一、说在前面
虽然之前写过很多的文件写入读出的程序,但是每次都得现成的上网搜索语法,记忆不够深刻,另外也没有系统的总结过java对文件的操作。
二、IO流
简单易学的简单方法:
使用PrintWriter写数据、使用try-with-resources自动关闭资源、使用Scanner读数据。
(1)写数据
java.io.PrintWriter 类可用来创建一个文件并向文本文件写入数据。首先创建一个 PrintWriter 对象,如下所示:
PrintWriter output = new PrintWriter(filename); // 若不存在则创建一个新文件
然后,可以调用 PrintWriter 对象上的 print, println, printf 方法向文件写入数据。下面展示一个小的测试案例:
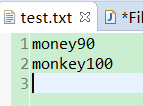
public class FileBuilt { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { File file = new File("test.txt"); if (file.exists()) { // 检查scores.txt是否存在 System.out.println("文件已经存在"); System.exit(1); // 如果存在则退出程序 } // 如果不存在则创建一个新文件 try (PrintWriter output = new PrintWriter(file);) { output.print("money"); output.println(90); output.print("monkey"); output.println(100); // 若没有try-with-resources结构则必须使用 close() 关闭文件,否则数据就不能正常地保存在文件中 // output.close(); } } }
输出结果:
(2)使用try-with-resource把对文件的操作包裹起来,避免因为忘记关闭IO流而引起的写入失败。
(3)使用Scanner读数据
Scanner经常用于从键盘的读取写入数据,读取时需要为System.in创建一个Scanner
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
同样地,想使用Scanner从文件中读取,也需要为文件创建一个Scanner,如下所示:
Scanner input = new Scanner(new File(filename));
下面展示一个使用Scanner读取文件的小案例,文件使用的就是上文使用PrintWriter创建的文件:
public class FileRead { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { File file = new File("test.txt"); Scanner input = new Scanner(file); while (input.hasNext()) { String line = input.next(); System.out.println(line); }
// 没必要关闭输入文件,但这样做是一种释放资源的好方法
input.close()
}
}
输出结果: