package org.yuan.my_project; class Grandparent { public Grandparent() { System.out.println("GrandParent Created."); } public Grandparent(String string) { System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:" + string); } } class Parent extends Grandparent { public Parent() { //super("Hello.Grandparent."); System.out.println("Parent Created"); //super("Hello.Grandparent."); } } class Child extends Parent { public Child() { System.out.println("Child Created"); } } public class TestInherits { public static void main(String args[]) { Child c=new Child(); //System.out.println(c); } }
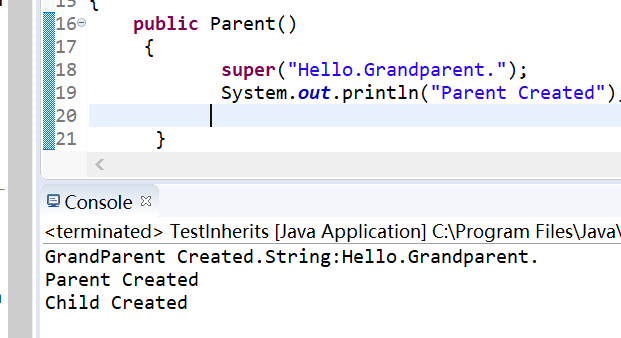
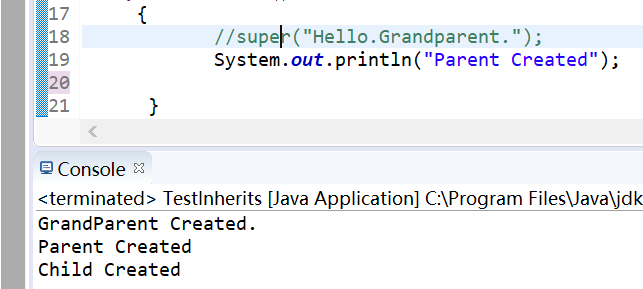
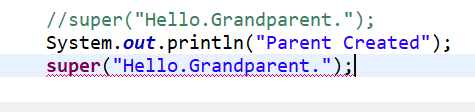
1、继承条件下构造方法的调用:通过super调用基类构造方法,必须是子类构造方法中的第一个语句。
2、方法覆盖:
package org.yuan.my_project; class Base { void method() { System.out.println("base"); } } class Sub extends Base { void method() { //super.method(); System.out.println("Sub"); } } public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Base sub1 = new Sub(); sub1.method(); Sub sub2 = new Sub(); sub2.method(); } }
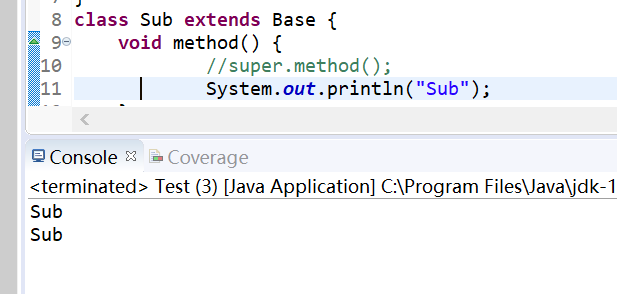
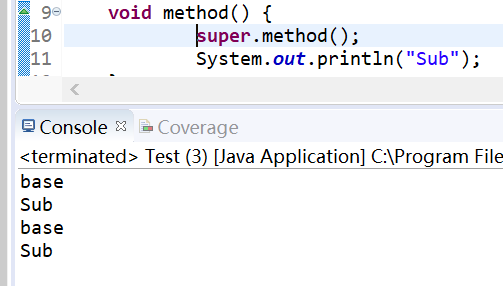
覆盖的语法规则:(1).覆盖方法的允许访问范围不能小于原方法;(2).覆盖方法所抛出的异常不能比原方法更多;(3).声明为final方法不允许覆盖;(4).不能覆盖静态方法。
3、
public class ParentChildTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Parent parent=new Parent(); parent.printValue(); Child child=new Child(); child.printValue(); parent=child; parent.printValue(); parent.myValue++; parent.printValue(); ((Child)parent).myValue++; parent.printValue(); } } class Parent{ public int myValue=100; public void printValue() { System.out.println("Parent.printValue(),myValue="+myValue); } } class Child extends Parent{ public int myValue=200; public void printValue() { System.out.println("Child.printValue(),myValue="+myValue); } }
运行结果:
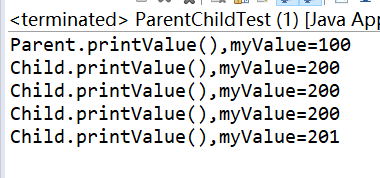
总结:(1)当子类与父类拥有一样的方法,并且让一个父类变量引用一个子类对象时,到底调用哪个方法,由对象自己的“真实”类型所决定,这就是说:对象是子类型的,就调用子类型的方法,是父类型的,就调用父类型的方法。(2)如果子类与父类有相同的字段,则子类中的字段会代替或隐藏父类的字段,子类方法访问的是子类的字段(而不是父类的字段)。如果子类方法确实想访问父类中被隐藏的字段,可以用super关键字来访问它。