配置文件能配置的属性参照 :https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/1.5.9.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#common-application-properties
1)、SpringBoot启动的时候加载主配置类,开启了自动配置功能
2)、@EnableAutoConfiguration 作用:
@Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @AutoConfigurationPackage @Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class}) //选择器 给容器导入一些组件 public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration { String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration"; Class<?>[] exclude() default {}; String[] excludeName() default {}; }
可以查看:
AutoConfigurationImportSelector类中的方法:
@Override public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) { if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) { return NO_IMPORTS; } AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader .loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader); AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = getAutoConfigurationEntry( autoConfigurationMetadata, annotationMetadata); return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations()); }
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, //获取到候选的配置 AnnotationAttributes attributes) { List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames( //从类路径下得到资源 getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), getBeanClassLoader()); Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you " + "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct."); return configurations; }
继续点击:
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName(); return (List)loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryClassName, Collections.emptyList()); }
查看方法:
loadSpringFactories
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { MultiValueMap<String, String> result = (MultiValueMap)cache.get(classLoader); if (result != null) { return result; } else { try { //扫描的文件 Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources("META-INF/spring.factories") : ClassLoader.getSystemResources("META-INF/spring.factories"); LinkedMultiValueMap result = new LinkedMultiValueMap(); while(urls.hasMoreElements()) { URL url = (URL)urls.nextElement(); UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url); Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); //最后做成了properties Iterator var6 = properties.entrySet().iterator(); while(var6.hasNext()) { Entry<?, ?> entry = (Entry)var6.next(); String factoryClassName = ((String)entry.getKey()).trim(); String[] var9 = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String)entry.getValue()); int var10 = var9.length; for(int var11 = 0; var11 < var10; ++var11) { String factoryName = var9[var11]; result.add(factoryClassName, factoryName.trim()); //遍历添加到结果集合中 } } } cache.put(classLoader, result); return result; } catch (IOException var13) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [META-INF/spring.factories]", var13); } } }
总结上面的步骤思路:
利用EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector给容器中导入一些组件?
可以查看selectImports()方法的内容;
List configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);获取候选的配置
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames()
扫描所有jar包类路径下 META‐INF/spring.factories
把扫描到的这些文件的内容包装成properties对象
从properties中获取到EnableAutoConfiguration.class类(类名)对应的值,然后把他们添加在容器
中
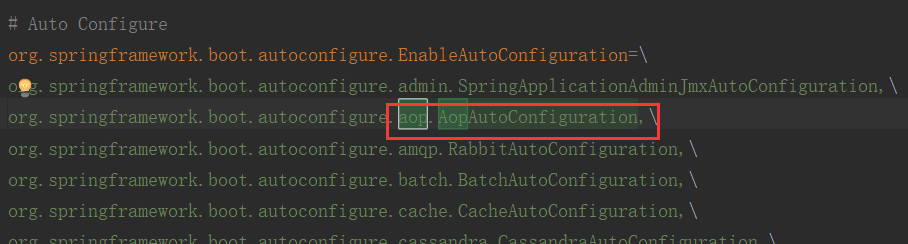
将META-INF/spring.factories EnableAutoConfiguration的值加入到了容器中:
有非常非常多我就不全部截图了,大家有兴趣可以自己看下。每一个这样的xxAutoConfiguration类都是容器总的一个组件,都加入到容器中
用他们做自动配置!
每一个自动配置类,进行自动配置功能。
举一个栗子:
以:org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration, 为例子进行解释自动配置原理
根据当前配置类,决定这个配置类是否生效。
生效了这些组件的属性是从对应的properties类中获取的,这些类是跟配置绑定的
最后通过@Bean给容器添加组件
* {@link EnableAutoConfiguration Auto-configuration} for configuring the encoding to use
* in web applications.
*
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @author Brian Clozel
* @since 1.2.0
*/
@Configuration //表示一个 配置类,以前编写的配置文件一样,也可以给容器中添加组件
@EnableConfigurationProperties(HttpProperties.class) //启用指定类的ConfigurationProperties功能 将配置文件中的值和HttpProperties类进行绑定了 并注册到容器中
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = ConditionalOnWebApplication.Type.SERVLET) //条件 底层spring的@Conditional注解 满足条件就整个配置类生效 当前应用内是否web应用
@ConditionalOnClass(CharacterEncodingFilter.class) //当前jar包(项目)里面有没有这个类 Spring mvc中解决乱码的过滤器 (以前是xml中配置的)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.http.encoding", value = "enabled", //判断配置文件中是否存在配置 spring.http.encoding
matchIfMissing = true) //即使我们配置文件中 不配置enable属性 也是默认生效的
public class HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration {
private final HttpProperties.Encoding properties;
//根据这个类去 编写properties类 属性进行赋值修改
public HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(HttpProperties properties) { //只有一个有参构造器的情况下 参数的值会从容器中获取 我们可以通过自定义properties进行修改配置!根据bean来的
this.properties = properties.getEncoding();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter() {
CharacterEncodingFilter filter = new OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter();
filter.setEncoding(this.properties.getCharset().name());
filter.setForceRequestEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(Type.REQUEST)); //从properties中获取! 这个类 已经和 springboot的配置文件绑定了
filter.setForceResponseEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(Type.RESPONSE));
return filter;
}
@Bean
public LocaleCharsetMappingsCustomizer localeCharsetMappingsCustomizer() {
return new LocaleCharsetMappingsCustomizer(this.properties);
}
private static class LocaleCharsetMappingsCustomizer implements
WebServerFactoryCustomizer<ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory>, Ordered {
private final HttpProperties.Encoding properties;
LocaleCharsetMappingsCustomizer(HttpProperties.Encoding properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
@Override
public void customize(ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory factory) {
if (this.properties.getMapping() != null) {
factory.setLocaleCharsetMappings(this.properties.getMapping());
}
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 0;
}
}
}
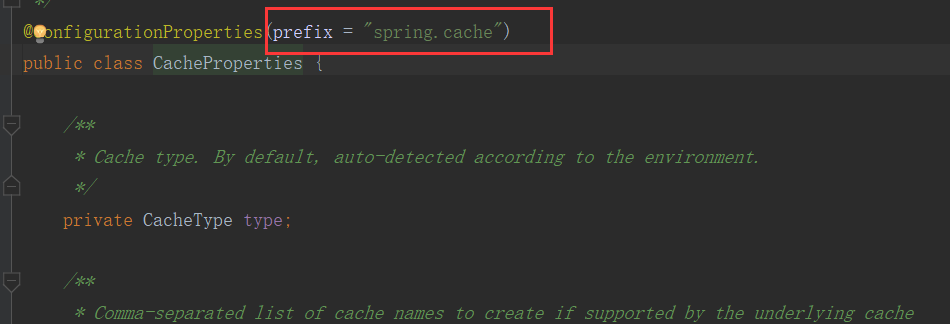
查看类 HttpProperties.class (所有配置文件中能配置的属性都是在xxProperties类中封装着),所以配置文件中能配置什么就可以参照某一个功能对应的这个属性类
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.http") //从配置文件中获取值和bean中的属性进行绑定 public class HttpProperties { /** * Whether logging of (potentially sensitive) request details at DEBUG and TRACE level * is allowed. */ private boolean logRequestDetails; /** * HTTP encoding properties. */ private final Encoding encoding = new Encoding();
所有在配置文件中能配置的属性都是在xxxxProperties类中封装者‘;配置文件能配置什么就可以参照某个功 能对应的这个属性类
精髓:
1)、SpringBoot启动会加载大量的自动配置类
2)、我们看我们需要的功能有没有SpringBoot默认写好的自动配置类;
3)、我们再来看这个自动配置类中到底配置了哪些组件;(只要我们要用的组件有,我们就不需要再来配置了) 没有就自己写配置类
4)、给容器中自动配置类添加组件的时候,会从properties类中获取某些属性。我们就可以在锁定配置文件,然后指定这 些属性的值;
归纳:
xxxxAutoConfigurartion:自动配置类; 给容器中添加组件
举个栗子看下:缓存的自动配置 包括了 属性的值获取
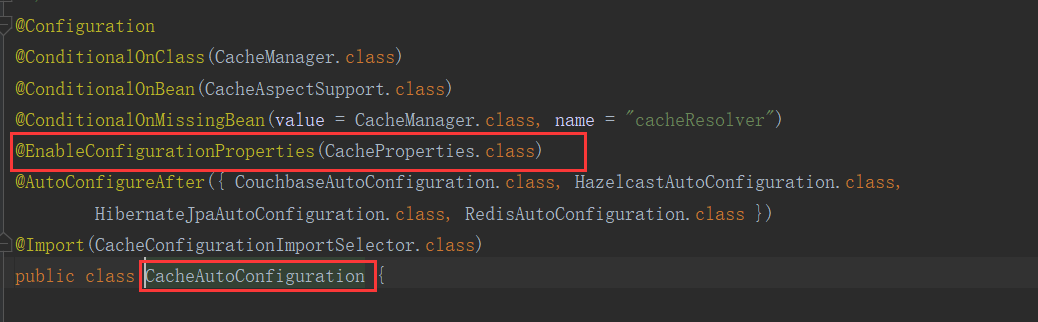
点进去看下缓存的配置:
1、@Conditional派生注解(Spring注解版原生的@Conditional作用) 作用:必须是@Conditional指定的条件成立,才给容器中添加组件,配置配里面的所有内容才生效;
|
@Conditional扩展注解 |
作用(判断是否满足当前指定条件) |
|
@ConditionalOnJava |
系统的java版本是否符合要求 |
|
@ConditionalOnBean |
容器中存在指定Bean; |
|
@ConditionalOnMissingBean |
容器中不存在指定Bean; |
|
@ConditionalOnExpression |
满足SpEL表达式指定 |
|
@ConditionalOnClass |
系统中有指定的类 |
|
@ConditionalOnMissingClass |
系统中没有指定的类 |
|
@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate |
容器中只有一个指定的Bean,或者这个Bean是首选Bean |
|
@ConditionalOnProperty |
系统中指定的属性是否有指定的值 |
|
@ConditionalOnResource |
类路径下是否存在指定资源文件 |
|
@ConditionalOnWebApplication |
当前是web环境 |
|
@ConditionalOnNotWebApplication |
当前不是web环境 |
|
@ConditionalOnJndi |
JNDI存在指定项 |
自动配置类必须在一定的条件下才能生效!就是 @Conditional搞的
比如进入AOP自动配置类中,
必须有三个类才能生效,如果当前类没有aspect 的jar包就能生效哦

那么我们怎么看,是否生效啊呢?
在properties中配置, 开启springboot的debug模式
debug=true,这样我们就可以很方便的知道哪些自动配置 类生效;
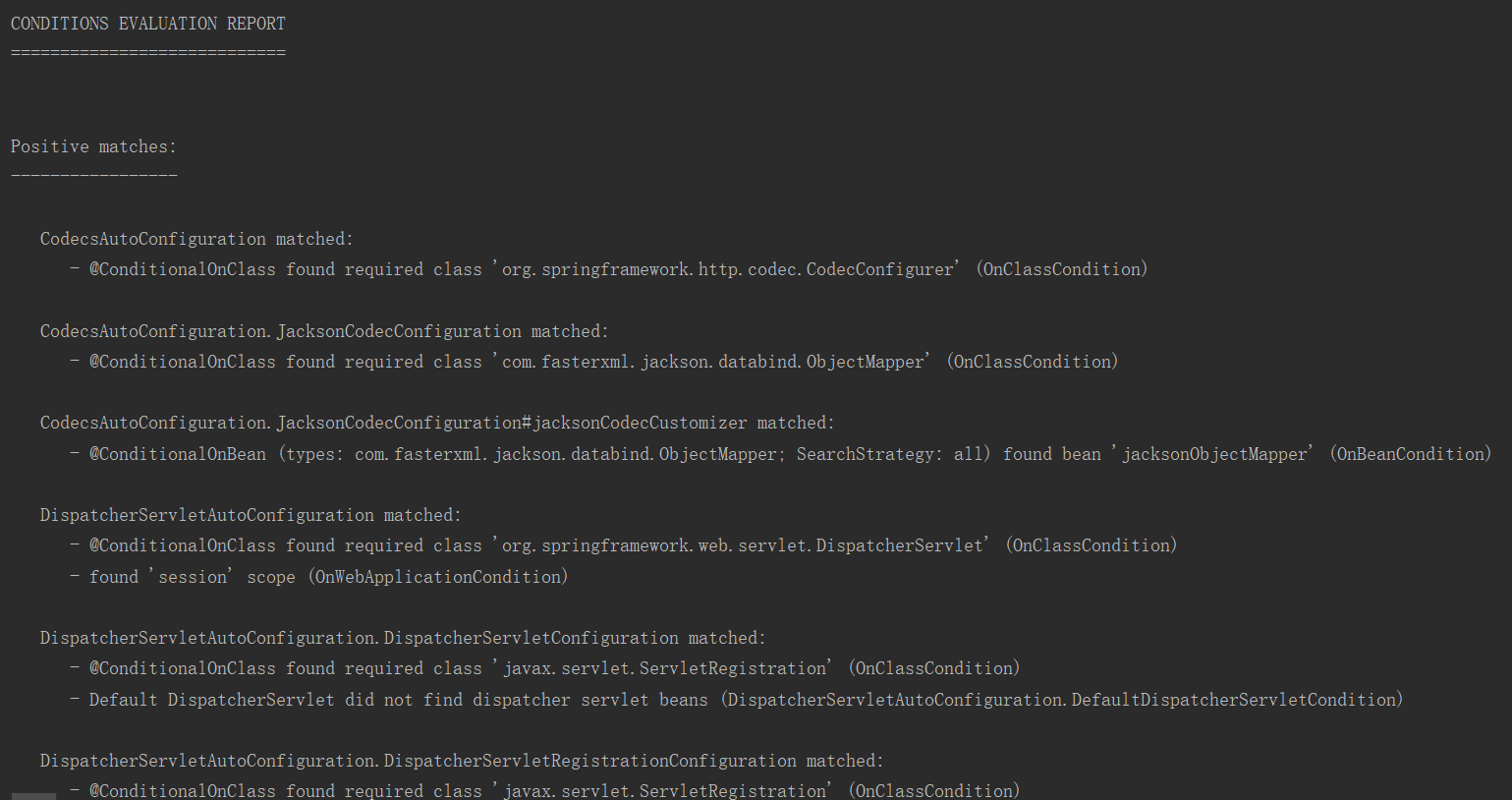
很多我贴出来了
=========================
AUTO‐CONFIGURATIONREPORT
=========================
Positivematches:(自动配置类启用的)
‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐
DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration matched:
‐ @ConditionalOnClass found required class
'org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet'; @ConditionalOnMissingClass did not find
unwanted class (OnClassCondition)
‐ @ConditionalOnWebApplication (required) found StandardServletEnvironment
(OnWebApplicationCondition)
Negativematches:(没有启动,没有匹配成功的自动配置类) ‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐
ActiveMQAutoConfiguration:
Did not match:
‐ @ConditionalOnClass did not find required classes 'javax.jms.ConnectionFactory',
'org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory' (OnClassCondition)
AopAutoConfiguration:
Did not match:
‐ @ConditionalOnClass did not find required classes
'org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect', 'org.aspectj.lang.reflect.Advice' (OnClassCondition)
模式:
1)、SpringBoot在自动配置很多组件的时候,先看容器中有没有用户自己配置的(@Bean、@Component)如
果有就用用户配置的,如果没有,才自动配置;如果有些组件可以有多个(ViewResolver)将用户配置的和自己默
认的组合起来;
2)、在SpringBoot中会有非常多的xxxConfigurer帮助我们进行扩展配置
3)、在SpringBoot中会有很多的xxxCustomizer帮助我们进行定制配置