Zookeeper 概念
•Zookeeper 是 Apache Hadoop 项目下的一个子项目,是一个树形目录服务。
•Zookeeper 翻译过来就是 动物园管理员,他是用来管 Hadoop(大象)、Hive(蜜蜂)、Pig(小猪)的管理员。
-
Hadoop: 存储海量数据和分析海量数据的工具
-
Hive: 基于Hadoop的一个数据仓库工具,用来进行数据提取、转化、加载
-
Pig: 基于Hadoop的大规模数据分析平台
•Zookeeper 是一个开源的,分布式应用程序的协调服务。
cd /opt/zooKeeper/apache-zooKeeper-3.5.6-bin/bin/
#启动
./zkServer.sh start
查看ZooKeeper状态**
./zkServer.sh status
关闭Linux防火墙
systemctl stop firewalld
#禁止开机启动
systemctl disable firewalld
ZooKeeper 命令操作
操作数据模型
• 节点可以拥有子节点,同时也允许少量(1MB)数据存储在该节点之下。
•节点可以分为四大类:
-
持久节点(PERSISTENT):创建后一直存在,直到主动删除此节点
-
临时节点(EPHEMERAL):生命周期依赖于客户端会话,对应客户端会话失效后节点自动清除 -e
-
持久顺序节点(PERSISTENT_SEQUENTIAL) :持久顺序节点,创建后一直存在,直到主动删除此节点 -s
-
临时顺序节点(EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL) :临时节点在客户端会话失效后节点自动清 -es
操作服务端命令
•启动 ZooKeeper 服务: ./zkServer.sh start
•查看 ZooKeeper 服务状态: ./zkServer.sh status
•停止 ZooKeeper 服务: ./zkServer.sh stop
•重启 ZooKeeper 服务: ./zkServer.sh restart
•连接ZooKeeper服务端
#Windows双击打开zkCli.cmd
#Mac&Linux
./zkCli.sh –server 127.0.0.1:2181
•查看命令帮助
help
•显示指定目录下节点
#查看根节点
ls /
#[dubbo, zk, zookeeper]
#查看指定节点
ls /zookeeper
•创建节点
create /节点path value
•获取节点值
get /节点path
•设置节点值
set /节点path value
•创建子节点
create /节点path/子节点
•删除单个节点
delete /节点path
•删除带有子节点的节点
deleteall /节点path
创建临时节点和顺序节点
•创建临时节点-e:生命周期依赖于客户端会话,对应客户端会话失效后节点自动清除 -e
create -e /节点path value
•退出
quit #再次使用zk-cli连接服务端,验证刚才创建的临时节点已经没了 ls /节点path
•创建顺序节点-s,zk会自动在节点路径后边添加序号
create -s /节点path value ls /zk #[20000000001, 30000000002, my0000000003, your0000000004]
•查询节点详细信息
ls –s /节点path
•czxid:节点被创建的事务ID
•ctime: 创建时间
•mZxid: 最后一次被更新的事务ID
•mtime: 修改时间
•pzxid:子节点列表最后一次被更新的事务ID
•cversion:子节点的版本号
•dataversion:数据版本号
•aclversion:权限版本号
•ephemeralOwner:用于临时节点,代表临时节点的事务ID,如果为持久节点则为0
•dataLength:节点存储的数据的长度
•numChildren:当前节点的子节点个数
ZooKeeper JavaAPI 操作
Curator介绍
•Curator 是 Apache ZooKeeper 的Java客户端库,目标是简化 ZooKeeper 客户端的使用。
•Curator 最初是 Netfix 研发的,后来捐献了 Apache 基金会,目前是 Apache 的顶级项目。
SpringCloud中很多组件都是Netfix提供的
创建项目curator-zk
-
pom.xml,添加Curator和日志坐标
<dependencies> <!--单元测试--> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.10</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <!--curator--> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId> <artifactId>curator-framework</artifactId> <version>4.0.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId> <artifactId>curator-recipes</artifactId> <version>4.0.0</version> </dependency> <!--日志--> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> <artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId> <version>1.7.21</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> <artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId> <version>1.7.21</version> </dependency> </dependencies> -
日志配置文件:log4j.properties
log4j.rootLogger=off,stdout log4j.appender.stdout = org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender log4j.appender.stdout.Target = System.out log4j.appender.stdout.layout = org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern = [%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH/:mm/:ss}]%-5p %c(line/:%L) %x-%m%n
@Before:初始化方法(对于每一个测试方法都要执行一次)
在执行初始方法之后和释放资源之前写代码
private CuratorFramework client;
@Before
public void testConnect() {
//重试策略
RetryPolicy retryPolicy = new ExponentialBackoffRetry(3000, 10);
//常用第二种方式,更直观
client = CuratorFrameworkFactory.builder()
.connectString("127.0.0.1:2181")
.sessionTimeoutMs(60 * 1000)
.connectionTimeoutMs(15 * 1000)
.retryPolicy(retryPolicy)
.namespace("itheima")
.build();
//开启连接
client.start();
}
@After:释放资源(对于每一个测试方法运行完后都要执行一次)
@After
public void close() {
if (client != null) {
client.close();
}
}
创建节点
@Test
public void testCreate() throws Exception {
//1. 基本创建 :create().forPath("")
//如果创建节点,没有指定数据,则默认将当前客户端的ip作为数据存储
String path = client.create().forPath("/app1"); //create /itheima/app1
System.out.println(path);
}
@Test
public void testCreate2() throws Exception {
//2. 创建节点 带有数据:create().forPath("",data)
//节点默认类型:持久化
String path = client.create().forPath("/app2", "hehe".getBytes());
System.out.println(path);
}
@Test
public void testCreate3() throws Exception {
//3. 设置节点的类型:create().withMode().forPath("",data)
//创建临时节点
String path = client.create().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL).forPath("/app3");
System.out.println(path);
}
@Test
public void testCreate4() throws Exception {
//创建多级节点 /app1/p1 :create().creatingParentsIfNeeded().forPath("",data)
//creatingParentsIfNeeded():如果父节点不存在,则创建父节点
String path = client.create().creatingParentsIfNeeded().forPath("/app4/p1");
System.out.println(path);
}
查询节点
/**
* 查询节点:
* 1. 查询数据:get: getData().forPath()
* 2. 查询子节点: ls: getChildren().forPath()
* 3. 查询节点状态信息:ls -s:getData().storingStatIn(状态对象).forPath()
*/
@Test
public void testGet1() throws Exception {
//1. 查询数据:get
byte[] data = client.getData().forPath("/app1");
System.out.println(new String(data));
}
@Test
public void testGet2() throws Exception {
// 2. 查询子节点: ls
List<String> path = client.getChildren().forPath("/");
System.out.println(path);
}
@Test
public void testGet3() throws Exception {
Stat status = new Stat();
System.out.println(status);
//3. 查询节点状态信息:ls -s
// store status in ...
client.getData().storingStatIn(status).forPath("/app1");
System.out.println(status);
}
修改节点
/**
* 修改数据
* 1. 基本修改数据:setData().forPath()
* 2. 根据版本修改: setData().withVersion().forPath()
* * version 是通过查询出来的。目的就是为了让其他客户端或者线程不干扰我。
*
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testSet() throws Exception {
client.setData().forPath("/app1", "itcast".getBytes());
}
@Test
public void testSetForVersion() throws Exception {
Stat status = new Stat();
//3. 查询节点状态信息:ls -s
client.getData().storingStatIn(status).forPath("/app1");
int version = status.getVersion();//查询出来的 3
System.out.println(version);
client.setData().withVersion(version).forPath("/app1", "hehe".getBytes());
}
删除节点
/**
* 删除节点: delete deleteall
* 1. 删除单个节点:delete().forPath("/app1");
* 2. 删除带有子节点的节点:delete().deletingChildrenIfNeeded().forPath("/app1");
* 3. 必须成功的删除:为了防止网络抖动。本质就是重试。 client.delete().guaranteed().forPath("/app2");
* 4. 回调:inBackground
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testDelete() throws Exception {
// 1. 删除单个节点
client.delete().forPath("/app1");
}
@Test
public void testDelete2() throws Exception {
//2. 删除带有子节点的节点
client.delete().deletingChildrenIfNeeded().forPath("/app4");
}
@Test
public void testDelete3() throws Exception {
//3. 必须成功的删除, 底层是自动重试
client.delete().guaranteed().forPath("/app2");
}
@Test
public void testDelete4() throws Exception {
//4. 回调
client.delete().guaranteed().inBackground(new BackgroundCallback(){
@Override
public void processResult(CuratorFramework client, CuratorEvent event) throws Exception {
System.out.println("我被删除了~");
System.out.println(event);
}
}).forPath("/app1");
}
Watch监听概述
NodeCache
只监听某一个特定的节点,子节点的变化并不能被监听
/**
* 演示 NodeCache:给指定一个节点注册监听器
*/
@Test
public void testNodeCache() throws Exception {
//1. 创建NodeCache对象
final NodeCache nodeCache = new NodeCache(client,"/app1");
//2. 注册监听
nodeCache.getListenable().addListener(new NodeCacheListener() {
@Override
public void nodeChanged() throws Exception {
System.out.println("节点变化了~");
//获取修改节点后的数据
byte[] data = nodeCache.getCurrentData().getData();
System.out.println(new String(data));
}
});
//3. 开启监听.如果设置为true,则开启监听是,加载缓冲数据
nodeCache.start(true);
while (true){
}
}
PathChildrenCache
监控一个ZNode的子节点,但不能监听当前节点的变化
@Test
public void testPathChildrenCache() throws Exception {
//1.创建监听对象
PathChildrenCache pathChildrenCache = new PathChildrenCache(client,"/app2",true);
//2. 绑定监听器
pathChildrenCache.getListenable().addListener(new PathChildrenCacheListener() { @Override
public void childEvent(CuratorFramework client, PathChildrenCacheEvent event) throws Exception {
System.out.println("子节点变化了~");
System.out.println(event);
//监听子节点的数据变更,并且拿到变更后的数据
//1.获取类型
PathChildrenCacheEvent.Type type = event.getType();
//2.判断类型是否是update
if(type.equals(PathChildrenCacheEvent.Type.CHILD_UPDATED)){
System.out.println("数据变了!!!");
byte[] data = event.getData().getData();
System.out.println(new String(data));
}
}
});
//3. 开启
pathChildrenCache.start();
while (true){
}
}
TreeCache
可以监控整个树上的所有节点,类似于PathChildrenCache和NodeCache的组合
/**
* 演示 TreeCache:监听某个节点自己和所有子节点们
*/
@Test
public void testTreeCache() throws Exception {
//1. 创建监听器
TreeCache treeCache = new TreeCache(client,"/app2");
//2. 注册监听
treeCache.getListenable().addListener(new TreeCacheListener() {
@Override
public void childEvent(CuratorFramework client, TreeCacheEvent event) throws Exception {
System.out.println("节点变化了");
System.out.println(event);
}
});
//3. 开启
treeCache.start();
while (true){
}
}
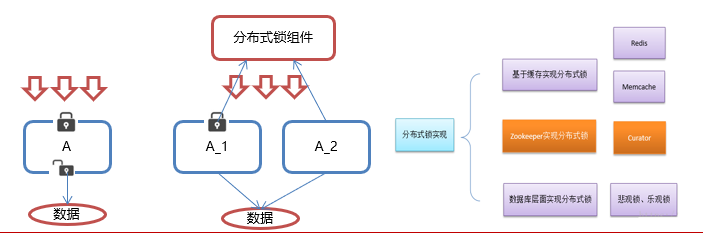
分布式锁-概念
•在我们进行单机应用开发,涉及并发同步的时候,我们往往采用synchronized(同步)或者Lock的方式来解决多线程间的代码同步问题,这时多线程的运行都是在同一个JVM之下,没有任何问题。
•但当我们的应用是分布式集群工作的情况下,属于多JVM下的工作环境,跨JVM之间已经无法通过多线程的锁解决同步问题。
•那么就需要一种更加高级的锁机制,来处理这种跨机器的进程之间的数据同步问题——这就是分布式锁。
分布式锁原理(理解)
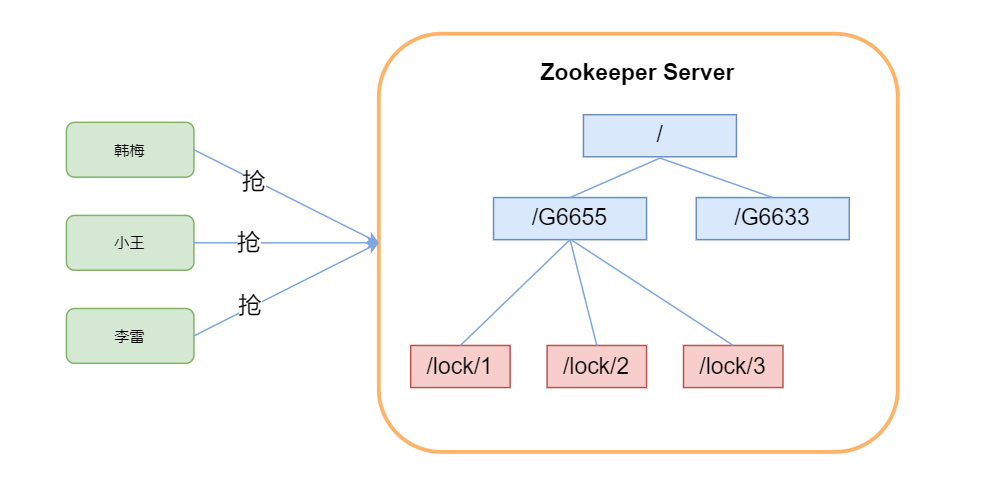
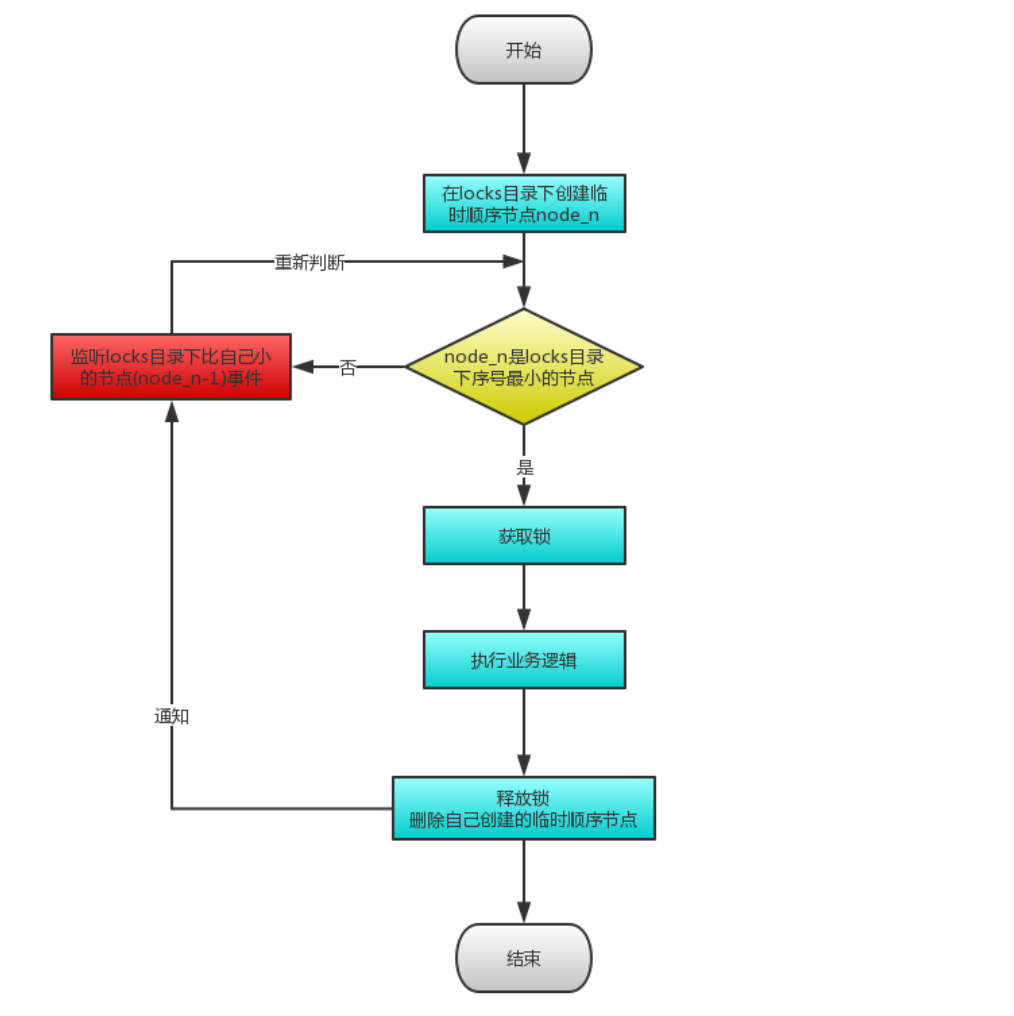
核心思想:当客户端要获取锁,则创建节点,使用完锁,则删除该节点。
-
客户端获取锁时,在lock节点下创建临时顺序节点。-es
-
然后获取lock下面的所有子节点,客户端获取到所有的子节点之后,如果发现自己创建的子节点序号最小,那么就认为该客户端获取到了锁。使用完锁后,将该节点删除。
-
如果发现自己创建的节点并非lock所有子节点中最小的,说明自己还没有获取到锁,此时客户端需要找到比自己小的那个节点,同时对其注册事件监听器,监听删除事件。
-
如果发现比自己小的那个节点被删除,则客户端的Watcher会收到相应通知,此时再次判断自己创建的节点是否是lock子节点中序号最小的;如果是则获取到了锁,如果不是则重复以上步骤继续获取到比自己小的一个节点并注册监听。
总结:
如果有个一个资源被多个人给竞争,此时多个人会排队,第一个拿到锁的人会执行,然后释放锁;后面的每个人都会去监听(watch)排在自己前面的那个人创建的节点;一旦某个人释放了锁,排在自己后面的人就会被 ZooKeeper 给通知,一旦被通知了之后,相当于自己就获取到了锁,就可以执行代码了。
具体执行过程如下:
分布式锁-模拟12306售票
-
在Curator中有五种锁方案:
-
InterProcessSemaphoreMutex:分布式排它锁(非可重入锁)
-
InterProcessMutex:分布式可重入排它锁
-
InterProcessReadWriteLock:分布式读写锁
-
InterProcessMultiLock:将多个锁作为单个实体管理的容器
-
InterProcessSemaphoreV2:共享信号量
-
-
使用分布式可重入排它锁-InterProcessMutex模拟12306售票过程:
1,在构造方法中创建连接,并且初始化锁
public Ticket12306() {
//重试策略
RetryPolicy retryPolicy = new ExponentialBackoffRetry(3000, 10);
//2.第二种方式
//CuratorFrameworkFactory.builder();
CuratorFramework client = CuratorFrameworkFactory.builder()
.connectString("localhost:2181")
.sessionTimeoutMs(60 * 1000)
.connectionTimeoutMs(15 * 1000)
.retryPolicy(retryPolicy)
.build();
//开启连接
client.start();
lock = new InterProcessMutex(client,
"/lock" + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
2,创建线程进行加锁设置
public class Ticket12306 implements Runnable{
private int tickets = 10;//数据库的票数
private InterProcessMutex lock ;
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
//获取锁
try {
lock.acquire(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if(tickets > 0){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+":"+tickets);
Thread.sleep(100);
tickets--;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//释放锁
try {
lock.release();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
3,运行多个线程进行测试
public class LockTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ticket12306 ticket12306 = new Ticket12306();
//创建客户端
Thread t1 = new Thread(ticket12306,"携程");
Thread t2 = new Thread(ticket12306,"飞猪");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}