前言:
本节来练习下logistic regression相关内容,参考的资料为网页:http://openclassroom.stanford.edu/MainFolder/DocumentPage.php?course=DeepLearning&doc=exercises/ex4/ex4.html。这里给出的训练样本的特征为80个学生的两门功课的分数,样本值为对应的同学是否允许被上大学,如果是允许的话则用’1’表示,否则不允许就用’0’表示,这是一个典型的二分类问题。在此问题中,给出的80个样本中正负样本各占40个。而这节采用的是logistic regression来求解,该求解后的结果其实是一个概率值,当然通过与0.5比较就可以变成一个二分类问题了。
实验基础:
在logistic regression问题中,logistic函数表达式如下:
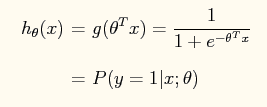
这样做的好处是可以把输出结果压缩到0~1之间。而在logistic回归问题中的损失函数与线性回归中的损失函数不同,这里定义的为:
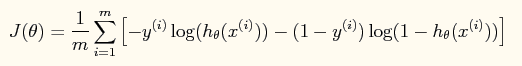
如果采用牛顿法来求解回归方程中的参数,则参数的迭代公式为:
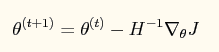
其中一阶导函数和hessian矩阵表达式如下:

当然了,在编程的时候为了避免使用for循环,而应该直接使用这些公式的矢量表达式(具体的见程序内容)。
一些matlab函数:
find:
是找到的一个向量,其结果是find函数括号值为真时的值的下标编号。
inline:
构造一个内嵌的函数,很类似于我们在草稿纸上写的数学推导公式一样。参数一般用单引号弄起来,里面就是函数的表达式,如果有多个参数,则后面用单引号隔开一一说明。比如:g = inline('sin(alpha*x)','x','alpha'),则该二元函数是g(x,alpha) = sin(alpha*x)。
实验结果:
训练样本的分布图以及所学习到的分类界面曲线:

损失函数值和迭代次数之间的曲线:
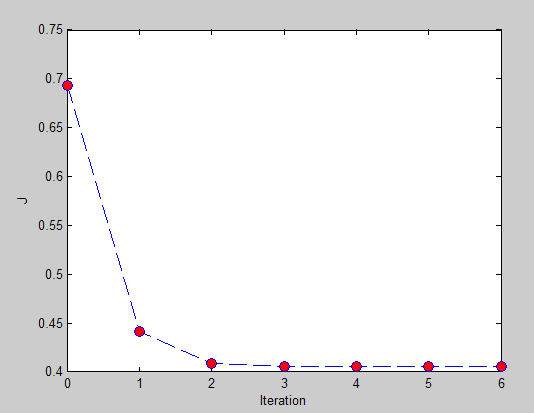
最终输出的结果:

可以看出当一个小孩的第一门功课为20分,第二门功课为80分时,这个小孩不允许上大学的概率为0.6680,因此如果作为二分类的话,就说明该小孩不会被允许上大学。
实验代码(原网页提供):
% Exercise 4 -- Logistic Regression clear all; close all; clc x = load('ex4x.dat'); y = load('ex4y.dat'); [m, n] = size(x); % Add intercept term to x x = [ones(m, 1), x]; % Plot the training data % Use different markers for positives and negatives figure pos = find(y); neg = find(y == 0);%find是找到的一个向量,其结果是find函数括号值为真时的值的编号 plot(x(pos, 2), x(pos,3), '+') hold on plot(x(neg, 2), x(neg, 3), 'o') hold on xlabel('Exam 1 score') ylabel('Exam 2 score') % Initialize fitting parameters theta = zeros(n+1, 1); % Define the sigmoid function g = inline('1.0 ./ (1.0 + exp(-z))'); % Newton's method MAX_ITR = 7; J = zeros(MAX_ITR, 1); for i = 1:MAX_ITR % Calculate the hypothesis function z = x * theta; h = g(z);%转换成logistic函数 % Calculate gradient and hessian. % The formulas below are equivalent to the summation formulas % given in the lecture videos. grad = (1/m).*x' * (h-y);%梯度的矢量表示法 H = (1/m).*x' * diag(h) * diag(1-h) * x;%hessian矩阵的矢量表示法 % Calculate J (for testing convergence) J(i) =(1/m)*sum(-y.*log(h) - (1-y).*log(1-h));%损失函数的矢量表示法 theta = theta - H\grad;%是这样子的吗? end % Display theta theta % Calculate the probability that a student with % Score 20 on exam 1 and score 80 on exam 2 % will not be admitted prob = 1 - g([1, 20, 80]*theta) %画出分界面 % Plot Newton's method result % Only need 2 points to define a line, so choose two endpoints plot_x = [min(x(:,2))-2, max(x(:,2))+2]; % Calculate the decision boundary line,plot_y的计算公式见博客下面的评论。 plot_y = (-1./theta(3)).*(theta(2).*plot_x +theta(1)); plot(plot_x, plot_y) legend('Admitted', 'Not admitted', 'Decision Boundary') hold off % Plot J figure plot(0:MAX_ITR-1, J, 'o--', 'MarkerFaceColor', 'r', 'MarkerSize', 8) xlabel('Iteration'); ylabel('J') % Display J J
参考资料: