Residual Network
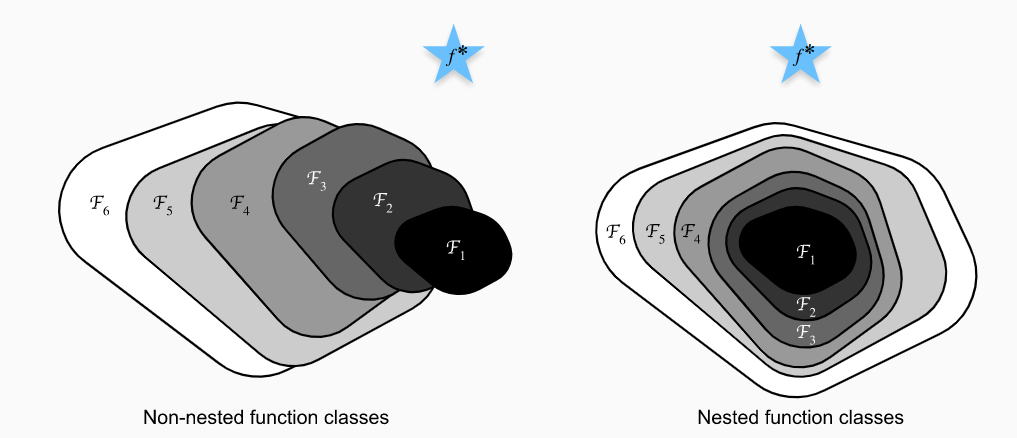
如左图所示,随着神经网络层数的加深,虽然网络代表的函数域在不断扩大($mathcal{F}_{1},ldots,mathcal{F}_{6}$),但可能整体上偏离了要寻找的最优函数$f^*$,这也是神经网络在加深到一定层数之后训练误差很难继续减小的原因。如果可以使函数域的扩大如右图所示满足$mathcal{F}_{1} subseteq ldots subseteq mathcal{F}_{6}$,就可以保证函数域不断逼近最优函数$f^*$,从而达到增加网络的复杂度来继续减小训练误差的目的。Residual Network的核心思想是新加入的网络层在使网络变得复杂的基础上还能够实现$f(x)=x$的自身映射,来确保$mathcal{F}_{1} subseteq mathcal{F}_{2} subseteq ldots$
典型的Residual Block如下图所示:
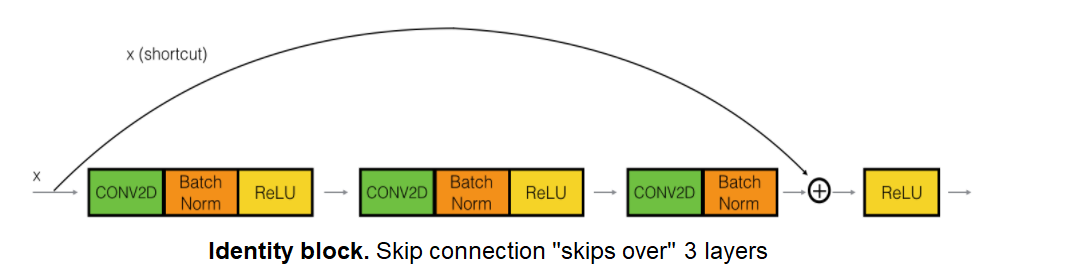

def identity_block(X, f, filters, stage, block): """ Implementation of the identity block Arguments: X -- input tensor of shape (m, n_H_prev, n_W_prev, n_C_prev) f -- integer, specifying the shape of the middle CONV's window for the main path filters -- python list of integers, defining the number of filters in the CONV layers of the main path stage -- integer, used to name the layers, depending on their position in the network block -- string/character, used to name the layers, depending on their position in the network Returns: X -- output of the identity block, tensor of shape (n_H, n_W, n_C) """ # defining name basis conv_name_base = 'res' + str(stage) + block + '_branch' bn_name_base = 'bn' + str(stage) + block + '_branch' # Retrieve Filters F1, F2, F3 = filters # Save the input value. You'll need this later to add back to the main path. X_shortcut = X # First component of main path X = Conv2D(filters = F1, kernel_size = (1, 1), strides = (1,1), padding = 'valid', name = conv_name_base + '2a', kernel_initializer = glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X) X = BatchNormalization(axis = 3, name = bn_name_base + '2a')(X) X = Activation('relu')(X) # Second component of main path X = Conv2D(filters = F2, kernel_size = (f, f), strides = (1,1), padding = 'same', name = conv_name_base + '2b', kernel_initializer = glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X) X = BatchNormalization(axis = 3, name = bn_name_base + '2b')(X) X = Activation('relu')(X) # Third component of main path X = Conv2D(filters = F3, kernel_size = (1, 1), strides = (1,1), padding = 'valid', name = conv_name_base + '2c', kernel_initializer = glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X) X = BatchNormalization(axis = 3, name = bn_name_base + '2c')(X) # Final step: Add shortcut value to main path, and pass it through a RELU activation X = Add()([X_shortcut, X]) X = Activation('relu')(X) return X
如果输入和输出的维数不匹配,可以采用如下图所示的结构调整:


def convolutional_block(X, f, filters, stage, block, s = 2): """ Implementation of the convolutional block Arguments: X -- input tensor of shape (m, n_H_prev, n_W_prev, n_C_prev) f -- integer, specifying the shape of the middle CONV's window for the main path filters -- python list of integers, defining the number of filters in the CONV layers of the main path stage -- integer, used to name the layers, depending on their position in the network block -- string/character, used to name the layers, depending on their position in the network s -- Integer, specifying the stride to be used Returns: X -- output of the convolutional block, tensor of shape (n_H, n_W, n_C) """ # defining name basis conv_name_base = 'res' + str(stage) + block + '_branch' bn_name_base = 'bn' + str(stage) + block + '_branch' # Retrieve Filters F1, F2, F3 = filters # Save the input value X_shortcut = X ##### MAIN PATH ##### # First component of main path X = Conv2D(F1, (1, 1), strides = (s,s), name = conv_name_base + '2a', kernel_initializer = glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X) X = BatchNormalization(axis = 3, name = bn_name_base + '2a')(X) X = Activation('relu')(X) # Second component of main path X = Conv2D(F2, (f, f), strides = (1,1), name = conv_name_base + '2b', padding='same', kernel_initializer = glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X) X = BatchNormalization(axis = 3, name = bn_name_base + '2b')(X) X = Activation('relu')(X) # Third component of main path X = Conv2D(F3, (1, 1), strides = (1,1), name = conv_name_base + '2c', kernel_initializer = glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X) X = BatchNormalization(axis = 3, name = bn_name_base + '2c')(X) ##### SHORTCUT PATH #### X_shortcut = Conv2D(F3, (1, 1), strides = (s,s), name = conv_name_base + '1', kernel_initializer = glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X_shortcut) X_shortcut = BatchNormalization(axis = 3, name = bn_name_base + '1')(X_shortcut) # Final step: Add shortcut value to main path, and pass it through a RELU activation X = Add()([X_shortcut, X]) X = Activation('relu')(X) return X
利用上述建立的两个block搭建一个ResNet50模型,模型架构如下图所示:
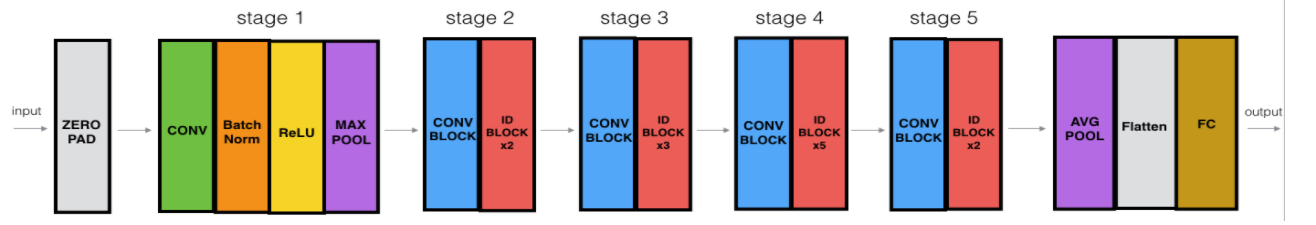

def ResNet50(input_shape = (64, 64, 3), classes = 6): """ Implementation of the popular ResNet50 the following architecture: CONV2D -> BATCHNORM -> RELU -> MAXPOOL -> CONVBLOCK -> IDBLOCK*2 -> CONVBLOCK -> IDBLOCK*3 -> CONVBLOCK -> IDBLOCK*5 -> CONVBLOCK -> IDBLOCK*2 -> AVGPOOL -> TOPLAYER Arguments: input_shape -- shape of the images of the dataset classes -- integer, number of classes Returns: model -- a Model() instance in Keras """ # Define the input as a tensor with shape input_shape X_input = Input(input_shape) # Zero-Padding X = ZeroPadding2D((3, 3))(X_input) # Stage 1 X = Conv2D(64, (7, 7), strides = (2, 2), name = 'conv1', kernel_initializer = glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X) X = BatchNormalization(axis = 3, name = 'bn_conv1')(X) X = Activation('relu')(X) X = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2, 2))(X) # Stage 2 X = convolutional_block(X, f = 3, filters = [64, 64, 256], stage = 2, block='a', s = 1) X = identity_block(X, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='b') X = identity_block(X, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='c') # Stage 3 X = convolutional_block(X, f = 3, filters = [128, 128, 512], stage = 3, block='a', s = 2) X = identity_block(X, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='b') X = identity_block(X, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='c') X = identity_block(X, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='d') # Stage 4 X = convolutional_block(X, f = 3, filters = [256, 256, 1024], stage = 4, block='a', s = 2) X = identity_block(X, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='b') X = identity_block(X, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='c') X = identity_block(X, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='d') X = identity_block(X, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='e') X = identity_block(X, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='f') # Stage 5 X = convolutional_block(X, f = 3, filters = [512, 512, 2048], stage = 5, block='a', s = 2) X = identity_block(X, 3, [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='b') X = identity_block(X, 3, [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='c') # AVGPOOL X = AveragePooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2), name='avg_pool')(X) # output layer X = Flatten()(X) X = Dense(classes, activation='softmax', name='fc' + str(classes), kernel_initializer = glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X) # Create model model = Model(inputs = X_input, outputs = X, name='ResNet50') return model
Inception Network
Inception Network的核心思想是在一个网络层上同时实现多种不同的操作,并通过1x1的卷积调整特征图的个数,减少参数数量。它的基本结构如下图所示:
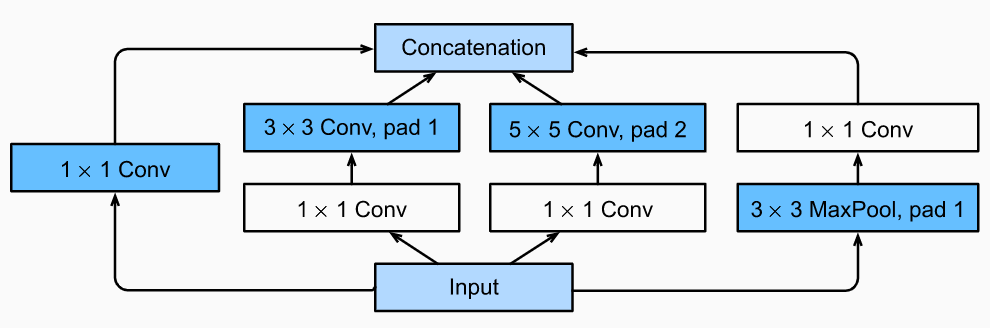

class Inception(tf.keras.Model): # `c1`--`c4` are the number of output channels for each path def __init__(self, c1, c2, c3, c4): super().__init__() # Path 1 is a single 1 x 1 convolutional layer self.p1_1 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(c1, 1, activation='relu') # Path 2 is a 1 x 1 convolutional layer followed by a 3 x 3 # convolutional layer self.p2_1 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(c2[0], 1, activation='relu') self.p2_2 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(c2[1], 3, padding='same', activation='relu') # Path 3 is a 1 x 1 convolutional layer followed by a 5 x 5 # convolutional layer self.p3_1 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(c3[0], 1, activation='relu') self.p3_2 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(c3[1], 5, padding='same', activation='relu') # Path 4 is a 3 x 3 maximum pooling layer followed by a 1 x 1 # convolutional layer self.p4_1 = tf.keras.layers.MaxPool2D(3, 1, padding='same') self.p4_2 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(c4, 1, activation='relu') def call(self, x): p1 = self.p1_1(x) p2 = self.p2_2(self.p2_1(x)) p3 = self.p3_2(self.p3_1(x)) p4 = self.p4_2(self.p4_1(x)) # Concatenate the outputs on the channel dimension return tf.keras.layers.Concatenate()([p1, p2, p3, p4])
利用上述的block搭建一个GoogLeNet (Inception V1)模型,模型架构如下图所示:


def b1(): return tf.keras.models.Sequential([ tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, 7, strides=2, padding='same', activation='relu'), tf.keras.layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=3, strides=2, padding='same')]) def b2(): return tf.keras.Sequential([ tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, 1, activation='relu'), tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(192, 3, padding='same', activation='relu'), tf.keras.layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=3, strides=2, padding='same')]) def b3(): return tf.keras.models.Sequential([ Inception(64, (96, 128), (16, 32), 32), Inception(128, (128, 192), (32, 96), 64), tf.keras.layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=3, strides=2, padding='same')]) def b4(): return tf.keras.Sequential([ Inception(192, (96, 208), (16, 48), 64), Inception(160, (112, 224), (24, 64), 64), Inception(128, (128, 256), (24, 64), 64), Inception(112, (144, 288), (32, 64), 64), Inception(256, (160, 320), (32, 128), 128), tf.keras.layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=3, strides=2, padding='same')]) def b5(): return tf.keras.Sequential([ Inception(256, (160, 320), (32, 128), 128), Inception(384, (192, 384), (48, 128), 128), tf.keras.layers.GlobalAvgPool2D(), tf.keras.layers.Flatten()]) def net(num_classes): return tf.keras.Sequential([b1(), b2(), b3(), b4(), b5(), tf.keras.layers.Dense(num_classes, activation='softmax')])
