么父线程的值是会被改变的 //value.set(new Value("父线程的值也被修改啦,因为是引用传递")); } }
运行结果:

任务【task1】获取到父线程的值为:dhytest
任务【task2】获取到父线程的值为:值被任务【task1】修改啦
父线程的值:dhytest
为什么第二个任务获取到的是第一个任务设置的值,而没有获取到父线程原本的值?
从实例化Thread的方法(init)中可以看出,实例化线程时,会检测是否需满足拷贝父线程的条件(inheritThreadLocals 是true并且父线程的inheritableThreadLocals不为空),若果满足,那么将父线程的inheritableThreadLocals变量拷贝给子线程的inheritableThrealLocals变量,也就是Thread类的ThreadLocal.createInheritedMap方法。
执行第一个任务时,创建一个线程,执行初始化,将父线程的inheritableThreadLocals拷贝给了子任务;调用get(InheritableThreadLocal 继承了ThreadLocal,重写了getMap方法)方法,会返回给线程持有的inheritableThreadLocals变量;
执行第二个任务时,由于使用的是同一个线程,因此调用get方法,返回的是这个线程持有的inheritableThreadLocals变量,而此时该变量中的value已被第一个任务改写,因此获取到并不是父线程原本的值
虽然任务对value进行了重新赋值,但是并不影响父线程的值,因为value指向了一个新的地址。如果直接更改value,那么会影响父线程的值,因为指向的是同一个地址
case2:使用线程池情况下,子任务由同一个线程处理,但是父线程是不同的线程

private void test() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { //父线程1 Thread parent1 = new Thread(() -> { threadLocal.set(new Value("parent1")); Future<?> task1 = executorService.submit((new ChildThread("task1-parent1"))); try { task1.get(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); parent1.start(); parent1.join(); //父线程2 Thread parent2 = new Thread(() -> { threadLocal.set(new Value("parent2")); Future<?> task2 = executorService.submit((new ChildThread("task2-parent2"))); try { task2.get(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); parent2.start(); }
运行结果:

任务【task1-parent1】获取到父线程的值为:parent1
任务【task2-parent2】获取到父线程的值为:parent1
从结果中可以看出任务2没有获取到父线程的值,而是获取到任务1的父线程的值,原因其实和case1差不多,本质原因都是因为任务1和任务2使用的是同一个线程,因此get的是同一个value
在使用线程池时,如何在子线程中正确的获取父线程的值?
既然问题的根源是由于使用同一个线程造成的,那么在任务执行完后,清空该线程持有的threadLocals或者inheritableThreadLocals中的value,执行其他任务时,能够重新拷贝父线程的值就好了
如何实现?
1.如前面的方法一,在执行任务前,备份父线程的值,任务结束后,清除该子线程的值
扩展下,可以使用装饰器模式来装饰我们的任务。首先在任务执行备份父线程的值;在任务执行时,拷贝父线程的值到子线程;任务执行结束后,清除子线程持有的备份数据

public class ExtRunnable implements Runnable { //父线程的值 Value value = AppContext.get(); private Runnable runnable; public ExtRunnable(Runnable runnable) { this.runnable = runnable; } @Override public void run() { //将父线程的值拷贝的子线程 AppContext.set(value); try { this.runnable.run(); } finally { //任务执行完后,将该子线程的值删除 AppContext.remove(); } } }
调用方式:

executorService.submit(new ExtRunnable(new ChildThread("task1-parent1")));
方法三:
阿里封装了一个工具,实现了在使用线程池等会池化复用线程的组件情况下,提供ThreadLocal值的传递功能,解决异步执行时上下文传递的问题
https://github.com/alibaba/transmittable-thread-local
官网中给出的示例代码 :

TransmittableThreadLocal<String> parent = new TransmittableThreadLocal<String>(); parent.set("value-set-in-parent"); Runnable task = new Task("1"); // 额外的处理,生成修饰了的对象ttlRunnable Runnable ttlRunnable = TtlRunnable.get(task); executorService.submit(ttlRunnable); // ===================================================== // Task中可以读取,值是"value-set-in-parent" String value = parent.get();
