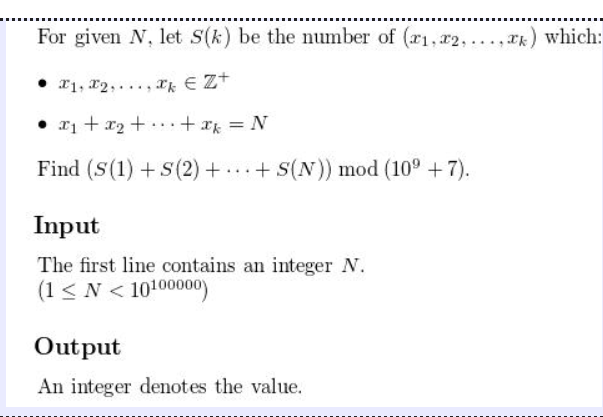
1 // 2018年全国多校算法寒假训练营练习比赛(第三场) 2 // 不凡的夫夫 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <cstdio> 5 #include <cstring> 6 #include <string> 7 #include <utility> 8 #include <algorithm> 9 #include <vector> 10 #include <queue> 11 #include <stack> 12 #include <cmath> 13 using namespace std; 14 #define max(x,y) x>=y?x:y 15 #define lowbit(x) x&(-x) 16 #define M 1e-8 17 #define pi acos(-1.0) 18 #define e 2.718281828 19 typedef unsigned long long ull; 20 typedef long long ll; 21 22 int n,t; 23 int main() 24 { 25 scanf("%d",&t); 26 while(t--) 27 { 28 29 scanf("%d",&n); 30 if(n==0)//特判 31 { 32 printf("1 "); 33 continue; 34 } 35 long double ans= (log10(2*pi*n)*0.5+n*log10(n/e))/log10(8); //换底公式,double 36 printf("%lld ",(ll)ans+1);//ll 37 } 38 return 0; 39 } 40 // Stirling公式)
//林公式是是一条用来取n的阶乘的近似值的数学公式:n!≈sqrt(2*π*n)*((n/e)^n) 41 // https://www.cnblogs.com/zhangshu/archive/2011/08/12/2135855.html
1 1 // 素数定理 2 2 // https://blog.csdn.net/kalilili/article/details/44835285 3 loge(x)==log(x)
1 //中国剩余定理 2 //poj 1006 3 4 /* 5 这里又有一个数学公式,如果a%b=c,那么(a+k*b)%b=c 6 那么(a*k)%b=a%b+a%b+…+a%b=c+c+…+c=(k*c)%b(k>0),也就是说,如果一个除法的余数为c, 7 那么被除数的k倍与除数相除的余数为(k*c)%b。展开式中已证明。 8 X被a,b,c处分别余r1,r2,r3。表示为: 9 10 X%a = r1 x%b = r2 x%c = r3 11 12 bc*k1 % a = 1 ac*k2 % b = 1 ab*k3 % c = 1 13 14 所以 15 16 x = bc * k1 * r1 + ac * k2 * r2 + ab * k3 * r3 17 */ 18 //模数要互质。28.23.33.(条件) 19 //p+23k1==e+28k2==i+33k3=ans+d 20 #include <iostream> 21 #include <cstdio> 22 #include <cstring> 23 #include <string> 24 #include <utility> 25 #include <algorithm> 26 #include <vector> 27 #include <queue> 28 #include <stack> 29 using namespace std; 30 #define max(x,y) x>=y?x:y 31 #define lowbit(x) x&(-x) 32 #define ll long long 33 int p,e,i,d,r1,r2,r3,r; 34 void init() 35 { 36 r1=28*33,r2=23*33,r3=23*28; 37 int i=1,j=1,k=1; 38 for(;;i++) 39 { 40 if(r1*i%23==1) 41 { 42 break; 43 } 44 } 45 r1*=i; 46 for(;;j++) 47 { 48 if(r2*j%28==1) 49 { 50 break; 51 } 52 } 53 r2*=j; 54 for(;;k++) 55 { 56 if(r3*k%33==1) 57 { 58 break; 59 } 60 } 61 r3*=k; 62 r=23*28*33; 63 } 64 int main() 65 { init(); 66 int f=1; 67 while(~scanf("%d%d%d%d",&p,&e,&i,&d)) 68 { 69 if(p==-1&&e==-1&&i==-1&&d==-1) 70 { 71 break; 72 } 73 int ans; 74 ans=(p*r1+e*r2+i*r3-d)%r; 75 ans=(ans+r-1)%r+1;//可能是负数或ans==0因此ans=(ans+r)%r是错的 76 printf("Case %d: the next triple peak occurs in %d days. ",f++,ans); 77 } 78 return 0; 79 }
/* char a[10000005]; long long quickmod(long long a, long long b) { long long ans=1; while(b) { if(b&1) { ans=(ans*a)%mod; } b=b/2; a=(a*a)%mod; } return ans; } int main() { long long sum,len; while(gets(a)) { len=strlen(a); sum=0; for(int i=0;i<len;i++) { sum=(sum*10+a[i]-'0')%(mod-1); } if(sum==0) cout<<quickmod(2,mod-2)<<endl; else {sum--; cout<<quickmod(2,sum)<<endl; } } return 0; } */ char s[N]; ll poww(ll a,ll b)//不要写成pow { ll ans=1; while(b) { if(b&1) { ans=(ans*a)%mod; } b>>=1; a=(a*a)%mod; } return ans%mod; } /* 3 (3) (1,2),(2,1) (1,1,1) 4 (4) (1,3),(2,2),(3,1) (1,1,2),(1,2,1)(2,1,1) (1,1,1,1) 其实就是2^(n-1)(%mod) 费马小定理 :2^((n-1)%(mod-1)(%mod) 先利用大数取余得到 (n-1)%(mod-1),注意0 在用快速幂 */ int main() { while(~scanf("%s",s)){ int l=strlen(s); ll sum=0; gep(i,0,l-1) { sum=(sum*10+s[i]-'0')%(mod-1); } if(!sum){//逆元 printf("%lld ",poww(2,mod-2)); } else{ sum--; printf("%lld ",poww(2,sum)); } } return 0; }
HDU 6440
Dream
Time Limit: 12000/6000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1090 Accepted Submission(s): 256
Special Judge
For instance, (1+4)2=52=25, but 12+42=17≠25. Moreover, 9+16−−−−−√=25−−√=5, which does not equal 3+4=7.
Fortunately, in some cases when p is a prime, the identity
holds true for every pair of non-negative integers m,n which are less than p, with appropriate definitions of addition and multiplication.
You are required to redefine the rules of addition and multiplication so as to make the beginner's dream realized.
Specifically, you need to create your custom addition and multiplication, so that when making calculation with your rules the equation (m+n)p=mp+np is a valid identity for all non-negative integers m,n less than p. Power is defined as
Obviously there exists an extremely simple solution that makes all operation just produce zero. So an extra constraint should be satisfied that there exists an integer q(0<q<p) to make the set {qk|0<k<p,k∈Z} equal to {k|0<k<p,k∈Z}. What's more, the set of non-negative integers less than p ought to be closed under the operation of your definitions.
Hint for sample input and output:
From the table we get 0+1=1, and thus (0+1)2=12=1⋅1=1. On the other hand, 02=0⋅0=0, 12=1⋅1=1, 02+12=0+1=1.
They are the same.
For every case, there is only one line contains an integer p(p<210), described in the problem description above. p is guranteed to be a prime.
The j-th(1≤j≤p) integer of i-th(1≤i≤p) line denotes the value of (i−1)+(j−1). The j-th(1≤j≤p) integer of (p+i)-th(1≤i≤p) line denotes the value of (i−1)⋅(j−1).

那么
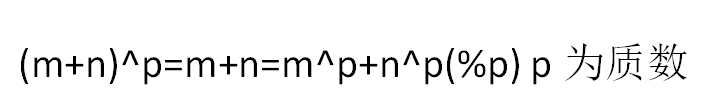
1 int t,p; 2 int main() 3 { 4 scanf("%d",&t); 5 while(t--) 6 { 7 scanf("%d",&p); 8 gep(i,0,p-1){ 9 printf("%d",i); 10 gep(j,1,p-1){ 11 printf(" %d",(i+j)%p); 12 } 13 printf(" "); 14 } 15 gep(i,0,p-1){ 16 printf("0"); 17 gep(j,1,p-1){ 18 printf(" %d",(i*j)%p); 19 } 20 printf(" "); 21 } 22 } 23 return 0; 24 }
Find Integer 费马大定理
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 1107 Accepted Submission(s): 290
Special Judge
give you two integers n,a,you are required to find 2 integers b,c such that an+bn=cn.
next T lines contains two integers n,a;(0≤n≤1000,000,000,3≤a≤40000)
else print two integers -1 -1 instead.
1 int t; 2 ll n,a; 3 int main() 4 { 5 scanf("%d",&t); 6 while(t--) 7 { 8 scanf("%lld%lld",&n,&a); 9 if(!n||n>2) printf("-1 -1 "); 10 else if(n==1){ 11 printf("1 %lld ",a+1); 12 } 13 else{ 14 ll x=a/2; 15 if(a&1){ 16 printf("%lld %lld ",2*x*x+2*x,2*x*x+2*x+1); 17 } 18 else{ 19 printf("%lld %lld ",x*x-1,x*x+1); 20 } 21 } 22 } 23 return 0; 24 } 25 /* 26 a^n+b^n=c^n 27 n>2 无正整数解费马大定理 28 n==0 1+1=1无意义 29 n==1 a+b=c即可 30 n==2 a^2+b^2=c^2 31 任意大于1的奇数2*n+1 (n>=1) 2*n+1,2*n*n+2*n,2*n*n+2*n+1 构成勾股数 32 任意大于2的偶数2*n (n>=1) 2*n,n*n-1,n*n+1 构成勾股数 33 若直角三角形的短直角边为奇数,另外两条边是连续的自然数 34 若直角三角形的短直角边为奇数,三角形的周长为短直角边的平方与短边自身的和 35 */
It's Saturday today, what day is it after 11 + 22 + 33 + ... + NN days?
Input
There are multiple test cases. The first line of input contains an integer T indicating the number of test cases. For each test case:
There is only one line containing one integer N (1 <= N <= 1000000000).
Output
For each test case, output one string indicating the day of week.
Sample Input
2 1 2
Sample Output
Sunday Thursday
Hint
A week consists of Sunday, Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday and Saturday.
都对7取模后

根据费马小定理x6≡1(mod 7)可得
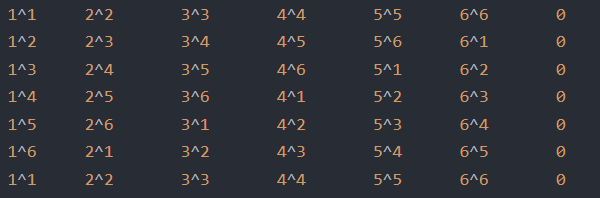
//找出循环节 42 bool check(int i) { int flag=1; for(int j=1;j<=i-1;j++) { if(num[j]!=num[j+i]) { flag=0; break; } } return flag; } //42为循环节 void init() { gep(i,1,45){ int x=i%7; int ans=1; gep(j,1,i){ ans=(ans*x)%7; } a[i]=ans; } gep(i,1,45) sum[i]=sum[i-1]+a[i]; } char p[]="affvg"; char p0[]={"afegrwg"};//注意写法 char s[10][10]={ "Sunday", "Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday", "Friday", "Saturday", }; int main() { scanf("%d",&t); init(); while(t--) { scanf("%d",&n); int ret=((n/42%7*sum[42]%7)%7+sum[n%42]%7)%7; ret=(ret+6)%7; printf("%s ",s[ret]); } return 0; }
裴蜀定理
「BZOJ1441」Min
Description
Input
Output
Sample Input
4059 -1782
Sample Output
题解
裴蜀定理
1 /* 2 3 在数论中,裴蜀定理是一个关于最大公约数(或最大公约式)的定理:若a,b是整数,且gcd(a,b)=d,那么对于任意的整数x,y,ax+by=m中的m一定是d的倍数。 4 特别地,一定存在整数x,y,使ax+by=d成立,且不止一组,例如(12,42)=6,则方程12x + 42y = 6有解,事实上有(-3)×12 + 1×42 = 6及4×12 + (-1)×42 = 6。 5 而ax+by=1是a,b两数互质的充要条件,同样地,x,y不止一组。 6 7 */ 8 9 int x,ans; 10 int main() 11 { 12 __gcd(0,x)=x; 13 __gcd(-2,4)=-2; 14 __gcd(-2,-4)=-2; 15 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 16 scanf("%d",&x); 17 ans=__gcd(ans,x); 18 } 19 printf("%d ",abs(ans)); 20 }
//BZOJ 2257
2257: [Jsoi2009]瓶子和燃料
Time Limit: 10 Sec Memory Limit: 128 MBSubmit: 1933 Solved: 1179
[Submit][Status][Discuss]
Description
jyy就一直想着尽快回地球,可惜他飞船的燃料不够了。
有一天他又去向火星人要燃料,这次火星人答应了,要jyy用飞船上的瓶子来换。jyy
的飞船上共有 N个瓶子(1<=N<=1000) ,经过协商,火星人只要其中的K 个 。 jyy
将 K个瓶子交给火星人之后,火星人用它们装一些燃料给 jyy。所有的瓶子都没有刻度,只
在瓶口标注了容量,第i个瓶子的容量为Vi(Vi 为整数,并且满足1<=Vi<=1000000000 ) 。
火星人比较吝啬,他们并不会把所有的瓶子都装满燃料。他们拿到瓶子后,会跑到燃料
库里鼓捣一通,弄出一小点燃料来交差。jyy当然知道他们会来这一手,于是事先了解了火
星人鼓捣的具体内容。火星人在燃料库里只会做如下的3种操作:1、将某个瓶子装满燃料;
2、将某个瓶子中的燃料全部倒回燃料库;3、将燃料从瓶子a倒向瓶子b,直到瓶子b满
或者瓶子a空。燃料倾倒过程中的损耗可以忽略。火星人拿出的燃料,当然是这些操作能
得到的最小正体积。
jyy知道,对于不同的瓶子组合,火星人可能会被迫给出不同体积的燃料。jyy希望找
到最优的瓶子组合,使得火星人给出尽量多的燃料。
Input
第1行:2个整数N,K,
第2..N 行:每行1个整数,第i+1 行的整数为Vi
Output
仅1行,一个整数,表示火星人给出燃料的最大值。
Sample Input
3
4
4
Sample Output
HINT
选择第2 个瓶子和第 个瓶子,火星人被迫会给出4 体积的容量。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 #include <cstdlib> 5 #include <cstring> 6 #include <string> 7 #include <deque> 8 using namespace std; 9 #define ll long long 10 #define N 1000009 11 #define gep(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<=b;i++) 12 #define gepp(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i>=b;i--) 13 #define gep1(i,a,b) for(ll i=a;i<=b;i++) 14 #define gepp1(i,a,b) for(ll i=a;i>=b;i--) 15 #define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a)) 16 /* 17 取某k个数,那么答案就是它们的最大公约数 18 那么我们可以把所有数的因子求出,在从大到小筛选,只要因子个数>=k 19 就是答案 20 */ 21 int n,k; 22 int a[N]; 23 int x,cnt; 24 void get(int x) 25 { 26 for(int i=1;i*i<=x;i++)//O(sqrt(N)) 27 { 28 if(x%i==0) a[cnt++]=i; 29 if(x%i==0&&x/i!=i) a[cnt++]=x/i; 30 } 31 } 32 int main() 33 { 34 scanf("%d%d",&n,&k); 35 gep(i,1,n) 36 { 37 scanf("%d",&x); 38 get(x); 39 } 40 sort(a,a+cnt); 41 int num=1,ans=1; 42 for(int j=cnt-2;j>=0;j--) 43 { 44 if(a[j]==a[j+1]) num++; 45 else{ 46 if(num>=k) { 47 ans=a[j+1]; 48 break; 49 } 50 num=1; 51 } 52 } 53 printf("%d ",ans); 54 return 0; 55 }
2299: [HAOI2011]向量
Time Limit: 10 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MBSubmit: 1754 Solved: 826
[Submit][Status][Discuss]
Description
给你一对数a,b,你可以任意使用(a,b), (a,-b), (-a,b), (-a,-b), (b,a), (b,-a), (-b,a), (-b,-a)这些向量,问你能不能拼出另一个向量(x,y)。
说明:这里的拼就是使得你选出的向量之和为(x,y)
Input
第一行数组组数t,(t<=50000)
接下来t行每行四个整数a,b,x,y (-2*109<=a,b,x,y<=2*109)
Output
t行每行为Y或者为N,分别表示可以拼出来,不能拼出来
Sample Input
2 1 3 3
1 1 0 1
1 0 -2 3
Sample Output
N
Y
HINT
样例解释:
第一组:(2,1)+(1,2)=(3,3)
第三组:(-1,0)+(-1,0)+(0,1)+(0,1)+(0,1)=(-2,3)
Source
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 #include <cstdlib> 5 #include <cstring> 6 #include <string> 7 #include <deque> 8 using namespace std; 9 #define ll long long 10 #define N 1009 11 #define gep(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<=b;i++) 12 #define gepp(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i>=b;i--) 13 #define gep1(i,a,b) for(ll i=a;i<=b;i++) 14 #define gepp1(i,a,b) for(ll i=a;i>=b;i--) 15 #define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a)) 16 bool ok(ll x,ll y,ll d) 17 { 18 if(x%d==0&&y%d==0) return 1; 19 return 0; 20 } 21 /* 22 8种情况 ,设每种情况用了ki次 23 那么 x=(k1+k2-k3-k4)*a+(k5+k6-k7-k8)*b 24 y=(k5+k7-k6-k8)*a+(k1+k3-k2-k4)*b 25 也可以写成 x=x1*a+y1*b 26 y=x2*a+y2*b 27 k1,k2,k3,k4 28 两个数的和减去另外两个数的和 ,可令k1+k2+k3+k4=M,其中两个数的和为x 29 那么 x-(M-x)=2*x-M ,因此 x1,y2 同奇偶,x2,y1同奇偶,再利用裴蜀定理 30 1:同偶 x=2*n1*a+2*n2*b ,y=2*n3*a+2*n4*b 那么 x,y都为 __gcd(2*a,2*b)的倍数 31 2:同奇 x2*(n1-1)*a+2*(n2-1)*b ,y=2*(n3-1)*a+2*(n4-1)*b ,那么x+a+b,y+a+b 都为__gcd(2*a,2*b)的倍数 32 3: 一奇一偶 x+a,y+b 33 4: 一偶一奇 x+b,y+a 34 */ 35 int main() 36 { 37 int t; 38 ll a,b,x,y; 39 scanf("%d",&t); 40 while(t--) 41 { 42 scanf("%lld%lld%lld%lld",&a,&b,&x,&y); 43 ll d=__gcd(2*a,2*b); 44 if(ok(x,y,d)||ok(x+a,y+b,d)||ok(x+b,y+a,d)||ok(x+a+b,y+a+b,d)) 45 printf("Y "); 46 else 47 printf("N "); 48 } 49 return 0; 50 }