明确是王道
——Clean Code
类图:
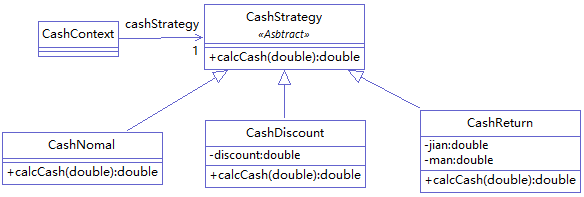
先定义策略类
1 package cn.no2.strategy; 2 3 public abstract class Strategy { 4 5 //省略属性 6 //算法方法 7 public abstract void algrithmInterface(); 8 }
在定义若干策略子类
1 package cn.no2.strategy; 2 3 public class ConcreteStrategyA extends Strategy { 4 5 @Override 6 public void algrithmInterface() { 7 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 8 System.out.println("算法A实现"); 9 } 10 11 } 12 public class ConcreteStrategyB extends Strategy { 13 14 @Override 15 public void algrithmInterface() { 16 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 17 System.out.println("算法B实现"); 18 } 19 20 } 21 public class ConcreteStrategyC extends Strategy { 22 23 @Override 24 public void algrithmInterface() { 25 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 26 System.out.println("算法C实现"); 27 } 28 29 }
最后定义业务逻辑"上下文类"
1 package cn.no2.strategy; 2 3 public class BizContext { 4 5 Strategy strategy = null; 6 7 public BizContext(String type) { 8 9 switch (type) { 10 case "策略A": 11 strategy= new ConcreteStrategyA(); 12 break; 13 case "策略B": 14 strategy= new ConcreteStrategyB(); 15 break; 16 case "策略C": 17 strategy= new ConcreteStrategyC(); 18 break; 19 } 20 } 21 22 public void ContextInterface(){ 23 strategy.algrithmInterface(); 24 } 25 }
测试类
1 package cn.no2.strategy; 2 3 public class _Text { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 BizContext biz; 7 biz = new BizContext("策略A"); 8 biz.ContextInterface(); 9 biz = new BizContext("策略B"); 10 biz.ContextInterface(); 11 biz = new BizContext("策略C"); 12 biz.ContextInterface(); 13 } 14 }
诚然,上面的程序只是明确了框架,并没有任何实际的业务逻辑.下面来写个需求
输入单价、数量、计价方式,其中计价方式就是策略:
策略1:正常收费
策略2:打X折
策略3:满X元减Y元
输出结果。
上代码:
Strategy类:
1 package cn.no2.strategy.instance; 2 3 public abstract class Strategy { 4 5 private double unitPrice; 6 private int count; 7 8 public double getUnitPrice() { 9 return unitPrice; 10 } 11 12 public void setUnitPrice(double unitPrice) { 13 this.unitPrice = unitPrice; 14 } 15 16 public int getCount() { 17 return count; 18 } 19 20 public void setCount(int count) { 21 this.count = count; 22 } 23 24 //计算结果,返回double值 25 public abstract double algrithmInterface(); 26 27 }
其子类:
1 package cn.no2.strategy.instance; 2 3 public class NomalStrategy extends Strategy { 4 5 @Override 6 public double algrithmInterface() { 7 // 使用清晰规范的代码,定义变量,计算,返回 8 double result = 0; 9 result = this.getUnitPrice()*this.getCount(); 10 return result; 11 } 12 13 } 14 public class DiscountStrategy extends Strategy { 15 16 private double discount; 17 18 public DiscountStrategy(double discount) { 19 super(); 20 this.discount = discount; 21 } 22 23 @Override 24 public double algrithmInterface() { 25 // 这里重写方法不能传入参数,所以需要定义该子类特有的属性,折扣 26 double result = 0; 27 result = this.getUnitPrice()*this.getCount()*discount; 28 return result; 29 } 30 31 } 32 public class FullReduceStrategy extends Strategy { 33 34 double full; 35 double reduction; 36 37 public FullReduceStrategy(double full, double reduction) { 38 super(); 39 this.full = full; 40 this.reduction = reduction; 41 } 42 43 @Override 44 public double algrithmInterface() { 45 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 46 double result = this.getUnitPrice()*this.getCount(); 47 if (result >= full) { 48 result -= reduction; 49 } 50 return result; 51 } 52 53 }
业务逻辑类:
1 package cn.no2.strategy.instance; 2 3 public class BizContext { 4 5 private Strategy strategy = null; 6 7 public BizContext(String type) { 8 9 switch (type) { 10 case "正常收费": 11 strategy= new NomalStrategy(); 12 break; 13 case "打8.5折": 14 strategy= new DiscountStrategy(8.5); 15 break; 16 case "满300减100": 17 strategy= new FullReduceStrategy(300,100); 18 break; 19 } 20 } 21 //彻底封装Strategy类 22 public void initStrategy(double unitPrice,int count) { 23 strategy.setUnitPrice(unitPrice); 24 strategy.setCount(count); 25 } 26 //这里实现的对strategy的封装,调用者只调用BizContext自己的方法 27 public double ContextInterface(){ 28 return strategy.algrithmInterface(); 29 } 30 }
Test类:
1 package cn.no2.strategy.instance; 2 3 import java.util.Scanner; 4 5 public class _Text { 6 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); 9 System.out.println("请输入单价:"); 10 double unitPrice = sc.nextDouble(); 11 System.out.println("请输入数量:"); 12 int count = sc.nextInt(); 13 System.out.println("请输入策略:(正常收费,打8.5折,满300减100)");//这里如果改动,只需增加BizContext的业务逻辑 14 String strategy = sc.next(); 15 BizContext biz = new BizContext(strategy); 16 biz.initStrategy(unitPrice,count); 17 double result = biz.ContextInterface(); 18 System.out.println("总价是:"+result); 19 sc.close(); 20 } 21 }
以上是策略模式的实际应用
策略模式与简单工厂对比:
简单工厂模式:客户端传一个条件进工厂类,工厂类根据条件创建相应的产品类对象,客户端使用该产品类对象.工厂类依赖产品类
策略模式:客户端创建一个Context类对象,并通过传入参数使用该对象。Context类中聚合了产品类,没有依赖关系