An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child subtrees of any node differ by at most one; if at any time they differ by more than one, rebalancing is done to restore this property. Figures 1-4 illustrate the rotation rules.
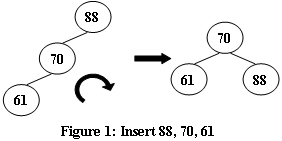 | 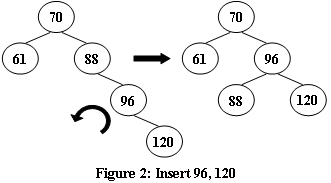 |
|---|---|
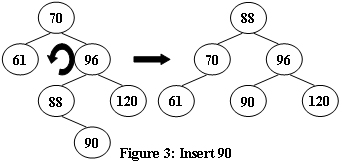 |
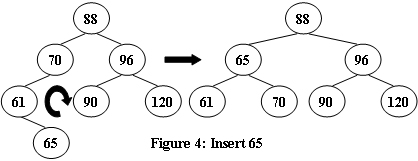 |
Now given a sequence of insertions, you are supposed to output the level-order traversal sequence of the resulting AVL tree, and to tell if it is a complete binary tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤ 20). Then N distinct integer keys are given in the next line. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, insert the keys one by one into an initially empty AVL tree. Then first print in a line the level-order traversal sequence of the resulting AVL tree. All the numbers in a line must be separated by a space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line. Then in the next line, print YES if the tree is complete, or NO if not.
Sample Input 1:
5
88 70 61 63 65
Sample Output 1:
70 63 88 61 65
YES
Sample Input 2:
8
88 70 61 96 120 90 65 68
Sample Output 2:
88 65 96 61 70 90 120 68
NO

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <map> 5 #include <vector> 6 #include <queue> 7 #include <set> 8 using namespace std; 9 struct node{ 10 int data,height; 11 node *lchild,*rchild; 12 }; 13 node* newNode(int v){ 14 node* root = new node; 15 root->data = v; 16 root->lchild = root->rchild = NULL; 17 root->height = 1; 18 return root; 19 } 20 int getHeight(node* root){ 21 if(root==NULL)return 0; 22 return root->height; 23 } 24 void updateHeight(node* root){ 25 root->height = max(getHeight(root->lchild),getHeight(root->rchild))+1; 26 } 27 int getBalanceFactor(node *root){ 28 return getHeight(root->lchild)-getHeight(root->rchild); 29 } 30 void L(node* &root){ 31 node* tmp=root->rchild; 32 root->rchild = tmp->lchild; 33 tmp->lchild = root; 34 updateHeight(root); 35 updateHeight(tmp); 36 root=tmp; 37 } 38 void R(node* &root){ 39 node* tmp=root->lchild; 40 root->lchild = tmp->rchild; 41 tmp->rchild = root; 42 updateHeight(root); 43 updateHeight(tmp); 44 root = tmp; 45 } 46 void insert(node* &root,int v){ 47 if(root==NULL){ 48 root = newNode(v); 49 return; 50 } 51 if(v<root->data){ 52 insert(root->lchild,v); 53 updateHeight(root); 54 if(getBalanceFactor(root)==2){ 55 if(getBalanceFactor(root->lchild)==1){ 56 R(root); 57 } 58 else if(getBalanceFactor(root->lchild)==-1){ 59 L(root->lchild); 60 R(root); 61 } 62 } 63 } 64 else{ 65 insert(root->rchild,v); 66 updateHeight(root); 67 if(getBalanceFactor(root)==-2){ 68 if(getBalanceFactor(root->rchild)==-1){ 69 L(root); 70 } 71 else if(getBalanceFactor(root->rchild)==1){ 72 R(root->rchild); 73 L(root); 74 } 75 } 76 } 77 } 78 node* create(int data[],int n){ 79 node* root = NULL; 80 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 81 insert(root,data[i]); 82 } 83 return root; 84 } 85 int flag=0,after=0; 86 void levelOrder(node* root,int n){ 87 queue<node*> q; 88 int num=0; 89 q.push(root); 90 while(!q.empty()){ 91 node* now = q.front(); 92 num++; 93 printf("%d",now->data); 94 if(num!=n)printf(" "); 95 else printf(" "); 96 q.pop(); 97 if(now->lchild!=NULL){ 98 if(after==1)flag=1; 99 q.push(now->lchild); 100 } 101 else after=1; 102 if(now->rchild!=NULL){ 103 if(after==1)flag=1; 104 q.push(now->rchild); 105 } 106 else after=1; 107 } 108 } 109 int main(){ 110 int n; 111 scanf("%d",&n); 112 int data[30]; 113 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 114 scanf("%d",&data[i]); 115 } 116 node* root = create(data,n); 117 levelOrder(root,n); 118 printf("%s",flag==0?"YES":"NO"); 119 }
注意点:第一次做到平衡二叉树和完全二叉树的判定的题目,重新看了一遍算法笔记,还是很生疏。AVL的插入左旋右旋要熟练记住,考前再看一眼。
完全二叉树的判定:层序遍历时,出现了有子节点为空的节点,后面的节点还出现子节点非空的情况,这就不是完全二叉树
