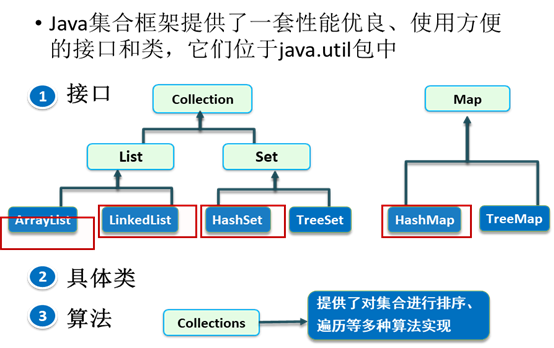
集合框架
Iterable<E>接口是Collection的父接口;
返回一个在一组 T 类型的元素上进行迭代的迭代器。
返回:
一个迭代器。
集合特点
类集实际上就是一个动态的对象数组,与一般的对象数组不同,类集中的对象内容可以任意扩充。
List接口—— ArrayList
List是Collection的子接口,里面可以保存各个重复的内容,此接口的定义如下:
public interface List<E> extends Collection<E>
有序的 collection(也称为序列)。此接口的用户可以对列表中每个元素的插入位置进行精确地控制。用户可以根据元素的整数索引(在列表中的位置)访问元素,并搜索列表中的元素。
ArrayList是List子类,可以直接通过对象的多态性,为List接口实例化
此类的定义如下:
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, Serializable
AbstractList类的定义如下:
public abstract class AbstractList<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements List<E>
Iterator 迭代器遍历集合
public class TestList3 { public static void main(String[] args) { /** * void add(int index, E element) 将指定的元素插入此列表中的指定位置。 */ List<String> list= new ArrayList<>(); list.add("a"); list.add("b"); list.add("c"); list.add(0, "dd"); list.add(2, "ee"); //Collections Collections.sort(list);//升序 /*for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { System.out.println(list.get(i)); }*/ //通过迭代器遍历集合 Iterator<String> it = list.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()){//是否存在下一个元素 String str = it.next();//获得元素 System.out.println(str); if(str.equals("dd")){ it.remove(); //Iterator中的方法 } } System.out.println(list);//展示集合中的数据 list.remove(2); //List接口中的方法 list.remove("b");//List接口中的方法 System.out.println(list);//展示集合中的数据 } }
ListIterator(了解)
双向遍历 public static void main(String[] args) { List<User> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add(new User("1001", 21, "张三1")); list.add(new User("1002", 22, "张三2")); list.add(new User("1003", 23, "张三3")); list.add(new User("1004", 24, "张三4")); for (User u1 : list) { System.out.println(u1); } System.out.println("----------------"); for (int i = list.size()-1; i >=0; i--) { System.out.println(list.get(i)); } System.out.println("----------------"); /*Iterator<User> it = list.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()){ System.out.println(it.next()); }*/ ListIterator<User> lt = list.listIterator(); while(lt.hasNext()){ lt.next(); } System.out.println("移动指针到集合末尾"); System.out.println("----------------"); //逆向遍历 while(lt.hasPrevious()){//有没有上一个元素 System.out.println(lt.previous()); } }
将集合变为对象数组
public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("aa1"); list.add("aa2"); list.add("aa3"); list.add("aa4"); // 将集合变为对象数组 Object[] arr =list.toArray(); for (Object s : arr) { String ss =(String) s; System.out.println(ss); } //把数组转成集合 int[] arr1={1,2,3}; List<int[]> list11 = Arrays.asList(arr1); int[] is = list11.get(0); for (int i : is) { System.out.println(i); } }
ArrayList其他常用方法
public class TestList5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
List<String> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
list1.add("1");
list1.add("2");
list1.add("3");
//boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)
// list.addAll(list1);
// System.out.println(list);
//boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c)
/*list.addAll(1, list1);
System.out.println(list);*/
// void clear()
// 移除此列表中的所有元素。
/* list.clear();
System.out.println(list);*/
if(list!=null){
System.out.println("------------");
}
if(list.isEmpty()){
System.out.println("-----------========");
}
//contains(Object o)
System.out.println(list.contains("a"));
//set(int index, E element)
// 用指定的元素替代此列表中指定位置上的元素。
System.out.println(list.set(0, "aa"));//a-->aa
System.out.println(list);
}
}
Vector (了解)
Vector 底层用的也是数组;扩容机制,线程安全的,效率低;
ArrayList与Vector的区别:
|
No. |
比较点 |
ArrayList |
Vector |
|
1 |
推出时间 |
JDK 1.2之后推出的,属于新的操作类 |
JDK 1.0时推出,属于旧的操作类 |
|
2 |
性能 |
采用异步处理方式,性能更高 |
采用同步处理方式,性能较低 |
|
3 |
线程安全 |
属于非线程安全的操作类 |
属于线程安全的操作类 |
|
4 |
输出 |
只能使用Iterator、foreach输出 |
可以使用Iterator、foreach、Enumeration输出 |
public static void main(String[] args) { Vector<String> v = new Vector<>(); v.add("aa1"); v.add("aa2"); v.add("aa3"); v.add("aa4"); //遍历 Enumeration<String> e = v.elements(); while(e.hasMoreElements()){ System.out.println(e.nextElement()); } }
List --LinkedList子类
public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> list = new LinkedList<>(); list.add("aa1"); list.add("aa2"); list.add("aa3"); list.add("aa3"); LinkedList llist=(LinkedList) list; llist.addFirst("aa"); System.out.println(llist); llist.addLast("dd"); System.out.println(llist); llist.add(2, "ee"); System.out.println(llist); llist.set(2, "ff"); System.out.println(llist); System.out.println(llist.indexOf("aa3")); System.out.println(llist.lastIndexOf("aa3")); }
栈(Stack) (了解)
栈是采用先进后出的数据存储方式,每一个栈都包含一个栈顶,每次出栈是将栈顶的数据取出 在Java中使用Stack类进行栈的操作,Stack类是Vector的子类,Stack类的定义如下: public class Stack<E> extends Vector<E> public static void main(String[] args) { Stack<String> s = new Stack<String>(); // public E push(E item) s.push("aa1");//压栈,入栈 s.push("aa2"); System.out.println(s.empty()); //public E pop() if(!s.empty()){ System.out.println(s.pop());//弹出,出栈 } if(!s.empty()){ System.out.println(s.pop()); } if(!s.empty()){ System.out.println(s.pop()); }else{ System.out.println("空栈!"); } }
Set-HashSet
Set接口也是Collection接口的子接口,但是与Collection或List接口不同的是,Set接口中不能加入重复的元素。 Set接口的定义: public interface Set<E> extends Collection<E> Set接口的主要方法与Collection是一致的 Set接口的实例无法像List接口那样进行双向输出 Set接口的常用子类 散列存放:HashSet 有序存放:TreeSet
public class Person implements Comparable<Person> { private int age; private String name; public Person() { super(); } public Person(int age, String name) { super(); this.age = age; this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person [age=" + age + ", name=" + name + "]"; } @Override public int hashCode() { final int prime = 31; int result = 1; result = prime * result + age; result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode()); return result; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj) return true; if (obj == null) return false; if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) return false; Person other = (Person) obj; if (age != other.age) return false; if (name == null) { if (other.name != null) return false; } else if (!name.equals(other.name)) return false; return true; } @Override public int compareTo(Person o) { if (this.age > o.getAge()) { return 1; } else if (this.age < o.getAge()) { return -1; } else { return 0; } } } public static void main(String[] args) { // 自然顺序 List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("1"); list.add("3"); list.add("4"); list.add("2"); System.out.println(list); // HashSet Set<String> se = new HashSet<>(); se.add("a1"); se.add("a1"); se.add("b1"); se.add("b2"); se.add("b3"); System.out.println(se); Set<Integer> s = new HashSet<>(); s.add(1); s.add(1); s.add(2); System.out.println(s); }
Set-TreeSet
TreeSet底层是树(红黑树)存储数据;
向TreeSet集合中存的数据,必须是可排序的;
Set<Person> p = new TreeSet<>(); p.add(new Person(12, "aa")); p.add(new Person(2, "aab")); p.add(new Person(5, "aasdf")); p.add(new Person(20, "asadfgdaa")); p.add(new Person(3, "afewra")); for (Person pp : p) { System.out.println(pp); }
集合的遍历
foreach:JDK 1.5之后提供的新功能,可以输出数组或集合
Iterator:迭代输出,是使用最多的输出方式;
ListIterator:是Iterator的子接口,专门用于输出List中的内容;(ArrayList LinkedList)双向迭代
Enumeration:是一个旧的接口,功能与Iterator类似;(了解)
遍历集合时删除指定元素,需要注意:
public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("aaa0"); list.add("aaa1"); list.add("aaa2"); list.add("aaa3"); //for循环中不能直接通过集合的删除方法删除指定元素 /* for (String s : list) { list.remove("aaa2"); System.out.println(s); }*/ //迭代器中可以直接通过集合的删除方法删除指定元素 Iterator<String> it = list.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()){ if(it.next().equals("aaa2")){ // it.remove(); list.remove("aaa2"); } } System.out.println(list); }
Map接口
key:唯一
value:任意
key=null key可以有一个null作为值;
之前所讲解的Collection、Set、List接口都属于单值的操作,即:每次只能操作一个对象,而Map与它们不同的是,每次操作的是键值对,即二元偶对象,Map中的每个元素都使用key à value的形式存储在集合之中,此接口定义如下:
public interface Map<K,V>
public static void main(String[] args) { Map<Integer, String> m = new HashMap<>(); // 添加 .key:value m.put(1, "aaa"); m.put(2, "aaa1"); m.put(3, "aaa2"); m.put(4, "aaa3"); System.out.println(m); //get(Object key) // 返回指定键所映射的值;如果对于该键来说,此映射不包含任何映射关系,则返回 null。 System.out.println(m.get(3)); //key 必须是唯一 m.put(1, "aaa1"); System.out.println(m);//展示集合中的数据 //遍历 Set<K> keySet() // 返回此映射中所包含的键的 Set 视图。 Set<Integer> s = m.keySet(); /*for (Integer i : s) { System.out.println(i+"--"+m.get(i)); }*/ /*Iterator<Integer> it = s.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()){ Integer key = it.next(); System.out.println(key+"--"+m.get(key)); }*/ //Collection<V> values() // 返回此映射所包含的值的 Collection 视图。 /* Collection<String> values = m.values(); for (String ss : values) { System.out.println(ss); }*/ // Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() // 返回此映射所包含的映射关系的 Set 视图。 Set<Entry<Integer, String>> en = m.entrySet(); for (Entry<Integer, String> e : en) { System.out.println(e.getKey()+"--"+e.getValue()); } }
public class TestHashMap1 { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String, String> m =new HashMap<>(); m.put("a", "张三1"); m.put("b", "张三2"); m.put("c", "张三3"); m.put("d", "张三4"); /* Map<String, String> m1 =new HashMap<>(); m1.put("a", "李四"); m1.put("b", "王五"); m.putAll(m1); System.out.println(m);*/ // remove(Object key) // 从此映射中移除指定键的映射关系(如果存在)。 m.remove("a"); System.out.println(m); System.out.println(m.size()); } }
HashMap存对象为key
public class TestPerson { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String, Person> m=new HashMap<>(); m.put("1001", new Person("1001", 20)); m.put("1002", new Person("1002", 21)); m.put("1003", new Person("1003", 22)); //keys /*Set<String> keys = m.keySet(); for (String s : keys) { System.out.println(s+"=>"+m.get(s)); }*/ Map<Person, String> m1=new HashMap<>(); m1.put(new Person("1001", 20),"1001"); m1.put(new Person("1002", 21),"1002"); m1.put(new Person("1002", 21),"1003"); System.out.println(m1); } }
Map接口的常用子类
HashMap:无序存放的,是新的操作类,key不允许重复。线程不安全,效率高
Hashtable:无序存放的,是旧的操作类,key不允许重复。线程安全,效率低
TreeMap: 可以排序的Map集合,按集合中的key排序,key不允许重复。
|
No. |
比较点 |
HashMap |
Hashtable |
|
1 |
推出时间 |
JDK 1.2之后推出的,属于新的操作类 |
JDK 1.0时推出,属于旧的操作类 |
|
2 |
性能 |
采用异步处理方式,性能更高 |
采用同步处理方式,性能较低 |
|
3 |
线程安全 |
属于非线程安全的操作类 |
属于线程安全的操作类 |
|
4 |
设置空值 |
允许设置null值 |
不能设置null,如果设置则出现NullPointerException异常 |
TreeMap:
可以排序的Map集合,按集合中的key排序,key不允许重复。
//TreeMap key 为可排序对象,并且key唯一
//TreeMap key 为可排序对象,并且key唯一 public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String, Person> map = new TreeMap<>(); map.put("1001", new Person("1001", 20)); map.put("1002", new Person("1002", 23)); map.put("1003", new Person("1003", 19)); map.put("1004", new Person("1004", 22)); /*Set<String> keys = map.keySet(); for (String k : keys) { System.out.println(k+" : "+map.get(k)); }*/ Map<Person,String> map1 = new TreeMap<>(); map1.put(new Person("1001", 20),"1001"); map1.put(new Person("1002", 23),"1002"); map1.put(new Person("1003", 19),"1003"); map1.put(new Person("1004", 29),"1004"); map1.put(new Person("1004", 29),"1004"); Set<Entry<Person,String>> en = map1.entrySet(); for (Entry<Person,String> e : en) { System.out.println(e.getKey()+":"+e.getValue()); } }
对象的引用强度说明
从JDK1.2版本开始,Java把对象的引用分为四种级别,从而使程度能更加灵活的控制对象的生命周期。这四种级别由高到低依次为:强引用、软引用、弱引用和虚引用,下面来简单了解以下这四种引用的区别:
强引用:当内存不足时,JVM宁可出现OutOfMemeryError错误而使程序停止,也不会回收此对象来释放空间;
软引用:当内存不足时,会回收这些对象的内存,用来实现内存敏感的高速缓存;
弱引用:无论内存是否紧张,被垃圾回收器发现立即回收;
虚引用:和没有任何引用一样。随时会被垃圾回收
Collections常用方法
public static void main(String[] args) { // static <T> boolean // addAll(Collection<? super T> c, T... elements) // 将所有指定元素添加到指定 collection 中。 List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("111"); list.add("121"); Collections.addAll(list, "aa","bb","cc"); System.out.println(list); Collections.reverse(list); System.out.println(list); //查找 int index = Collections.binarySearch(list, "aa"); System.out.println(index); //替换 boolean flag = Collections.replaceAll(list, "bb", "bbb"); if(flag){ System.out.println("ok"); }else{ System.out.println("no"); } System.out.println(list); //static void swap(List<?> list, int i, int j) // 在指定列表的指定位置处交换元素。 Collections.swap(list, 0, 4); System.out.println(list); //线程安全 Collections.synchronizedList(list); System.out.println(list); }
Map复杂操作
public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String,Map<String,String>> m = new HashMap<>();//主集合 Map<String,String> mm = new HashMap<>(); mm.put("one", "数据1"); mm.put("two", "数据2"); Map<String,String> mm1 = new HashMap<>(); mm1.put("one1", "数据11"); mm1.put("two1", "数据22"); m.put("1111", mm); m.put("2222", mm1); //获得主集合m的keys Set<String> mkeys = m.keySet(); for (String s : mkeys) { System.out.println(s); Map<String, String> mvalue = m.get(s); Set<Entry<String, String>> es = mvalue.entrySet(); for (Entry<String, String> e : es) { System.out.println(e.getKey()+":"+e.getValue()); } } System.out.println("========================"); Map<String,List<String>> m1= new HashMap<>(); //内 层List List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("aaaaaaaa1"); list.add("aaaaaaaa2"); list.add("aaaaaaaa3"); List<String> list1 = new ArrayList<>(); list1.add("aaaaaaaa1bbbb"); list1.add("aaaaaaaa2bbb"); list1.add("aaaaaaaa3bbb"); //map Map<String,List<String>> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("第1个数据", list); map.put("第2个数据", list1); Set<Entry<String, List<String>>> es = map.entrySet(); Iterator<Entry<String, List<String>>> it = es.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()){ Entry<String, List<String>> n = it.next(); System.out.println(n.getKey()+":"); List<String> ls = n.getValue(); for (String s : ls) { System.out.println(s); } } }