1.错误类型
- 在程序中发生的错误的类型有三种。它们是: 语法错误:语法错误发生在语句没有适当构造、关键字被拼错或标点被忽略的时候。
- 逻辑错误:逻辑错误发生在程序编译和运行正常但没有产生预期的结果的时候。
- 运行时错误:运行时错误发生在程序试图完成一个操作,但它在运行时不被允许。
2.异常类
许多异常类都是直接或者间接的派生自System.Exception类
3.通用的异常类
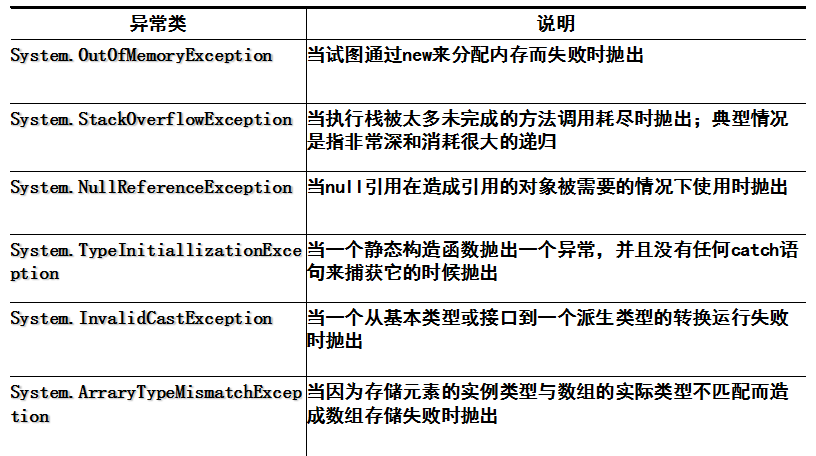
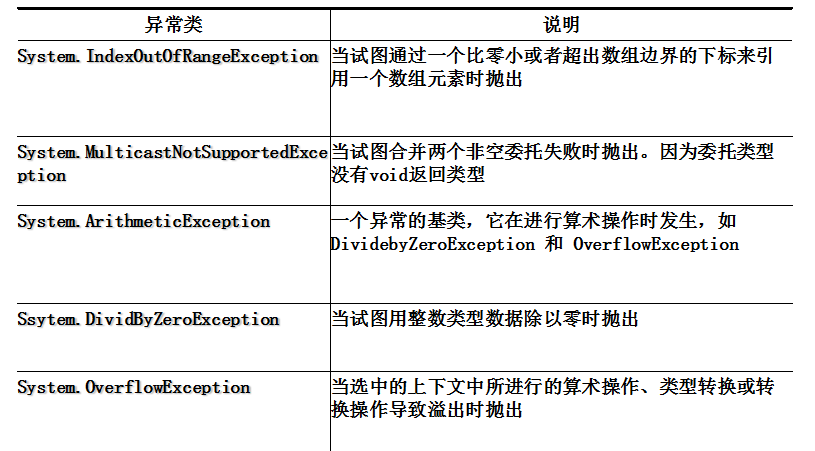
4.C#中异常处理是通过4个关键字来实现的:try catch finally throw
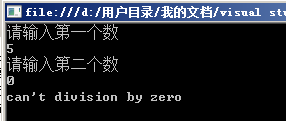
5.try catch:
namespace ConsoleApplication10
{
class Excep
{
public int division(int a, int b)
{
return a / b;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("请输入第一个数");
int a = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("请输入第二个数");
int b = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Excep excep = new Excep();
try
{
excep.division(a, b);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine("can't division by zero");
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
6.在try/catch后加入finally块,可以确保无论是否发生异常,finally块中的代码总能被执行
namespace ConsoleApplication10
{
class Excep
{
public int division(int a, int b)
{
return a / b;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("请输入第一个数");
int a = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("请输入第二个数");
int b = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Excep excep = new Excep();
try
{
Console.WriteLine("code1");
excep.division(a, b);
Console.WriteLine("code2");
}
catch (DivideByZeroException e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
}
finally
{
Console.WriteLine("finsh");
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}

注:捕捉类型的判断
7.课堂练习题一:
编写一个类ExceptionTest1,在main方法中使用try、catch、finally: 在try块中,编写数组访问越界的代码 在catch块中,捕获数组访问越界所产生的异常,并且打印异常信息 在finally块中,打印一条语句。
namespace ConsoleApplication10
{
class ExceptionTest1
{
public int division(int[] ss)
{
return ss[5];
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] number={0,1,2,3};
try
{
ExceptionTest1 ex = new ExceptionTest1();
ex.division(number);
}
catch (IndexOutOfRangeException e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
}
finally
{
Console.WriteLine("finsh");
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}

8.多重catch块
课堂练习题二:
David正在为一个项目工作,其中他正在计算一个整型数组中的总和。
David需要处理当他使用数组时发生的异常。如果David在执行程序的时候遇到了任何异常情况,程序需要显示一个异常消息
namespace ConsoleApplication10
{
class Exceptest1
{
int[] m;
int s;
public Exceptest1(int[] m,int s)
{
this.m = m;
this.s = s;
}
public int countsum()
{
for (int i = 0; i <=m.Length; i++) //应该是小于数组长度所以索引越界
{
s = s + m[i];
}
return s;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] num = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 7, 5 };
int su = 0;
try
{
Exceptest1 excep = new Exceptest1(num,su);
su=excep.countsum();
Console.WriteLine(su);
}
catch (IndexOutOfRangeException e)
{
Console.WriteLine("数组越界:"+e.Message);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine("其他错误"+e.Message);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}

9.用户自定义异常出现
在c#中Exception必须是所有异常的基类,用户定义异常类必须遵守要么异常类的层次或者一个标准
10.用户自定义异常类派生自ApplicationException类
为了用户自定义异常,需要:
- 生成自己的异常,可以使用throw语句来产生自己的异常
- 抛出对象:可以抛出一个对象,如果对象是直接或者间接派生自己System.Exception。可以使用在catch中的throw语句来抛出当前对象
11.用户自定义异常例题:
namespace ConsoleApplication10
{
class SavingsAccout
{
private double balance;
public SavingsAccout( double balance)
{
this.balance = balance;
}
public void Withdraw(double amount)
{
balance = balance - amount;
if (balance < 0)
{
throw new OverdramException("enenen",balance);
}
}
}
class OverdramException : ApplicationException
{
public double Balance;
public OverdramException(string message, double balance)
: base(message)
{
this.Balance = balance;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
SavingsAccout account = new SavingsAccout(2000);
account.Withdraw(3000);
}
catch (OverdramException e)
{
Console.Write(e.Message);
Console.WriteLine(e.Balance);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
