1、AQS是什么
AQS同步器是Java并发编程的基础,从资源共享的角度分成独占和共享两种模式,像ReentrantLock、ThreadPoolExecutor、CountDownLatch等都是基于AQS来实现的,如图:

2、AQS同步队列的基本结构
AQS维护了一个头节点(head)和一个尾节点(tail)结构的双向链表,当一个线程获取锁失败时,会将该线程打包成一个Node节点,挂到同步队列尾节点
private transient volatile Node head;//同步队列头结点 private transient volatile Node tail;//同步队列尾结点 private volatile int state;//同步状态
2.1、同步队列内部结构
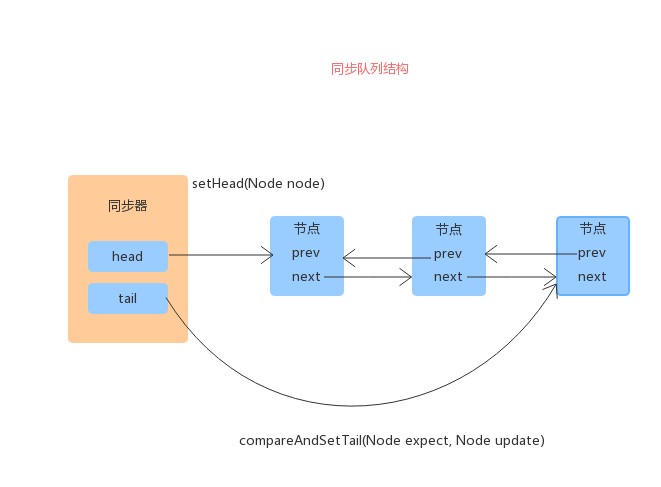
2.2、获取同步状态失败,将当前线程和节点模式打包成一个节点,放入同步队列尾部

2.3、前驱节点是头节点并且获取同步状态成功,设置当前节点为头节点,并将前驱节点指针清空,方便GC回收

2.4、Node节点类(双向链表挂在同步器中)

1 static final class Node {
2
3 static final Node SHARED = new Node();//共享模式
4
5 static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null;//独占模式
6
7 static final int CANCELLED = 1;//线程已取消
8
9 static final int SIGNAL = -1;//后继线程需要取消挂起
10
11 static final int CONDITION = -2;//线程正在等待条件
12
13 static final int PROPAGATE = -3;
14
15 volatile int waitStatus;
16
17 volatile Node prev;//前驱结点
18
19 volatile Node next;//后继结点
20
21 volatile Thread thread;//当前线程
22
23 Node nextWaiter;
24
25 final boolean isShared() {
26 return nextWaiter == SHARED;
27 }
28 //获取前驱节点
29 final Node predecessor() throws NullPointerException {
30 Node p = prev;
31 if (p == null)
32 throw new NullPointerException();
33 else
34 return p;
35 }
36
37 Node() {
38 }
39 //当前线程和节点模式
40 Node(Thread thread, Node mode) {
41 this.nextWaiter = mode;
42 this.thread = thread;
43 }
44
45 Node(Thread thread, int waitStatus) {
46 this.waitStatus = waitStatus;
47 this.thread = thread;
48 }
49 }
2.5、state同步状态(AQS重要的成员变量)
1 //同步状态 2 private volatile int state; 3 //获取同步状态 4 protected final int getState() { 5 return state; 6 } 7 //设置同步状态 8 protected final void setState(int newState) { 9 state = newState; 10 } 11 //CAS设置同步状态 12 protected final boolean compareAndSetState(int expect, int update) { 13 // See below for intrinsics setup to support this 14 return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, expect, update); 15 }
3、子类需重写的方法
AQS使用了模板方法设计模式,核心框架JDK已经写好,子类(自定义同步器)只需重写如下几个方法,即可实现不同的同步器:
1 //用于判断当前方法是否被线程独占,独占锁需重写 2 protected boolean isHeldExclusively() { 3 throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); 4 } 5 6 //独占式获取锁 7 protected boolean tryAcquire(int arg) { 8 throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); 9 } 10 11 //独占式释放锁 12 protected boolean tryRelease(int arg) { 13 throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); 14 } 15 16 //共享式获取锁 17 protected int tryAcquireShared(int arg) { 18 throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); 19 } 20 21 //共享式释放锁 22 protected int tryReleaseShared(int arg) { 23 throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); 24 }
4、独占模式分析
4.1、acquire独占锁获取(ReentrantLock的lock方法就是调用该方法)
1、tryAcquire(子类实现的方法,此时派上用场)
尝试获取同步状态,获取成功则直接使用
2、addWaiter
将当前线程打包成一个独占模式节点,放入同步队列的尾部
3、acquireQueued
进入等待状态,直到其他线程唤醒自己
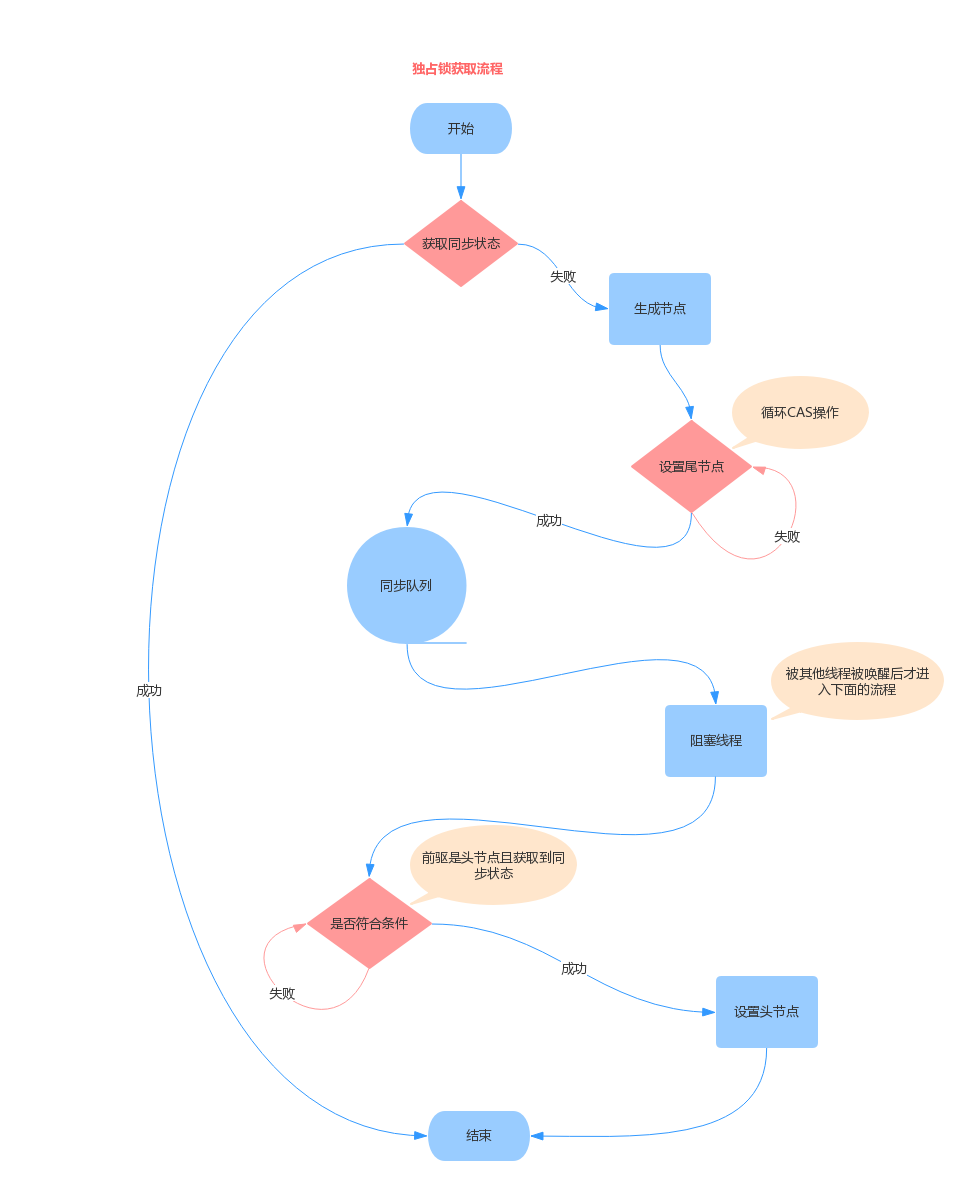

1 //获取独占锁入口方法 2 public final void acquire(int arg) { 3 if (!tryAcquire(arg) && 4 acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)) 5 selfInterrupt(); 6 } 7 //放入队列 8 private Node addWaiter(Node mode) { 9 Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode); 10 // 快速尝试将其放入尾部节点 11 Node pred = tail; 12 if (pred != null) { 13 node.prev = pred; 14 if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) { 15 pred.next = node; 16 return node; 17 } 18 } 19 enq(node);//循环CAS方式将节点放入队列尾部 20 return node; 21 } 22 //入队 23 private Node enq(final Node node) { 24 for (; ; ) {//循环CAS添加尾部节点 25 Node t = tail; 26 if (t == null) { //队列为空,初始化一个空节点 27 if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))//CAS防止产生多个队列 28 tail = head; 29 } else { 30 node.prev = t; 31 if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {//CAS设置尾节点 32 t.next = node; 33 return t; 34 } 35 } 36 } 37 } 38 //阻塞等待 39 final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) { 40 boolean failed = true; 41 try { 42 boolean interrupted = false;//是否被中断 43 for (; ; ) { 44 final Node p = node.predecessor();//获取前驱节点 45 if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {//前驱节点是头节点 且 自己获取到锁 46 setHead(node);//将当前节点设置为头节点 47 p.next = null; //便于GC回收以前的头节点 48 failed = false; 49 return interrupted; 50 } 51 if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&//设置前驱节点状态 52 parkAndCheckInterrupt())//阻塞线程 53 interrupted = true;//被中断一次就设置为true 54 } 55 } finally { 56 if (failed) 57 cancelAcquire(node); 58 } 59 } 60 //设置前驱节点 61 private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) { 62 int ws = pred.waitStatus;//前驱节点的状态 63 if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) 64 return true; 65 if (ws > 0) {//目的是为了剔除取消的节点 66 do { 67 node.prev = pred = pred.prev; 68 } while (pred.waitStatus > 0);//找到一个没有被取消的节点 69 pred.next = node; 70 } else { 71 compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);//将前驱节点设置为SIGNAL 72 } 73 return false; 74 } 75 //阻塞线程 76 private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() { 77 LockSupport.park(this);//阻塞线程,直到被唤醒(发生中断或被其他线程调用unpark) 78 return Thread.interrupted();//线程是否中断 79 }
4.2、release独占锁释放(ReentrantLock的unlock方法就是调用该方法)
1、tryRelease(子类实现的方法,自定义释放的逻辑)
尝试获取同步状态,成功则继续
2、unparkSuccessor
找到头节点,唤醒后继线程

1 public final boolean release(int arg) { 2 if (tryRelease(arg)) { 3 Node h = head;//找到头节点 4 if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0) 5 unparkSuccessor(h);//唤醒后继线程 6 return true; 7 } 8 return false; 9 } 10 //唤醒后继线程 11 private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) { 12 /* 13 * If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try 14 * to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this 15 * fails or if status is changed by waiting thread. 16 */ 17 int ws = node.waitStatus; 18 if (ws < 0) 19 compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0); 20 21 Node s = node.next;//获取后继节点 22 if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) { 23 s = null; 24 for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev) 25 if (t.waitStatus <= 0) 26 s = t; 27 } 28 if (s != null) 29 LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);//唤醒后继线程 30 }
5、共享模式分析
5.1、acquireSharedInterruptibly共享锁获取(Semaphore的acquire方法就是调用该方法)
1、线程是否中断,是则抛出异常
2、tryAcquireShared(子类实现的方法)
尝试获取资源,成功直接返回,失败进入下面流程
3、doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(和独占锁类似)
将当前线程打包成共享节点,放入同步队列并阻塞,直到被唤醒并成功获取到资源才返回

1 public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg) 2 throws InterruptedException { 3 if (Thread.interrupted()) 4 throw new InterruptedException(); 5 if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)//子类实现的方法,一般用来判断是否还有资源 6 doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);//放入同步队列等待 7 } 8 9 private void doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg) 10 throws InterruptedException { 11 final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);//将当前线程打包成一个共享节点,放入同步队列尾部 12 boolean failed = true; 13 try { 14 for (;;) {//自旋 15 final Node p = node.predecessor();//获取前驱节点 16 if (p == head) {//前驱节点是头节点 17 int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);//尝试获取资源 18 if (r >= 0) {//大于0代表有资源可用 19 setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);//设置自己为head,还有剩余资源则唤醒后继线程 20 p.next = null; // help GC 21 failed = false; 22 return; 23 } 24 } 25 if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&//设置前驱节点状态 26 parkAndCheckInterrupt())//阻塞线程,等待其他线程唤醒或线程被中断 27 throw new InterruptedException(); 28 } 29 } finally { 30 if (failed) 31 cancelAcquire(node); 32 } 33 }
5.2、releaseShared共享锁释放(Semaphore的release方法就是调用该方法)

1 public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) { 2 if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) { 3 doReleaseShared(); 4 return true; 5 } 6 return false; 7 } 8 9 private void doReleaseShared() { 10 for (;;) { 11 Node h = head; 12 if (h != null && h != tail) { 13 int ws = h.waitStatus; 14 if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) { 15 if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0)) 16 continue; // loop to recheck cases 17 unparkSuccessor(h);//唤醒后继线程 18 } 19 else if (ws == 0 && 20 !compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE)) 21 continue; // loop on failed CAS 22 } 23 if (h == head) // loop if head changed 24 break; 25 } 26 }
待续...
