1、移除重复节点
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicate-node-lcci/
编写代码,移除未排序链表中的重复节点。保留最开始出现的节点。
示例1:
输入:[1, 2, 3, 3, 2, 1]
输出:[1, 2, 3]
示例2:
输入:[1, 1, 1, 1, 2]
输出:[1, 2]
提示:
链表长度在[0, 20000]范围内。
链表元素在[0, 20000]范围内。
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode removeDuplicateNodes(ListNode head) { if(head == null){ return null; } Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>(); ListNode cur = head; set.add(cur.val); while (cur.next != null){ if(set.add(cur.next.val)){ cur = cur.next; }else{ cur.next = cur.next.next; } } return head; } }
解析:
哈希表法:对给定的链表进行一次遍历,并用一个哈希集合(HashSet)来存储所有出现过的节点。在哈希集合中存储链表元素的值,方便直接使用等号进行比较。
2、回文链表
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/palindrome-linked-list-lcci/
编写一个函数,检查输入的链表是否是回文的。
示例 1:
输入: 1->2
输出: false
示例 2:
输入: 1->2->2->1
输出: true
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ class Solution { public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); ListNode cur = head; while(cur != null){ list.add(cur.val); cur = cur.next; } int front = 0; int backend = list.size()-1; while(front<backend){ if(!list.get(front).equals(list.get(backend))){ return false; } front++; backend--; } return true; } }
解析:
一共为两个步骤:
1、复制链表值到数组列表中。
2、使用双指针法判断是否为回文。
第一步,我们需要遍历链表将值复制到数组列表中。我们用 currentNode 指向当前节点。每次迭代向数组添加 currentNode.val,并更新 currentNode = currentNode.next,当 currentNode = null 时停止循环。
最好使用双指针法来检查是否为回文。我们在起点放置一个指针,在结尾放置一个指针,每一次迭代判断两个指针指向的元素是否相同,若不同,返回 false;相同则将两个指针向内移动,并继续判断,直到两个指针相遇。
3、链表相交
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists-lcci/
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null 。
图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交:
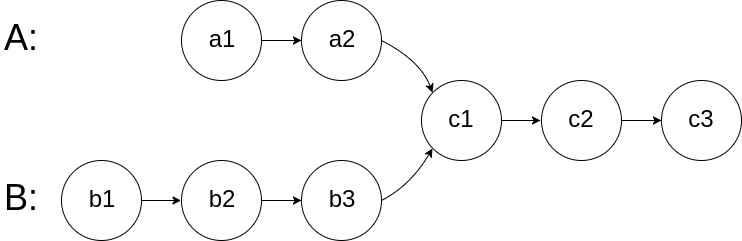
题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
注意,函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
示例 1:
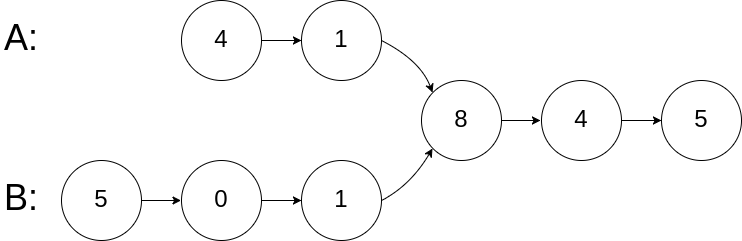
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Intersected at '8'
解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
示例 2:
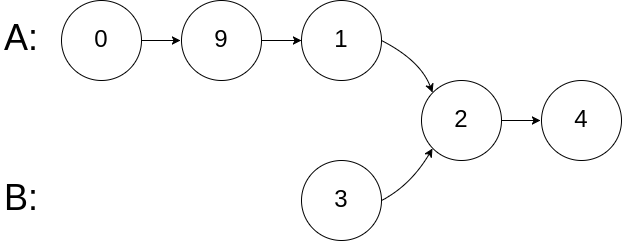
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
输出:Intersected at '2'
解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
示例 3:
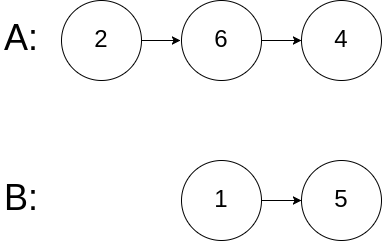
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
输出:null
解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。
由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null 。
提示:
listA 中节点数目为 m
listB 中节点数目为 n
0 <= m, n <= 3 * 104
1 <= Node.val <= 105
0 <= skipA <= m
0 <= skipB <= n
如果 listA 和 listB 没有交点,intersectVal 为 0
如果 listA 和 listB 有交点,intersectVal == listA[skipA + 1] == listB[skipB + 1]
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { * val = x; * next = null; * } * } */ public class Solution { public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { int aLength = 0; int bLength = 0; ListNode tmpA = headA; ListNode tmpB = headB; while(tmpA != null){ tmpA = tmpA.next; aLength++; } while(tmpB != null){ tmpB = tmpB.next; bLength++; } int grep = Math.abs(aLength - bLength);
// 这里可以交换两个链表,让tmpA始终是较长的那个; tmpA = aLength > bLength ? headA : headB; tmpB = aLength > bLength ? headB : headA; while(grep > 0){ tmpA = tmpA.next; grep--; } while(tmpA != null){ if(tmpA == tmpB){ return tmpA; } tmpA = tmpA.next; tmpB = tmpB.next; } return null; } }
解析:
这个题要找到相同的节点,其实就是理解相同的含义。
如果两个节点相同,那么这两个节点之后的节点也肯定都相同;
那么意味着如果有相同的节点,从相同的节点往后长度一定相同。
所以只需要让两个链表长度对齐,让长的链表先走一个长度差,再一起往后遍历,遇到相同的就结束。
4、环路检测
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-lcci/
给定一个链表,如果它是有环链表,实现一个算法返回环路的开头节点。若环不存在,请返回 null。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
示例 1:
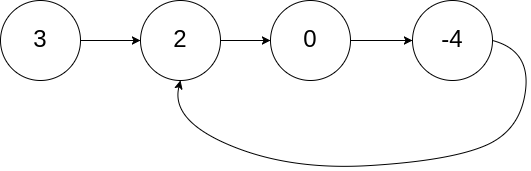
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:tail connects to node index 1
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:
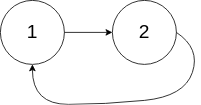
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:tail connects to node index 0
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:

输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:no cycle
解释:链表中没有环。
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { * val = x; * next = null; * } * } */ public class Solution { public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) { ListNode pos = head; Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>(); while(pos != null){ if(set.contains(pos)){ return pos; }else{ set.add(pos); } pos = pos.next; } return null; } }
解析:
遍历链表中的每个节点,并将它记录下来;一旦遇到了此前遍历过的节点,就可以判定链表中存在环。借助哈希表可以很方便地实现