CW攻击原论文地址——https://arxiv.org/pdf/1608.04644.pdf
1.CW攻击的原理
CW攻击是一种基于优化的攻击,攻击的名称是两个作者的首字母。首先还是贴出攻击算法的公式表达:
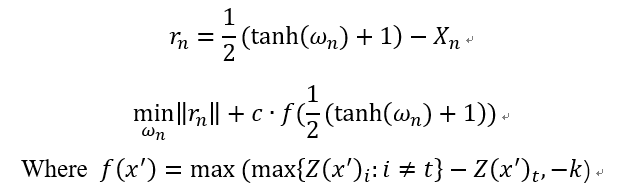
下面解释下算法的大概思想,该算法将对抗样本当成一个变量,那么现在如果要使得攻击成功就要满足两个条件:(1)对抗样本和对应的干净样本应该差距越小越好;(2)对抗样本应该使得模型分类错,且错的那一类的概率越高越好。
其实上述公式的两部分loss也就是基于这两点而得到的,首先说第一部分,rn对应着干净样本和对抗样本的差,但作者在这里有个小trick,他把对抗样本映射到了tanh空间里面,这样做有什么好处呢?如果不做变换,那么x只能在(0,1)这个范围内变换,做了这个变换 ,x可以在-inf到+inf做变换,有利于优化。
再来说说第二部分,公式中的Z(x)表示的是样本x通过模型未经过softmax的输出向量,对于干净的样本来说,这个这个向量的最大值对应的就是正确的类别(如果分类正确的话),现在我们将类别t(也就是我们最后想要攻击成的类别)所对应的逻辑值记为![]() ,将最大的值(对应类别不同于t)记为
,将最大的值(对应类别不同于t)记为![]() ,如果通过优化使得
,如果通过优化使得![]() 变小,攻击不就离成功了更近嘛。那么式子中的k是什么呢?k其实就是置信度(confidence),可以理解为,k越大,那么模型分错,且错成的那一类的概率越大。但与此同时,这样的对抗样本就更难找了。最后就是常数c,这是一个超参数,用来权衡两个loss之间的关系,在原论文中,作者使用二分查找来确定c值。
变小,攻击不就离成功了更近嘛。那么式子中的k是什么呢?k其实就是置信度(confidence),可以理解为,k越大,那么模型分错,且错成的那一类的概率越大。但与此同时,这样的对抗样本就更难找了。最后就是常数c,这是一个超参数,用来权衡两个loss之间的关系,在原论文中,作者使用二分查找来确定c值。
下面总结一下CW攻击:
CW是一个基于优化的攻击,主要调节的参数是c和k,看你自己的需要了。它的优点在于,可以调节置信度,生成的扰动小,可以破解很多的防御方法,缺点是,很慢~~~
最后在说一下,就是在某些防御论文中,它实现CW攻击,是直接用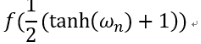 替换PGD中的loss,其余步骤和PGD一模一样。
替换PGD中的loss,其余步骤和PGD一模一样。
2.CW代码实现

1 class CarliniWagnerL2Attack(Attack, LabelMixin): 2 3 def __init__(self, predict, num_classes, confidence=0, 4 targeted=False, learning_rate=0.01, 5 binary_search_steps=9, max_iterations=10000, 6 abort_early=True, initial_const=1e-3, 7 clip_min=0., clip_max=1., loss_fn=None): 8 """ 9 Carlini Wagner L2 Attack implementation in pytorch 10 11 Carlini, Nicholas, and David Wagner. "Towards evaluating the 12 robustness of neural networks." 2017 IEEE Symposium on Security and 13 Privacy (SP). IEEE, 2017. 14 https://arxiv.org/abs/1608.04644 15 16 learning_rate: the learning rate for the attack algorithm 17 max_iterations: the maximum number of iterations 18 binary_search_steps: number of binary search times to find the optimum 19 abort_early: if set to true, abort early if getting stuck in local min 20 confidence: confidence of the adversarial examples 21 targeted: TODO 22 """ 23 24 if loss_fn is not None: 25 import warnings 26 warnings.warn( 27 "This Attack currently do not support a different loss" 28 " function other than the default. Setting loss_fn manually" 29 " is not effective." 30 ) 31 32 loss_fn = None 33 34 super(CarliniWagnerL2Attack, self).__init__( 35 predict, loss_fn, clip_min, clip_max) 36 37 self.learning_rate = learning_rate 38 self.max_iterations = max_iterations 39 self.binary_search_steps = binary_search_steps 40 self.abort_early = abort_early 41 self.confidence = confidence 42 self.initial_const = initial_const 43 self.num_classes = num_classes 44 # The last iteration (if we run many steps) repeat the search once. 45 self.repeat = binary_search_steps >= REPEAT_STEP 46 self.targeted = targeted 47 48 def _loss_fn(self, output, y_onehot, l2distsq, const): 49 # TODO: move this out of the class and make this the default loss_fn 50 # after having targeted tests implemented 51 real = (y_onehot * output).sum(dim=1) 52 53 # TODO: make loss modular, write a loss class 54 other = ((1.0 - y_onehot) * output - (y_onehot * TARGET_MULT) 55 ).max(1)[0] 56 # - (y_onehot * TARGET_MULT) is for the true label not to be selected 57 58 if self.targeted: 59 loss1 = clamp(other - real + self.confidence, min=0.) 60 else: 61 loss1 = clamp(real - other + self.confidence, min=0.) 62 loss2 = (l2distsq).sum() 63 loss1 = torch.sum(const * loss1) 64 loss = loss1 + loss2 65 return loss 66 67 def _is_successful(self, output, label, is_logits): 68 # determine success, see if confidence-adjusted logits give the right 69 # label 70 71 if is_logits: 72 output = output.detach().clone() 73 if self.targeted: 74 output[torch.arange(len(label)), label] -= self.confidence 75 else: 76 output[torch.arange(len(label)), label] += self.confidence 77 pred = torch.argmax(output, dim=1) 78 else: 79 pred = output 80 if pred == INVALID_LABEL: 81 return pred.new_zeros(pred.shape).byte() 82 83 return is_successful(pred, label, self.targeted) 84 85 86 def _forward_and_update_delta( 87 self, optimizer, x_atanh, delta, y_onehot, loss_coeffs): 88 89 optimizer.zero_grad() 90 adv = tanh_rescale(delta + x_atanh, self.clip_min, self.clip_max) 91 transimgs_rescale = tanh_rescale(x_atanh, self.clip_min, self.clip_max) 92 output = self.predict(adv) 93 l2distsq = calc_l2distsq(adv, transimgs_rescale) 94 loss = self._loss_fn(output, y_onehot, l2distsq, loss_coeffs) 95 loss.backward() 96 optimizer.step() 97 98 return loss.item(), l2distsq.data, output.data, adv.data 99 100 101 def _get_arctanh_x(self, x): 102 result = clamp((x - self.clip_min) / (self.clip_max - self.clip_min), 103 min=self.clip_min, max=self.clip_max) * 2 - 1 104 return torch_arctanh(result * ONE_MINUS_EPS) 105 106 def _update_if_smaller_dist_succeed( 107 self, adv_img, labs, output, l2distsq, batch_size, 108 cur_l2distsqs, cur_labels, 109 final_l2distsqs, final_labels, final_advs): 110 111 target_label = labs 112 output_logits = output 113 _, output_label = torch.max(output_logits, 1) 114 115 mask = (l2distsq < cur_l2distsqs) & self._is_successful( 116 output_logits, target_label, True) 117 118 cur_l2distsqs[mask] = l2distsq[mask] # redundant 119 cur_labels[mask] = output_label[mask] 120 121 mask = (l2distsq < final_l2distsqs) & self._is_successful( 122 output_logits, target_label, True) 123 final_l2distsqs[mask] = l2distsq[mask] 124 final_labels[mask] = output_label[mask] 125 final_advs[mask] = adv_img[mask] 126 127 def _update_loss_coeffs( 128 self, labs, cur_labels, batch_size, loss_coeffs, 129 coeff_upper_bound, coeff_lower_bound): 130 131 # TODO: remove for loop, not significant, since only called during each 132 # binary search step 133 for ii in range(batch_size): 134 cur_labels[ii] = int(cur_labels[ii]) 135 if self._is_successful(cur_labels[ii], labs[ii], False): 136 coeff_upper_bound[ii] = min( 137 coeff_upper_bound[ii], loss_coeffs[ii]) 138 139 if coeff_upper_bound[ii] < UPPER_CHECK: 140 loss_coeffs[ii] = ( 141 coeff_lower_bound[ii] + coeff_upper_bound[ii]) / 2 142 else: 143 coeff_lower_bound[ii] = max( 144 coeff_lower_bound[ii], loss_coeffs[ii]) 145 if coeff_upper_bound[ii] < UPPER_CHECK: 146 loss_coeffs[ii] = ( 147 coeff_lower_bound[ii] + coeff_upper_bound[ii]) / 2 148 else: 149 loss_coeffs[ii] *= 10 150 151 152 def perturb(self, x, y=None): 153 x, y = self._verify_and_process_inputs(x, y) 154 155 # Initialization 156 if y is None: 157 y = self._get_predicted_label(x) 158 x = replicate_input(x) 159 batch_size = len(x) 160 coeff_lower_bound = x.new_zeros(batch_size) 161 coeff_upper_bound = x.new_ones(batch_size) * CARLINI_COEFF_UPPER 162 loss_coeffs = torch.ones_like(y).float() * self.initial_const 163 final_l2distsqs = [CARLINI_L2DIST_UPPER] * batch_size 164 final_labels = [INVALID_LABEL] * batch_size 165 final_advs = x 166 x_atanh = self._get_arctanh_x(x) 167 y_onehot = to_one_hot(y, self.num_classes).float() 168 169 final_l2distsqs = torch.FloatTensor(final_l2distsqs).to(x.device) 170 final_labels = torch.LongTensor(final_labels).to(x.device) 171 172 # Start binary search 173 for outer_step in range(self.binary_search_steps): 174 delta = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros_like(x)) 175 optimizer = optim.Adam([delta], lr=self.learning_rate) 176 cur_l2distsqs = [CARLINI_L2DIST_UPPER] * batch_size 177 cur_labels = [INVALID_LABEL] * batch_size 178 cur_l2distsqs = torch.FloatTensor(cur_l2distsqs).to(x.device) 179 cur_labels = torch.LongTensor(cur_labels).to(x.device) 180 prevloss = PREV_LOSS_INIT 181 182 if (self.repeat and outer_step == (self.binary_search_steps - 1)): 183 loss_coeffs = coeff_upper_bound 184 for ii in range(self.max_iterations): 185 loss, l2distsq, output, adv_img = \ 186 self._forward_and_update_delta( 187 optimizer, x_atanh, delta, y_onehot, loss_coeffs) 188 if self.abort_early: 189 if ii % (self.max_iterations // NUM_CHECKS or 1) == 0: 190 if loss > prevloss * ONE_MINUS_EPS: 191 break 192 prevloss = loss 193 194 self._update_if_smaller_dist_succeed( 195 adv_img, y, output, l2distsq, batch_size, 196 cur_l2distsqs, cur_labels, 197 final_l2distsqs, final_labels, final_advs) 198 199 self._update_loss_coeffs( 200 y, cur_labels, batch_size, 201 loss_coeffs, coeff_upper_bound, coeff_lower_bound) 202 203 return final_advs
