PnP(Perspective-n-Point)是求解3D到2D点的对应方法。不论是相机和雷达的标定还是相机和相机的标定都可以使用PNP来解决,即通过不同坐标系下相同的点对求解变换矩阵。
这里相机多用棋盘格中的角点来实现点的提取。流行方法为张正友标定法,至于详细原理可点击我的博客https://www.cnblogs.com/tangjunjun/p/16240878.html查看,本博客主要使用代码
实现外参求解与相机标定的内参和畸变系数求解。
代码及标定图链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1ujX19IUV0EPSIMyIcBnClA?pwd=r63z (相机标定与外参求解.zip文件)
提取码:r63z
提取码:r63z
①相机标定,求解内参与畸变系数;
# 相机标定,主要求内参和畸变系数 def calibration_camera(img_root, rand_count=20): board_h = 8 board_w = 11 objp = np.zeros((board_h * board_w, 3), np.float32) objp[:, :2] = np.mgrid[0:board_w, 0:board_h].T.reshape(-1, 2) # 将世界坐标系建在标定板上,所有点的Z坐标全部为0,所以只需要赋值x和y objp = 60 * objp # 打印棋盘格一格的边长为2.6cm obj_points = [] # 存储3D点 img_points = [] # 存储2D点 images = glob.glob(os.path.join(img_root, '*.jpg')) # 黑白棋盘的图片路径 random.shuffle(images) if rand_count > len(images): rand_count = len(images) for fname in images[:rand_count]: img = cv2.imread(fname) gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) size = gray.shape[::-1] ret, corners = cv2.findChessboardCorners(gray, (board_w, board_h), None) if ret: obj_points.append(objp) corners2 = cv2.cornerSubPix(gray, corners, (5, 5), (-1, -1), (cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER | cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS, 30, 0.001)) if [corners2]: img_points.append(corners2) else: img_points.append(corners) cv2.drawChessboardCorners(img, (board_w, board_h), corners, ret) # 记住,OpenCV的绘制函数一般无返回值 cv2.imshow("img", img) cv2.waitKey(10) ret, mtx, dist, rvecs, tvecs = cv2.calibrateCamera(obj_points, img_points, size, None, None) # v_rot_mat, _ = cv2.Rodrigues(np.array(v_rot).reshape(-1)) # print("旋转矩阵=", v_rot_mat) # print("内参=", mtx) # print("畸变系数=", dist) # print("旋转向量=", rvecs) # print("平移向量=", tvecs) # 反投影误差 total_error = 0 for i in range(len(obj_points)): imgpoints2, _ = cv2.projectPoints(obj_points[i], rvecs[i], tvecs[i], mtx, dist) error = cv2.norm(img_points[i], imgpoints2, cv2.NORM_L2) / len(imgpoints2) total_error += error # print("total error: ", total_error / len(obj_points)) return mtx, dist, total_error
②通过畸变系数矫正,获得矫正的图像;
# 消除畸变 def revise_img(img_root, mtx, dist): mtx = np.array(mtx) dist = np.array(dist).reshape(1, 5) img = cv2.imread(img_root) h, w = img.shape[:2] newcameramtx, roi = cv2.getOptimalNewCameraMatrix(mtx, dist, (w, h), 1, (w, h)) # undistort dst = cv2.undistort(img, mtx, dist, None, newcameramtx) # crop the image x, y, w, h = roi dst = dst[y:y + h, x:x + w] cv2.imwrite('./revise_img.jpg', dst) return dst
③使用PnP方法求解外参;
# 旋转向量和平移向量求解 def calibration_RT(points_3D, points_2D, cameraMatrix, distCoeffs): points_3D = np.array(points_3D) points_2D = np.array(points_2D) cameraMatrix = np.array(cameraMatrix).astype(np.float32) distCoeffs = np.array(distCoeffs).astype(np.float32) _, rvecs, tvecs, inliers = cv2.solvePnPRansac(points_3D.reshape(-1, 1, 3), points_2D.reshape(-1, 1, 2), cameraMatrix, distCoeffs ) R, _ = cv2.Rodrigues(rvecs) print('R:\n', R) print('rvecs:\n', rvecs) print('tvecs:\n', tvecs) return R, tvecs
④附带三点对应求解空间变换的旋转向量(矩阵)和平移向量(主要记录此方法);
def rigid_transform_RT(lidarPoints, rtkPoints): ''' :param lidarPoints: 世界坐标系<---原始坐标,需要转换的坐标系 :param rtkPoints: 目标世界坐标系<---目标三维坐标,已转换的坐标 :return: # Input: expects Nx3 matrix of points # Returns R,t # R = 3x3 rotation matrix # t = 3x1 column vector demo: rigid_transform_RT(L1,S1) ''' Pa = np.array(lidarPoints) Pb = np.array(rtkPoints) N = Pa.shape[0] # total points centroid_Pa = np.mean(Pa, axis=0) centroid_Pb = np.mean(Pb, axis=0) # centre the points H_Pa = Pa - np.tile(centroid_Pa, (N, 1)) H_Pb = Pb - np.tile(centroid_Pb, (N, 1)) H = np.matmul(np.transpose(H_Pa), H_Pb) U, S, V = np.linalg.svd(H) R = np.matmul(V.T, U.T) if np.linalg.det(R) < 0: print("det(R) < R, reflection detected!, correcting for it ...\n") V[2, :] *= -1 R = np.matmul(V.T, U.T) T = centroid_Pb - np.matmul(R, centroid_Pa) print("R:\n{}\nT:\n{}".format(R, T)) return R, T
以上为世界坐标系转到像素坐标系方法的代码,以下代码为整体代码:

import numpy as np import os import cv2 import glob # *******************utils*********************# import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import random def draw_circle(img, coord): coord = np.array(coord).reshape(-1) cv2.circle(img, (int(coord[0]), int(coord[1])), 2, (0, 0, 255), -1) return img def draw_axis(img, O, OX, OY, OZ): color = (0, 0, 255) frontsize = 0.5 img = cv2.line(img, (int(O[0]), int(O[1])), (int(OX[0]), int(OX[1])), color, 1) cv2.putText(img, 'X', (int(OX[0]), int(OX[1])), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, frontsize, color, 1) img = cv2.line(img, (int(O[0]), int(O[1])), (int(OY[0]), int(OY[1])), color, 1) cv2.putText(img, 'Y', (int(OY[0]), int(OY[1])), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, frontsize, color, 1) img = cv2.line(img, (int(O[0]), int(O[1])), (int(OZ[0]), int(OZ[1])), color, 1) cv2.putText(img, 'Z', (int(OZ[0]), int(OZ[1])), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, frontsize, color, 1) return img def show_img(img): plt.imshow(img) plt.show() # *******************************通过内参联合求解外参*******************# def get_pixel(coord, mtx, R, T): mtx = np.array(mtx) R = np.array(R) T = np.array(T).reshape(3, 1) coord = np.array(coord).reshape(-1, 1) RT = np.hstack((R, T)) XYZ_camera = np.matmul(RT, coord) # XYZ_camera = XYZ_camera / XYZ_camera[-1, -1] x, y, z = np.matmul(mtx, XYZ_camera) x = x / z y = y / z print('x={}\ty={}'.format(x[0], y[0])) return [x[0], y[0]] # ***********************利用opencv相机标定**************# # 相机标定,主要求内参和畸变系数 def calibration_camera(img_root, rand_count=20): board_h = 8 board_w = 11 objp = np.zeros((board_h * board_w, 3), np.float32) objp[:, :2] = np.mgrid[0:board_w, 0:board_h].T.reshape(-1, 2) # 将世界坐标系建在标定板上,所有点的Z坐标全部为0,所以只需要赋值x和y objp = 60 * objp # 打印棋盘格一格的边长为2.6cm obj_points = [] # 存储3D点 img_points = [] # 存储2D点 images = glob.glob(os.path.join(img_root, '*.jpg')) # 黑白棋盘的图片路径 random.shuffle(images) if rand_count > len(images): rand_count = len(images) for fname in images[:rand_count]: img = cv2.imread(fname) gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) size = gray.shape[::-1] ret, corners = cv2.findChessboardCorners(gray, (board_w, board_h), None) if ret: obj_points.append(objp) corners2 = cv2.cornerSubPix(gray, corners, (5, 5), (-1, -1), (cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER | cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS, 30, 0.001)) if [corners2]: img_points.append(corners2) else: img_points.append(corners) cv2.drawChessboardCorners(img, (board_w, board_h), corners, ret) # 记住,OpenCV的绘制函数一般无返回值 cv2.imshow("img", img) cv2.waitKey(10) ret, mtx, dist, rvecs, tvecs = cv2.calibrateCamera(obj_points, img_points, size, None, None) # v_rot_mat, _ = cv2.Rodrigues(np.array(v_rot).reshape(-1)) # print("旋转矩阵=", v_rot_mat) # print("内参=", mtx) # print("畸变系数=", dist) # print("旋转向量=", rvecs) # print("平移向量=", tvecs) # 反投影误差 total_error = 0 for i in range(len(obj_points)): imgpoints2, _ = cv2.projectPoints(obj_points[i], rvecs[i], tvecs[i], mtx, dist) error = cv2.norm(img_points[i], imgpoints2, cv2.NORM_L2) / len(imgpoints2) total_error += error # print("total error: ", total_error / len(obj_points)) return mtx, dist, total_error # 旋转向量和平移向量求解 def calibration_RT(points_3D, points_2D, cameraMatrix, distCoeffs): points_3D = np.array(points_3D) points_2D = np.array(points_2D) cameraMatrix = np.array(cameraMatrix).astype(np.float32) distCoeffs = np.array(distCoeffs).astype(np.float32) _, rvecs, tvecs, inliers = cv2.solvePnPRansac(points_3D.reshape(-1, 1, 3), points_2D.reshape(-1, 1, 2), cameraMatrix, distCoeffs ) R, _ = cv2.Rodrigues(rvecs) print('R:\n', R) print('rvecs:\n', rvecs) print('tvecs:\n', tvecs) return R, tvecs def get_calibration_pixel(coord, rvecs, tvecs, mtx, dist): imgpts, jac = cv2.projectPoints(coord, rvecs, tvecs, mtx, dist) return imgpts # 消除畸变 def revise_img(img_root, mtx, dist): mtx = np.array(mtx) dist = np.array(dist).reshape(1, 5) img = cv2.imread(img_root) h, w = img.shape[:2] newcameramtx, roi = cv2.getOptimalNewCameraMatrix(mtx, dist, (w, h), 1, (w, h)) # undistort dst = cv2.undistort(img, mtx, dist, None, newcameramtx) # crop the image x, y, w, h = roi dst = dst[y:y + h, x:x + w] cv2.imwrite('./revise_img.jpg', dst) return dst # 自动寻找3d点与像素点对应坐标(只针对标定版) def find_point_3d2d(img_root, save=True): board_h = 8 board_w = 11 objp = np.zeros((board_h * board_w, 3), np.float32) objp[:, :2] = np.mgrid[0:board_w, 0:board_h].T.reshape(-1, 2) # 将世界坐标系建在标定板上,所有点的Z坐标全部为0,所以只需要赋值x和y points_3d = 60 * objp # 打印棋盘格一格的边长为2.6cm points_2d = None # 存储2D点 img = cv2.imread(img_root) img_rand = img.copy() gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) rand_p2, rand_p3 = None, None ret, corners = cv2.findChessboardCorners(gray, (board_w, board_h), None) print('ret=', ret) if ret: corners = cv2.cornerSubPix(gray, corners, (5, 5), (-1, -1), (cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER | cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS, 30, 0.001)) cv2.drawChessboardCorners(img, (board_w, board_h), corners, ret) # 记住,OpenCV的绘制函数一般无返回值 points_2d = corners.reshape(-1, 2) if save: file_write_obj = open('./save_points_3d2d.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') # 以写的方式打开文件,如果文件不存在,就会自动创建 for i, p2 in enumerate(points_2d): text = '3d:\t' + str(points_3d[i]) + '\t2d\t' + str(p2) + '\n' file_write_obj.writelines(text) k = 10 rand_int = random.sample(range(1, len(points_2d)), k) # print('rand_int=',rand_int) rand_int = [48, 55, 85, 22, 73, 39, 68, 31, 78, 71] rand_p2 = points_2d[rand_int] rand_p3 = points_3d[rand_int] file_write_obj.close() # 图像展示选择坐标点 for inds in rand_int: pp2 = points_2d[inds] img_rand = draw_circle(img_rand, pp2) cv2.imwrite('./calibration_point.jpg', img_rand) show_img(img) return points_3d, points_2d, rand_p3, rand_p2 def draw_board(img_root, mtx, R, T, dist=None): img = cv2.imread(img_root) mtx = np.array(mtx) dist = np.array(dist).reshape(1, 5) if dist is not None else None for i in range(10): for j in range(8): coord = [i * 60, j * 60, 0.0, 1] coord = np.array(coord) coord_pixel = get_pixel(coord, mtx, R, T) RMat = cv2.Rodrigues(R)[0] coord = [[i * 60, j * 60, 0.0]] # coord_pixel, _ = cv2.projectPoints(coord,RMat, T, mtx, dist) img = draw_circle(img, coord_pixel) # # 画坐标轴 L = 80 O = get_pixel([0, 0, 0, 1], mtx, R, T) OX = get_pixel([L, 0, 0, 1], mtx, R, T) OY = get_pixel([0, L, 0, 1], mtx, R, T) OZ = get_pixel([0, 0, L, 1], mtx, R, T) img = draw_axis(img, O, OX, OY, OZ) show_img(img) cv2.imwrite('./predict_result.jpg', img) def draw_space(img_root, coord, mtx, R, T): img = cv2.imread(img_root) for c in coord: c = np.array(c) coord_pixel = get_pixel(c, mtx, R, T) img = draw_circle(img, coord_pixel) # # 画坐标轴 L = 2 O = get_pixel([0, 0, 0, 1], mtx, R, T) OX = get_pixel([L, 0, 0, 1], mtx, R, T) OY = get_pixel([0, L, 0, 1], mtx, R, T) OZ = get_pixel([0, 0, L, 1], mtx, R, T) img = draw_axis(img, O, OX, OY, OZ) show_img(img) cv2.imwrite('./predict_result.jpg', img) def get_coord(M=6, N=15): # M, N = 6, 15 # 行与列 coord_size = 1 coord = [] for i in range(M): for j in range(N): coord.append([i * coord_size, j * coord_size, 0, 1]) # for i in [-1, -2, -3, -4]: # for j in range(N): # coord.append([i * coord_size, j * coord_size, 0, 1]) return coord if __name__ == '__main__': predict_space = False # 实际空间坐标标定 predict_board = False # 决定测试标定版输出结果 calibration = True if calibration: img_root = r'C:\Users\vrc\Desktop\RadarCamera\code\camera_main\data\data09206\img_ori' mtx_best, dist_best, total_error_best = None, None, 100000 for i in range(50): mtx, dist, total_error = calibration_camera(img_root, rand_count=14) if total_error < total_error_best: total_error_best = total_error mtx_best = mtx dist_best = dist print("最小误差=", total_error_best) print("最优内参=", mtx_best) print("最优畸变系数=", dist_best) print("最小误差=", total_error_best) mtx = [[1.90555223e+03, 0.00000000e+00, 1.01084265e+03], [0.00000000e+00, 1.89395850e+03, 5.29217920e+02], [0.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00, 1.00000000e+00]] dist = [-0.39262705, 0.16798904, -0.00529946, 0.0008667, -0.37552875] if predict_board: #只针对标定板 img_root = r'C:\Users\vrc\Desktop\RadarCamera\data\phone\2.jpg' img = revise_img(img_root, mtx, dist) img_root = './revise_img.jpg' _, _, rand_p3, rand_p2 = find_point_3d2d(img_root) # dist = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0] R, T = calibration_RT(rand_p3, rand_p2, mtx, dist) # 通过内外参求解像素坐标 # img_root = './revise_img.jpg' draw_board(img_root, mtx, R, T, dist=dist) if predict_space: img_root = r'C:\Users\vrc\Desktop\RadarCamera\code\camera_main\data\data0926-2\1.png' img = revise_img(img_root, mtx, dist) img_root = './revise_img.jpg' p3 = [[1, 1, 0], [0.0, 3, 0], [2, 2.0, 0], [1, 5, 0], [2, 1, 0]] p2 = [[939.0, 462], [702.0, 234], [1239, 344], [947, 134], [1312, 478]] dist = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0] R, T = calibration_RT(p3, p2, mtx, dist) # coord = [[1, 3.0, 0, 1], [4, 5, 0, 1], [2, 6, 0, 1], [2, 2,0, 1], [-1, 4, 0, 1]] coord = get_coord(M=3, N=15) draw_space(img_root, coord, mtx, R, T)
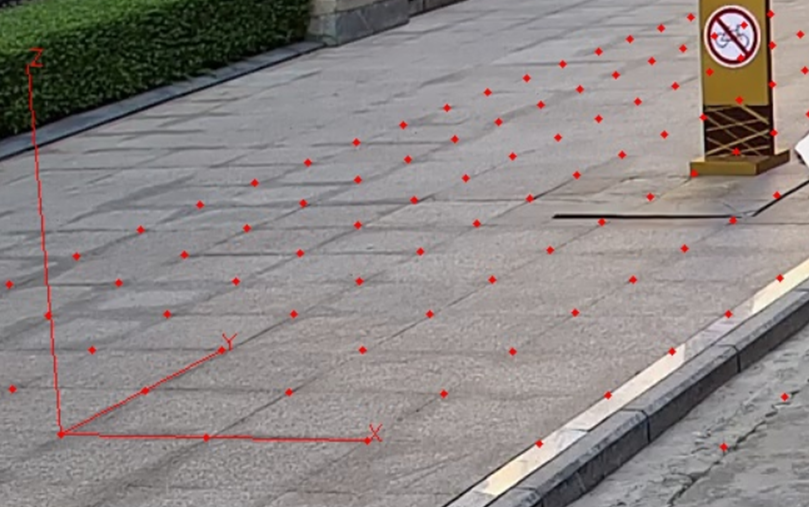
世界坐标系转像素结果展示:
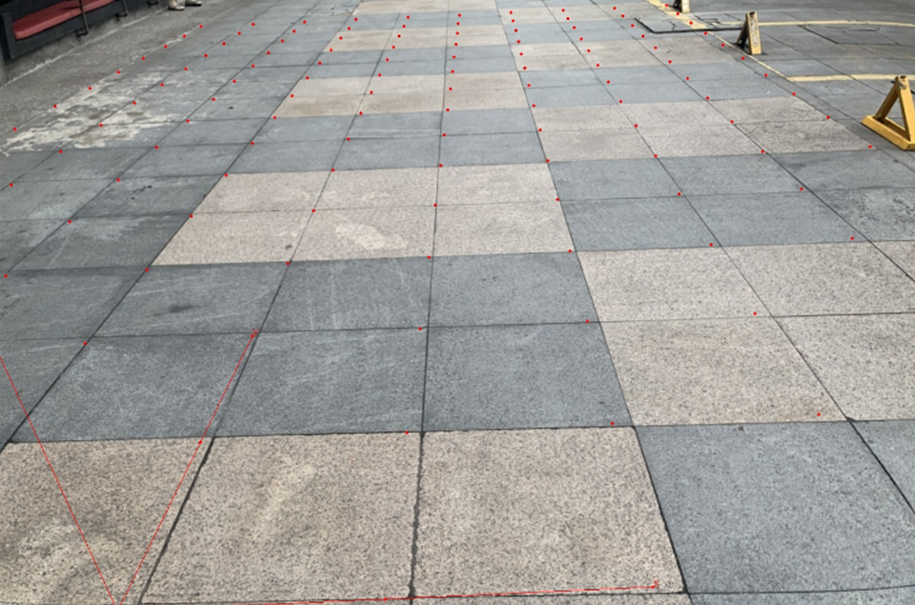
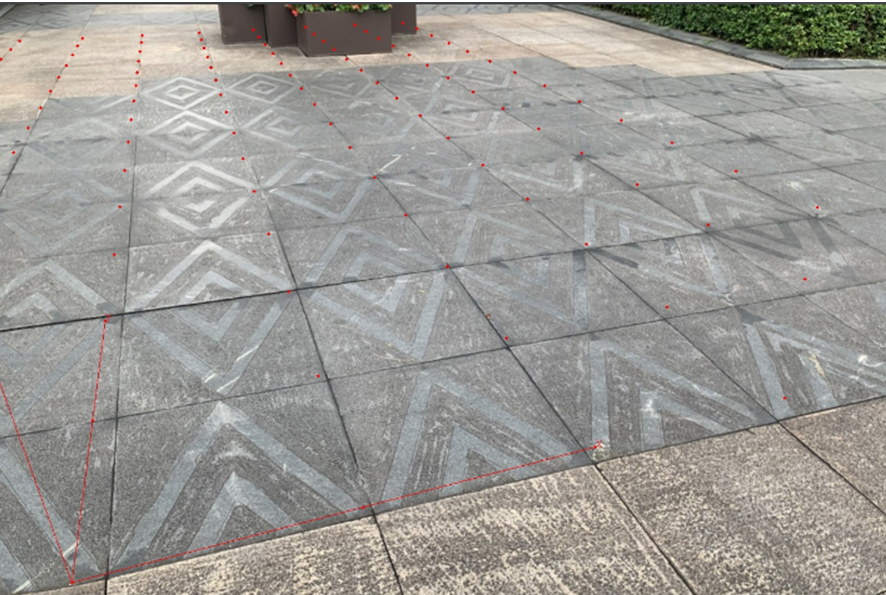


添加验证场景(2022-0929):
添加场景一:
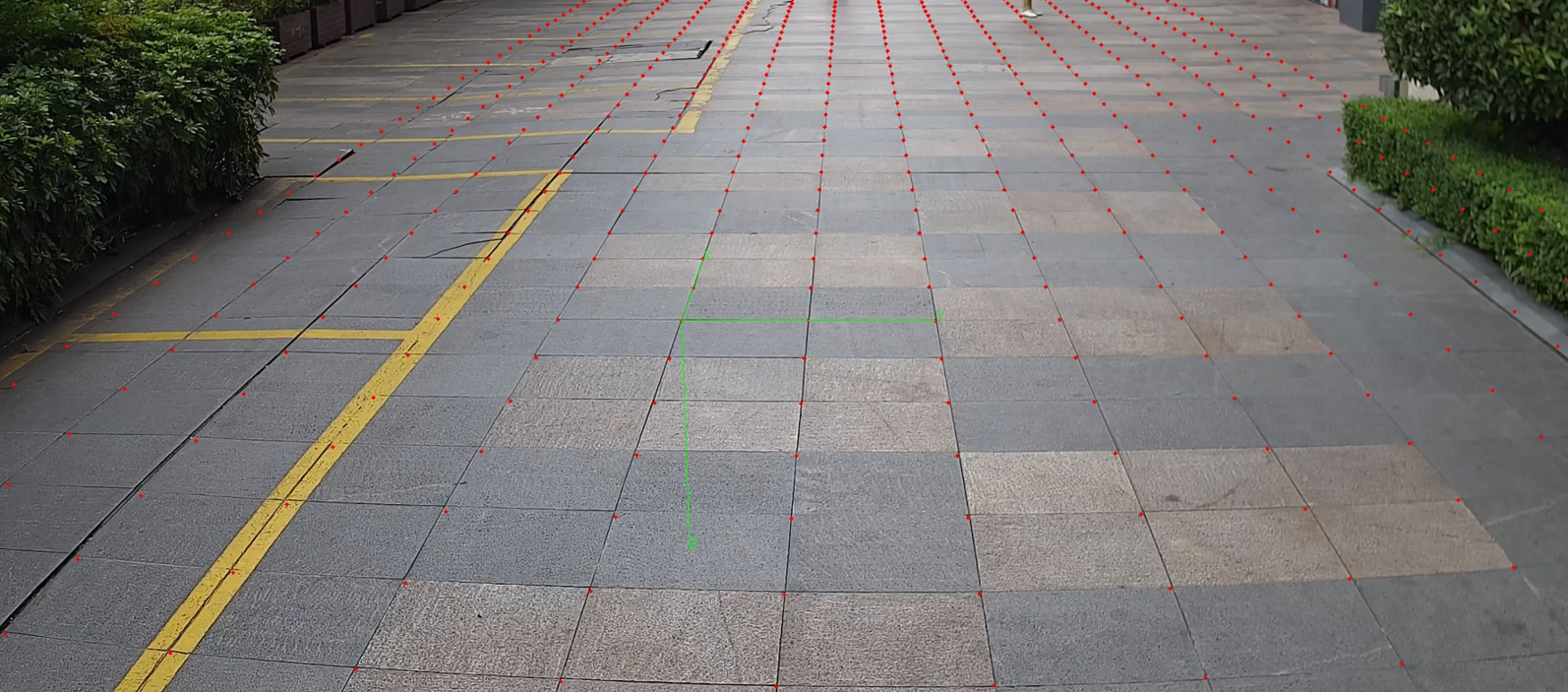

添加场景二:
介绍cv2.projectPoints函数,该函数可以将世界坐标系转为对应原始图像像素坐标系,无需上面那样矫正。
imgpts, jac = cv2.projectPoints(coord, rvecs, tvecs, mtx, dist)
参数格式如下图:
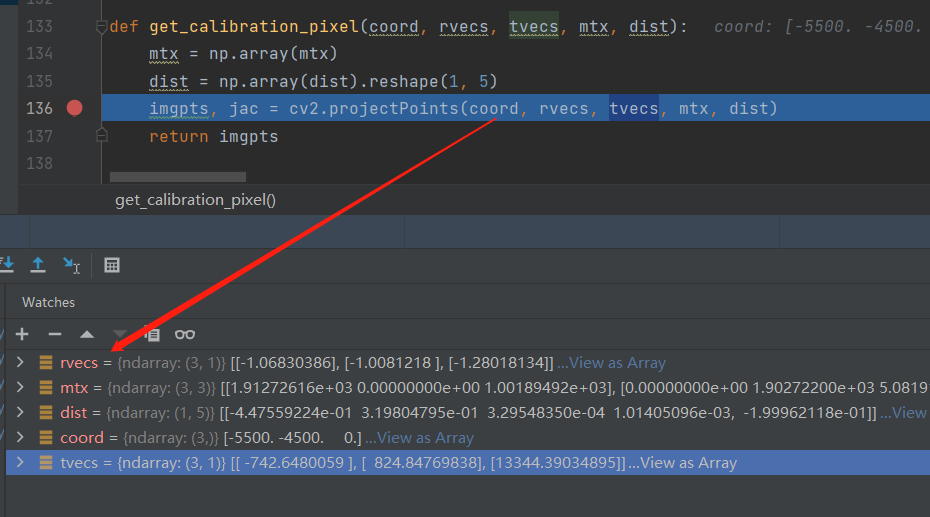
其中mtx与dist分别为相机标定求解的内参与畸变系数,rvecs与tvecs为旋转向量和平移向量,即为外参,返回imgpts坐标为
原始图像坐标(未矫正的坐标)。
我也将直接使用原始图像求解代码直接粘贴此处:

import numpy as np import os import cv2 import glob # *******************utils*********************# import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import random import shutil def draw_circle(img, coord): coord = np.array(coord).reshape(-1) try: cv2.circle(img, (int(coord[0]), int(coord[1])), 2, (0, 0, 255), -1) except: pass return img def build_dir(root): import os if not os.path.exists(root): os.makedirs(root) return root def draw_axis(img, O, OX, OY, OZ): color = (0, 255, 0) frontsize = 0.5 img = cv2.line(img, (int(O[0]), int(O[1])), (int(OX[0]), int(OX[1])), color, 1) cv2.putText(img, 'X', (int(OX[0]), int(OX[1])), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, frontsize, color, 1) img = cv2.line(img, (int(O[0]), int(O[1])), (int(OY[0]), int(OY[1])), color, 1) cv2.putText(img, 'Y', (int(OY[0]), int(OY[1])), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, frontsize, color, 1) img = cv2.line(img, (int(O[0]), int(O[1])), (int(OZ[0]), int(OZ[1])), color, 1) cv2.putText(img, 'Z', (int(OZ[0]), int(OZ[1])), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, frontsize, color, 1) return img def show_img(img): plt.imshow(img) plt.show() # *******************************通过内参联合求解外参*******************# def get_pixel(coord, mtx, R, T): mtx = np.array(mtx) R = np.array(R) T = np.array(T).reshape(3, 1) coord = np.array(coord).reshape(-1, 1) RT = np.hstack((R, T)) XYZ_camera = np.matmul(RT, coord) # XYZ_camera = XYZ_camera / XYZ_camera[-1, -1] x, y, z = np.matmul(mtx, XYZ_camera) x = x / z y = y / z # print('x={}\ty={}'.format(x[0], y[0])) return [x[0], y[0]] # ***********************利用opencv相机标定**************# # 相机标定,主要求内参和畸变系数 def calibration_camera(img_root, rand_count=6): board_h = 8 board_w = 11 objp = np.zeros((board_h * board_w, 3), np.float32) objp[:, :2] = np.mgrid[0:board_w, 0:board_h].T.reshape(-1, 2) # 将世界坐标系建在标定板上,所有点的Z坐标全部为0,所以只需要赋值x和y objp = 60 * objp # 打印棋盘格一格的边长为2.6cm obj_points = [] # 存储3D点 img_points = [] # 存储2D点 images = glob.glob(os.path.join(img_root, '*.jpg')) # 黑白棋盘的图片路径 random.shuffle(images) if rand_count > len(images): rand_count = len(images) for fname in images[:rand_count]: img = cv2.imread(fname) gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) size = gray.shape[::-1] ret, corners = cv2.findChessboardCorners(gray, (board_w, board_h), None) if ret: obj_points.append(objp) corners2 = cv2.cornerSubPix(gray, corners, (5, 5), (-1, -1), (cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER | cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS, 30, 0.001)) if [corners2]: img_points.append(corners2) else: img_points.append(corners) cv2.drawChessboardCorners(img, (board_w, board_h), corners, ret) # 记住,OpenCV的绘制函数一般无返回值 cv2.imshow("img", img) cv2.waitKey(10) ret, mtx, dist, rvecs, tvecs = cv2.calibrateCamera(obj_points, img_points, size, None, None) # v_rot_mat, _ = cv2.Rodrigues(np.array(v_rot).reshape(-1)) # print("旋转矩阵=", v_rot_mat) # print("内参=", mtx) # print("畸变系数=", dist) # print("旋转向量=", rvecs) # print("平移向量=", tvecs) # 反投影误差 total_error = 0 for i in range(len(obj_points)): imgpoints2, _ = cv2.projectPoints(obj_points[i], rvecs[i], tvecs[i], mtx, dist) error = cv2.norm(img_points[i], imgpoints2, cv2.NORM_L2) / len(imgpoints2) total_error += error # print("total error: ", total_error / len(obj_points)) return mtx, dist, total_error # 旋转向量和平移向量求解 def calibration_RT(points_3D, points_2D, cameraMatrix, distCoeffs): points_3D = np.array(points_3D) points_2D = np.array(points_2D) cameraMatrix = np.array(cameraMatrix).astype(np.float32) distCoeffs = np.array(distCoeffs).astype(np.float32) _, rvecs, tvecs, inliers = cv2.solvePnPRansac(points_3D.reshape(-1, 1, 3), points_2D.reshape(-1, 1, 2), cameraMatrix, distCoeffs ) R, _ = cv2.Rodrigues(rvecs) # print('R:\n', R) # print('rvecs:\n', rvecs) # print('tvecs:\n', tvecs) return R, rvecs, tvecs def get_calibration_pixel(coord, rvecs, tvecs, mtx, dist): mtx = np.array(mtx) dist = np.array(dist).reshape(1, 5) imgpts, jac = cv2.projectPoints(coord, rvecs, tvecs, mtx, dist) return imgpts # 消除畸变 def revise_img(img_root, mtx, dist): mtx = np.array(mtx) dist = np.array(dist).reshape(1, 5) img = cv2.imread(img_root) h, w = img.shape[:2] newcameramtx, roi = cv2.getOptimalNewCameraMatrix(mtx, dist, (w, h), 1, (w, h)) # undistort dst = cv2.undistort(img, mtx, dist, None, newcameramtx) # crop the image x, y, w, h = roi dst = dst[y:y + h, x:x + w] cv2.imwrite('./revise_img.jpg', dst) return dst # 自动寻找3d点与像素点对应坐标(只针对标定版) def find_point_3d2d(img_root, save=True): board_h = 8 board_w = 11 objp = np.zeros((board_h * board_w, 3), np.float32) objp[:, :2] = np.mgrid[0:board_w, 0:board_h].T.reshape(-1, 2) # 将世界坐标系建在标定板上,所有点的Z坐标全部为0,所以只需要赋值x和y points_3d = 60 * objp # 打印棋盘格一格的边长为2.6cm points_2d = None # 存储2D点 img = cv2.imread(img_root) img_rand = img.copy() gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) rand_p2, rand_p3 = None, None ret, corners = cv2.findChessboardCorners(gray, (board_w, board_h), None) print('ret=', ret) if ret: corners = cv2.cornerSubPix(gray, corners, (5, 5), (-1, -1), (cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER | cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS, 30, 0.001)) cv2.drawChessboardCorners(img, (board_w, board_h), corners, ret) # 记住,OpenCV的绘制函数一般无返回值 points_2d = corners.reshape(-1, 2) if save: file_write_obj = open('./save_points_3d2d.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') # 以写的方式打开文件,如果文件不存在,就会自动创建 for i, p2 in enumerate(points_2d): text = '3d:\t' + str(points_3d[i]) + '\t2d\t' + str(p2) + '\n' file_write_obj.writelines(text) k = 10 rand_int = random.sample(range(1, len(points_2d)), k) # print('rand_int=',rand_int) rand_int = [48, 55, 85, 22, 73, 39, 68, 31, 78, 71] rand_p2 = points_2d[rand_int] rand_p3 = points_3d[rand_int] file_write_obj.close() # 图像展示选择坐标点 for inds in rand_int: pp2 = points_2d[inds] img_rand = draw_circle(img_rand, pp2) cv2.imwrite('./calibration_point.jpg', img_rand) show_img(img) return points_3d, points_2d, rand_p3, rand_p2 def draw_board(img_root, mtx, R, T, dist=None): img = cv2.imread(img_root) mtx = np.array(mtx) dist = np.array(dist).reshape(1, 5) if dist is not None else None for i in range(10): for j in range(8): coord = [i * 60, j * 60, 0.0, 1] coord = np.array(coord) coord_pixel = get_pixel(coord, mtx, R, T) RMat = cv2.Rodrigues(R)[0] coord = [[i * 60, j * 60, 0.0]] # coord_pixel, _ = cv2.projectPoints(coord,RMat, T, mtx, dist) img = draw_circle(img, coord_pixel) # # 画坐标轴 L = 80 O = get_pixel([0, 0, 0, 1], mtx, R, T) OX = get_pixel([L, 0, 0, 1], mtx, R, T) OY = get_pixel([0, L, 0, 1], mtx, R, T) OZ = get_pixel([0, 0, L, 1], mtx, R, T) img = draw_axis(img, O, OX, OY, OZ) show_img(img) cv2.imwrite('./predict_result.jpg', img) def draw_space(img_root, coord, mtx, R, T): img = cv2.imread(img_root) for c in coord: c = np.array(c) coord_pixel = get_pixel(c, mtx, R, T) img = draw_circle(img, coord_pixel) # # 画坐标轴 L = 2000 O = get_pixel([0, 0, 0, 1], mtx, R, T) OX = get_pixel([L, 0, 0, 1], mtx, R, T) OY = get_pixel([0, L, 0, 1], mtx, R, T) OZ = get_pixel([0, 0, L, 1], mtx, R, T) img = draw_axis(img, O, OX, OY, OZ) show_img(img) cv2.imwrite('./predict_result.jpg', img) def draw_space_new(img_root, coord, mtx, rvecs, tvecs, dist): img = cv2.imread(img_root) for c in coord: c = np.array(c) c = np.array([c[0], c[1], c[2]], dtype=np.float32) coord_pixel = get_calibration_pixel(c, rvecs, tvecs, mtx, dist) coord_pixel = coord_pixel.reshape(1, 2) img = draw_circle(img, coord_pixel) # # 画坐标轴 L = 2000 coord_pixel = get_calibration_pixel(np.array([0, 0, 0.0]), rvecs, tvecs, mtx, dist) O = coord_pixel.reshape(-1) coord_pixel = get_calibration_pixel(np.array([L, 0, 0.0]), rvecs, tvecs, mtx, dist) OX = coord_pixel.reshape(-1) coord_pixel = get_calibration_pixel(np.array([0, L, 0.0]), rvecs, tvecs, mtx, dist) OY = coord_pixel.reshape(-1) coord_pixel = get_calibration_pixel(np.array([0, 0.0, L]), rvecs, tvecs, mtx, dist) OZ = coord_pixel.reshape(-1) img = draw_axis(img, O, OX, OY, OZ) show_img(img) cv2.imwrite('./predict_result.jpg', img) def get_coord(X_range=[-5,8], Y_range=[-3,15], coord_size=1): # M, N = 6, 15 # 行与列 # coord_size = 1 coord = [] for i in list(range(X_range[0], X_range[1], 1)): for j in list(range(Y_range[0], Y_range[1], 1)): coord.append([i * coord_size+500, j * coord_size+500, 0, 1]) return coord def get_best_pnp_index(p3, p2, mtx, dist, N_pnp=4, loop_n=200): ''' :param p3: 空间坐标 :param p2: 图像坐标 :param mtx: 内参 :param dist: 畸变系数 :param N_pnp: 决定多少个点求解pnp外参 :param loop_n: 迭代次数 :return: p3与p2对应中用于求解pnp的索引对应及最佳R与T ''' N_p3 = N_pnp # 设置选择计算pnp点数 index = np.arange(len(p3)) p3 = np.array(p3) p2 = np.array(p2) d_error_best = 10000000 index_best = None for _ in range(loop_n): random.shuffle(index) index_pnp = index[:N_p3] index_test = index[N_p3:] p3_new = p3[index_pnp, :] p2_new = p2[index_pnp, :] R, rvecs, tvecs = calibration_RT(p3_new, p2_new, mtx, dist) p3_test = p3[index_test, :] p2_test = p2[index_test, :] d_error = 0 print('\n\n') for i, p in enumerate(p3_test): coord = np.array([p[0], p[1], p[2]], dtype=np.float32) pre_xy = get_calibration_pixel(coord, rvecs, tvecs, mtx, dist) x, y = np.array(pre_xy).reshape(-1) d = np.sqrt(np.square(p2_test[i][0] - x) + np.square(p2_test[i][1] - y)) d_error = d_error + d print("坐标索引:{}\t原始坐标--预测坐标:{}--{}\terror:{}".format(index_test[i], (p2[i][0], p2[i][1]), (x, y), d)) d_error = d_error / (len(p3) - N_pnp) if d_error < d_error_best: d_error_best = d_error index_best = index[:N_p3] print("更新pnp最佳点index:", index_best) print("更新最佳距离误差:", d_error) print("pnp最佳点index:", index[:N_p3]) print("最佳距离误差:", d_error_best) # 求解最佳对应外参值 p3_new = p3[index_best, :] p2_new = p2[index_best, :] R, rvecs, tvecs = calibration_RT(p3_new, p2_new, mtx, dist) print("best rvecs=", rvecs) print("best tvecs=", tvecs) return index_best, rvecs, tvecs if __name__ == '__main__': calibration = False predict_space = True # 实际空间坐标标定 predict_space_onepoint = False # 测试空间中一点 predict_board = False # 决定测试标定版输出结果 resize_img = False # 将一个文件夹图片进行resize畸变矫正 if calibration: img_root = r'C:\Users\vrc\Desktop\RadarCamera\data\123_0927\3' mtx_best, dist_best, total_error_best = None, None, 100000 for i in range(60): mtx, dist, total_error = calibration_camera(img_root, rand_count=20) if total_error < total_error_best: total_error_best = total_error mtx_best = mtx dist_best = dist print("最小误差=", total_error_best) print("最优内参=", mtx_best) print("最优畸变系数=", dist_best) print("最小误差=", total_error_best) mtx = [[1.91272616e+03, 0.00000000e+00, 1.00189492e+03], [0.00000000e+00, 1.90272200e+03, 5.08191451e+02], [0.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00, 1.00000000e+00]] dist = [-4.47559224e-01, 3.19804795e-01, 3.29548350e-04, 1.01405096e-03, -1.99962118e-01] if predict_board: # 只针对标定板 img_root = r'C:\Users\vrc\Desktop\RadarCamera\data\123_0927\2\5.jpg' img = revise_img(img_root, mtx, dist) img_root = './revise_img.jpg' _, _, rand_p3, rand_p2 = find_point_3d2d(img_root) # dist = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0] R, rvecs, T = calibration_RT(rand_p3, rand_p2, mtx, dist) # 通过内外参求解像素坐标 # img_root = './revise_img.jpg' draw_board(img_root, mtx, R, T, dist=dist) if predict_space: img_root = r'C:\Users\vrc\Desktop\RadarCamera\data\data_0929\img_ori\13.jpg' # p3 = [[1000, 1000, 0], [-1000, 11000.0, 0], [-1000, 2000, 100], [1000, 2000, 0]] # p2 = [[861, 755.0], [320, 236], [178, 639], [787, 634]] p3 = [[2000, 2000, 0.0], [6000, 3000, 0], [3000, 5000, 0], [10000, 4000, 0]] p2 = [[1170, 555.0], [1252, 457], [1508, 525], [1303, 393]] R, rvecs, T = calibration_RT(p3, p2, mtx, dist) # coord = [[1, 3.0, 0, 1], [4, 5, 0, 1], [2, 6, 0, 1], [2, 2, 0, 1], [-1, 4, 0, 1]] coord = get_coord(X_range=[-6,40], Y_range=[-5,10], coord_size=1000) draw_space_new(img_root, coord, mtx, rvecs, T, dist) if predict_space_onepoint: p3 = [[1, 5.1, 0.77, 0], [2, 6.14, -0.26, 0], [3, 4.86, -0.9, 0], [4, 7.42, -1.28, 0], [5, 8.7, 0.51, 0], [6, 11.14, -1.41, 0], [7, 12.29, -0.26, 0], [8, 14.72, 1.79, 0], [9, 15.74, -7.4, 0], [10, 16.64, 1.79, 0], [12, 28.67, 3.33, 0], [13, 26.24, -2.05, 0], [15, 11.78, -2.05, 0], [16, 10.37, 3.2, 0], [17, 5.76, 2.56, 0], [18, 7.68, 0.51, 0]] p2 = [[1, 590, 359.0], [2, 1023, 309.0], [3, 1189, 352.0], [4, 1174, 274.0], [5, 778, 255.0], [6, 1143, 215], [7, 957, 204], [8, 670, 206], [9, 979, 186], [10, 710, 188], [12, 698, 147.0], [13, 1069, 141], [15, 1242, 211], [16, 1316, 259], [17, 156, 352], [18, 745, 283.0]] p3 = np.array(p3, dtype=np.float32)[:, 1:] p2 = np.array(p2, dtype=np.float32)[:, 1:] index=[0,3,8,12] p3_new,p2_new=p3[index],p2[index] R, rvecs, tvecs = calibration_RT(p3_new, p2_new, mtx, dist) # index, rvecs, tvecs = get_best_pnp_index(p3, p2, mtx, dist, N_pnp=6, loop_n=10000) # 计算剩余点坐标 # img_root=r'' for i, p in enumerate(p3): if i not in index: coord = np.array([p[0], p[1], p[2]], dtype=np.float32) pre_xy = get_calibration_pixel(coord, rvecs, tvecs, mtx, dist) x, y = np.array(pre_xy).reshape(-1) print("坐标索引:{}\t原始坐标--预测坐标:{}--{}".format(i, (p2[i][0], p2[i][1]), (x, y))) if resize_img: img_file = r'C:\Users\vrc\Desktop\RadarCamera\data\data_0928\img_ori' out_dir = build_dir(os.path.join(img_file, 'out_dir')) for img_name in os.listdir(img_file): if img_name[-3:] == 'jpg': img_root = os.path.join(img_file, img_name) img = revise_img(img_root, mtx, dist) cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(out_dir, img_name), img)
以上代码包含相机标定/原始图像外参求解
推荐标定误差分析博客:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_48934707/article/details/124295140
