一,思维模式图
二,代码验证
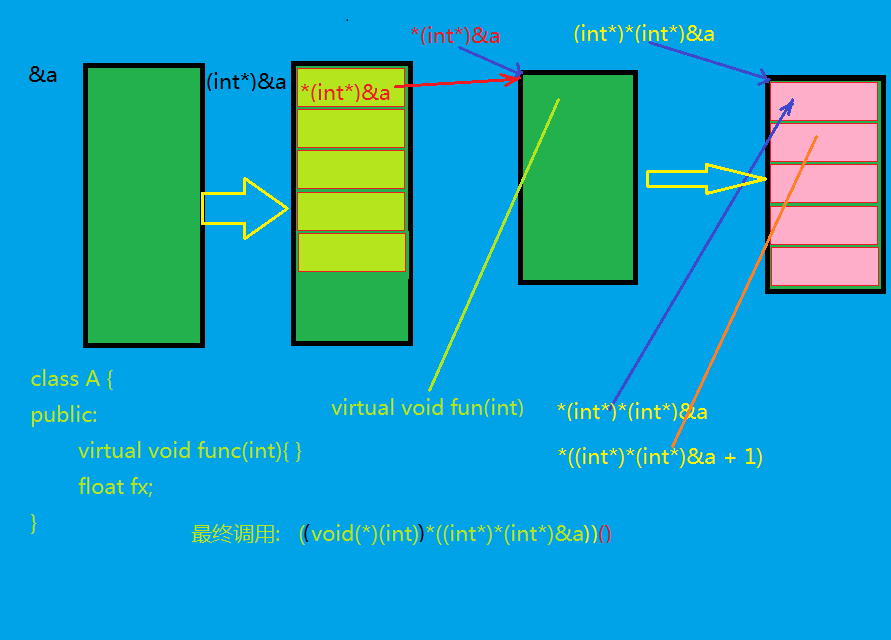
class A { public: A(int x) { fProtected = x; } float GetFProtected() { return fProtected; } public: float fpublic = 2.3f; //c++11支持了初始化,但不能使用auto string sname = "liqi"; CMyNumOperator<int>* on = new CMyNumOperator<int>(); //对象也可以 void TestFunc() { cout << "TestFunc" << endl; } static void StaticTestFunc() { cout << "Static-TestFunc" << endl; } virtual void ToString() { cout << "A::ToString" << endl; } protected: float fProtected; void ProtectedFunc() { cout << "PRotectedFunc" << endl; } private: void PrivateFunc() { cout << "PrivateFunc" << endl; } }; //只管公有继承,不管保护继承和私有继承,意义不大,也太复杂 class B : public A { public: friend void TestProtectedDerive(); B() :A(1) {} void TestForDerive() { //公有继承下 //1,子类可以访问父类的保护成员,不能访问父类的私有成员 B ob; //PrivateFunc(); //error,子类不能访问基类的私有成员 ProtectedFunc(); //right fProtected = 10; //right ob.fProtected = 20; //right } //1,c++中只要基类有相同签名虚函数,则默认为此基类函数也是虚函数[与C#不同],如下情形都成立 // (1) 函数不声明 virtual // (2) 函数声明了 virtual // (3) 函数声明了 override // (4) 函数声明了 virtual 和 override //2,c++中两个关键词作用不同,可以同时存在 // virtual仅表明函数是虚函数,override是C++11中出现的,明确说明是对基类的重写 // 它的好处是当函数声明不符合规则时,编译器会报错 void virtual ToString() override{ cout << "B::ToString" << endl; } }; void TestVirtualFunctionTable() { cout << hex; typedef void(*PFUNC)(); offsetof(A, fpublic); //利用此函数可以算函数布局 A oa(0); B ob; //一,通过内存地址修改不可访问的保护变量 *(float*)((int*)&oa + 1) = 123.4f; //类的第一个变量fpublic赋值,(int*)&oa + 1是跳过虚函数指针 float fpublic = oa.fpublic; //二,通过内存地址调用虚函数 //A和B的虚函数表地址不一样,也就是说父类和子类各有一张虚函数表 int* pvptr = (int*)(*((int*)(&oa))); cout << "A的虚函数表地址:" << pvptr << endl; //000DB0D4 ((void(*)())(*pvptr))(); //A::ToString pvptr = (int*)(*((int*)(&ob))); cout << "B的虚函数表地址:" << pvptr << endl; //000DB128 ((void(*)())(*pvptr))(); //B::ToString cout << "--------------------------" << endl; //最简写法 ((void(*)())(*((int*)*(int*)&oa)))(); ((void(*)())(*((int*)*(int*)&ob)))(); }