★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★
➤微信公众号:山青咏芝(let_us_code)
➤博主域名:https://www.zengqiang.org
➤GitHub地址:https://github.com/strengthen/LeetCode
➤原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/strengthen/p/11566907.html
➤如果链接不是山青咏芝的博客园地址,则可能是爬取作者的文章。
➤原文已修改更新!强烈建议点击原文地址阅读!支持作者!支持原创!
★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★
In an n*n grid, there is a snake that spans 2 cells and starts moving from the top left corner at (0, 0) and (0, 1). The grid has empty cells represented by zeros and blocked cells represented by ones. The snake wants to reach the lower right corner at (n-1, n-2) and (n-1, n-1).
In one move the snake can:
- Move one cell to the right if there are no blocked cells there. This move keeps the horizontal/vertical position of the snake as it is.
- Move down one cell if there are no blocked cells there. This move keeps the horizontal/vertical position of the snake as it is.
- Rotate clockwise if it's in a horizontal position and the two cells under it are both empty. In that case the snake moves from
(r, c)and(r, c+1)to(r, c)and(r+1, c).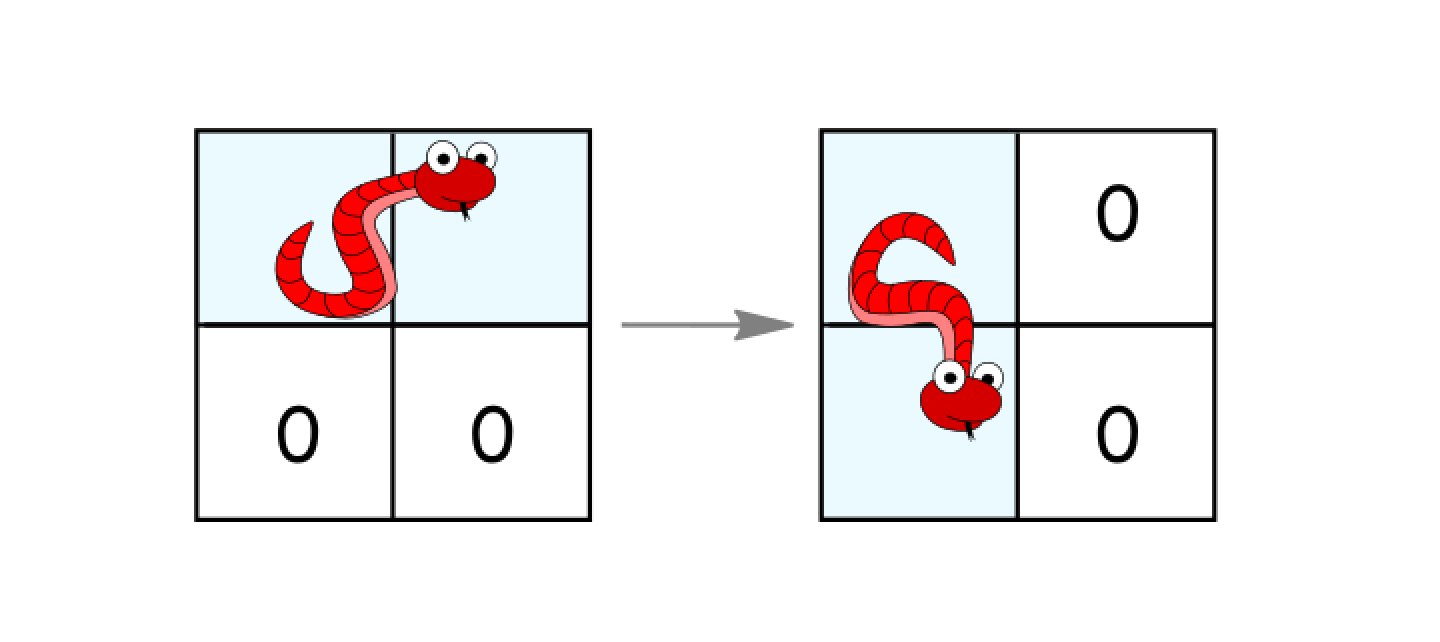
- Rotate counterclockwise if it's in a vertical position and the two cells to its right are both empty. In that case the snake moves from
(r, c)and(r+1, c)to(r, c)and(r, c+1).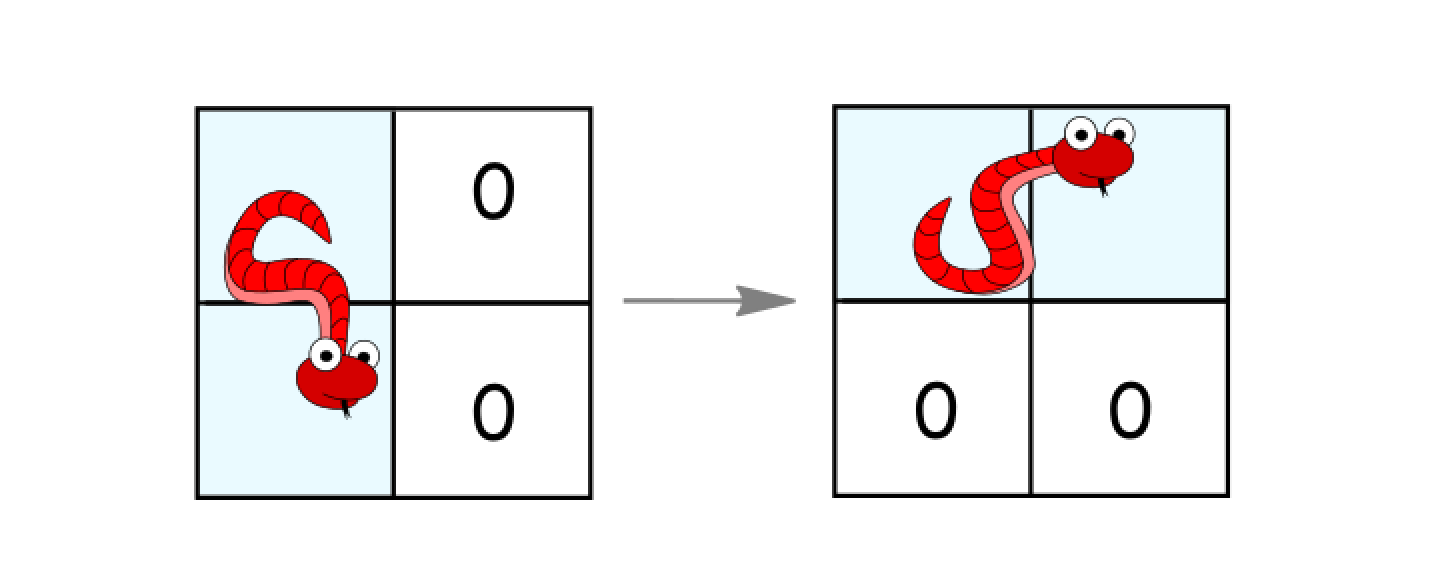
Return the minimum number of moves to reach the target.
If there is no way to reach the target, return -1.
Example 1:
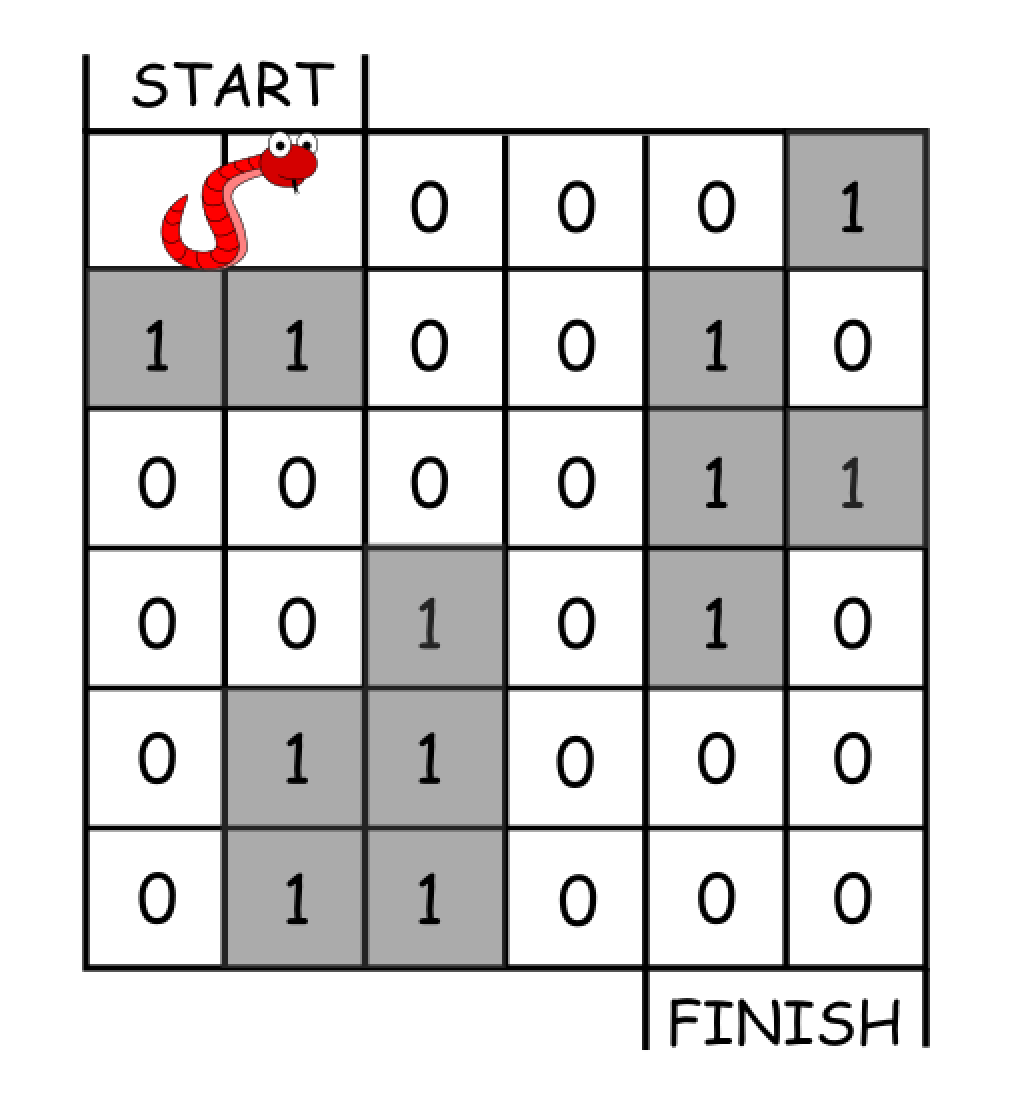
Input: grid = [[0,0,0,0,0,1],
[1,1,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,0,0,1,1],
[0,0,1,0,1,0],
[0,1,1,0,0,0],
[0,1,1,0,0,0]]
Output: 11
Explanation:
One possible solution is [right, right, rotate clockwise, right, down, down, down, down, rotate counterclockwise, right, down].
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[0,0,1,1,1,1], [0,0,0,0,1,1], [1,1,0,0,0,1], [1,1,1,0,0,1], [1,1,1,0,0,1], [1,1,1,0,0,0]] Output: 9
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 1000 <= grid[i][j] <= 1- It is guaranteed that the snake starts at empty cells.
你还记得那条风靡全球的贪吃蛇吗?
我们在一个 n*n 的网格上构建了新的迷宫地图,蛇的长度为 2,也就是说它会占去两个单元格。蛇会从左上角((0, 0) 和 (0, 1))开始移动。我们用 0 表示空单元格,用 1 表示障碍物。蛇需要移动到迷宫的右下角((n-1, n-2) 和 (n-1, n-1))。
每次移动,蛇可以这样走:
- 如果没有障碍,则向右移动一个单元格。并仍然保持身体的水平/竖直状态。
- 如果没有障碍,则向下移动一个单元格。并仍然保持身体的水平/竖直状态。
- 如果它处于水平状态并且其下面的两个单元都是空的,就顺时针旋转 90 度。蛇从(
(r, c)、(r, c+1))移动到 ((r, c)、(r+1, c))。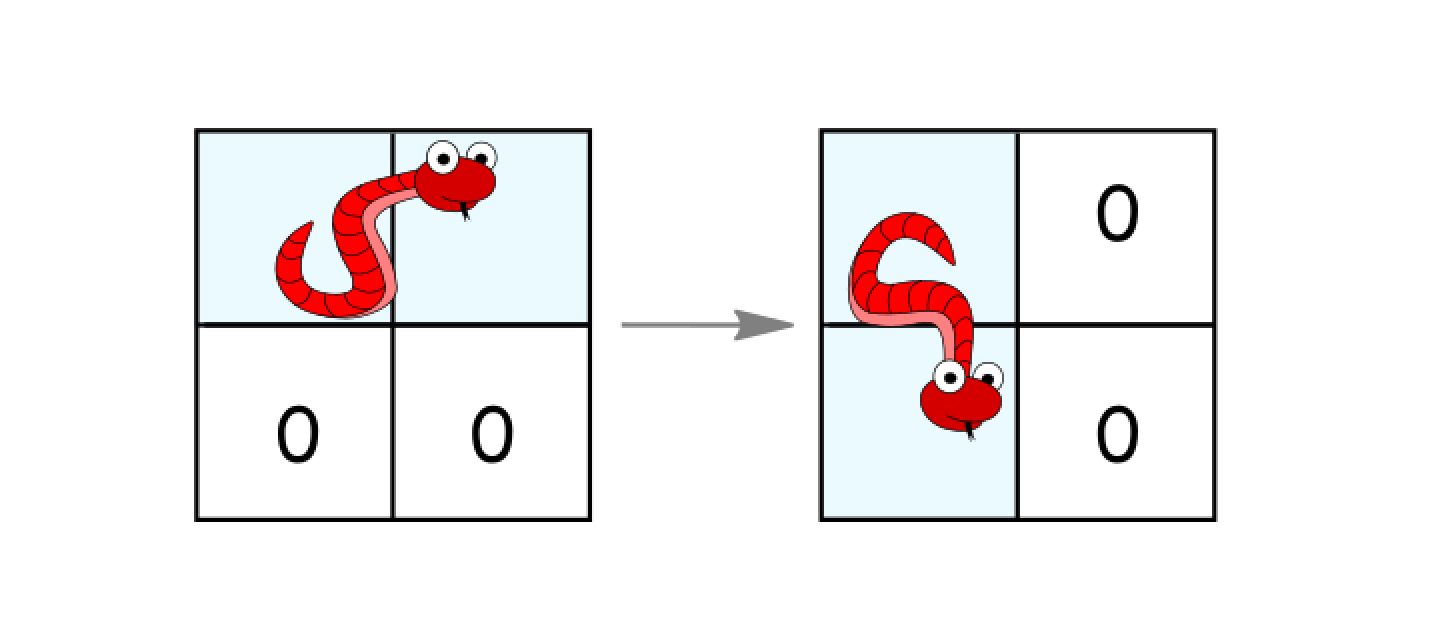
- 如果它处于竖直状态并且其右面的两个单元都是空的,就逆时针旋转 90 度。蛇从(
(r, c)、(r+1, c))移动到((r, c)、(r, c+1))。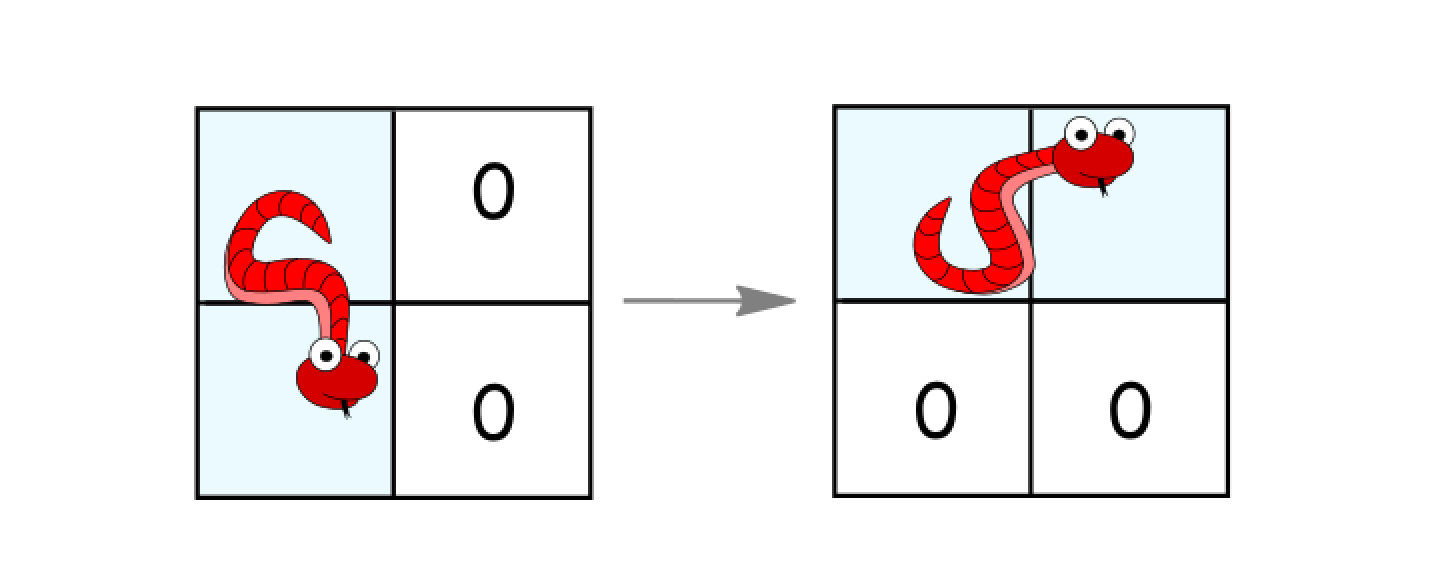
返回蛇抵达目的地所需的最少移动次数。
如果无法到达目的地,请返回 -1。
示例 1:
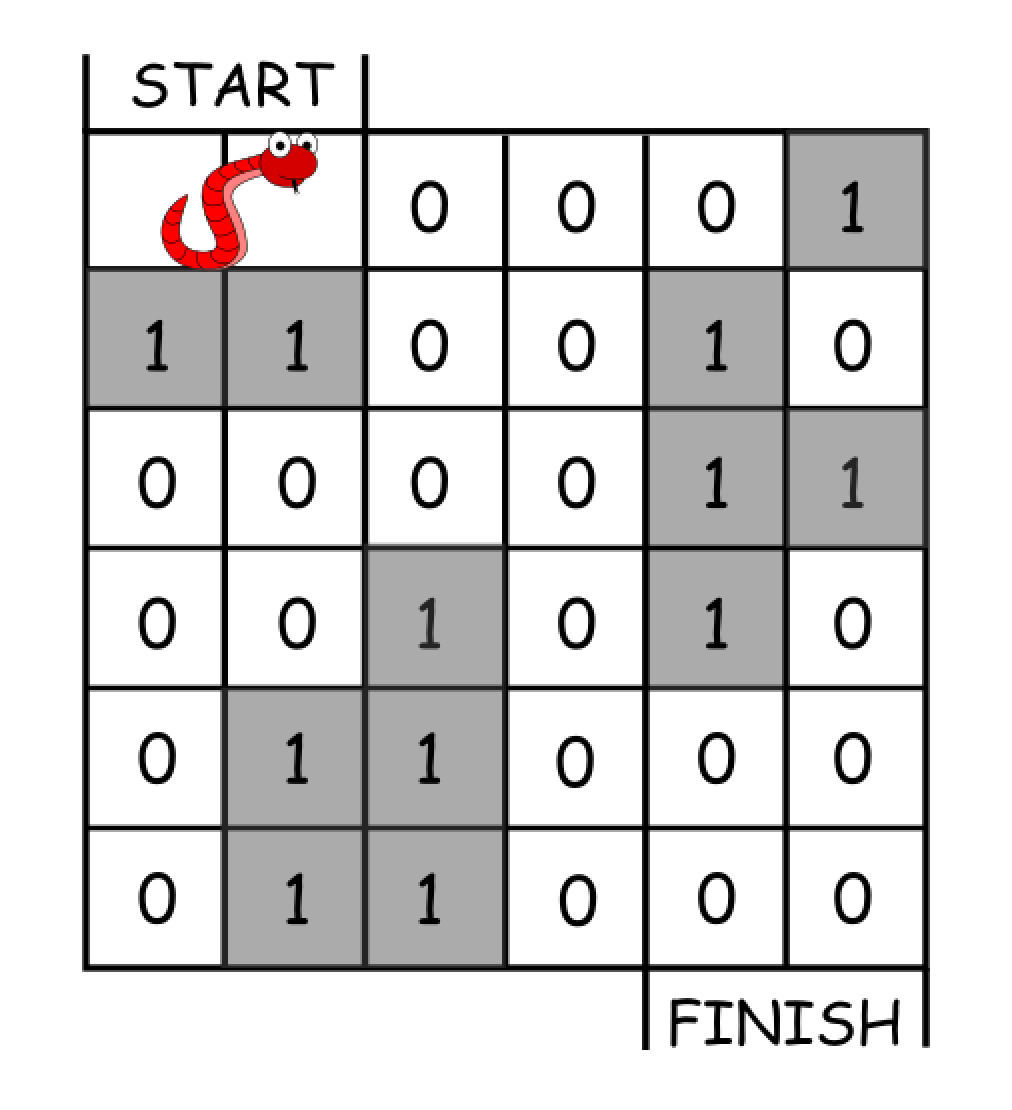
输入:grid = [[0,0,0,0,0,1],
[1,1,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,0,0,1,1],
[0,0,1,0,1,0],
[0,1,1,0,0,0],
[0,1,1,0,0,0]]
输出:11
解释:
一种可能的解决方案是 [右, 右, 顺时针旋转, 右, 下, 下, 下, 下, 逆时针旋转, 右, 下]。
示例 2:
输入:grid = [[0,0,1,1,1,1], [0,0,0,0,1,1], [1,1,0,0,0,1], [1,1,1,0,0,1], [1,1,1,0,0,1], [1,1,1,0,0,0]] 输出:9
提示:
2 <= n <= 1000 <= grid[i][j] <= 1- 蛇保证从空单元格开始出发。
1 class Solution { 2 func minimumMoves(_ grid: [[Int]]) -> Int { 3 let n:Int = grid.count 4 var mem:[[[Bool]]] = [[[Bool]]](repeating: [[Bool]](repeating: [Bool](repeating: false, count: 2), count: n), count: n) 5 var q:[Pos] = [Pos]() 6 q.append(Pos(0, 0, 0, 0)) 7 while(!q.isEmpty) 8 { 9 let cur:Pos = q.removeFirst() 10 if cur.s == 0 && cur.x == n - 1 && cur.y == n - 2 11 { 12 return cur.step 13 } 14 for i in 0..<4 15 { 16 if canMove(cur, i, grid, mem) 17 { 18 let next:Pos = move(cur, i) 19 mem[next.x][next.y][next.s] = true 20 q.append(next) 21 } 22 } 23 } 24 return -1 25 } 26 27 func canMove(_ cur:Pos,_ s:Int,_ grid:[[Int]],_ mem:[[[Bool]]]) -> Bool 28 { 29 let n:Int = grid.count 30 let x:Int = cur.x 31 let y:Int = cur.y 32 if s == 0 33 { 34 if cur.s == 0 35 { 36 return y + 2 < n && !mem[x][y + 1][0] && grid[x][y + 2] != 1 37 } 38 else 39 { 40 return y + 1 < n && !mem[x][y + 1][1] && grid[x][y + 1] != 1 && grid[x + 1][y + 1] != 1 41 } 42 } 43 else if s == 1 44 { 45 if cur.s == 0 46 { 47 return x + 1 < n && !mem[x + 1][y][0] && grid[x + 1][y] != 1 && grid[x + 1][y + 1] != 1 48 } 49 else 50 { 51 return x + 2 < n && !mem[x + 1][y][1] && grid[x + 2][y] != 1 52 } 53 } 54 else if s == 2 55 { 56 if cur.s != 0 57 { 58 return false 59 } 60 return x + 1 < n && !mem[x][y][1] && grid[x + 1][y] != 1 && grid[x + 1][y + 1] != 1 61 } 62 else 63 { 64 if cur.s != 1 65 { 66 return false 67 } 68 return y + 1 < n && !mem[x][y][0] && grid[x][y + 1] != 1 && grid[x + 1][y + 1] != 1 69 } 70 } 71 72 func move(_ cur:Pos,_ s:Int) -> Pos 73 { 74 var x:Int = cur.x 75 var y:Int = cur.y 76 var pp = cur.s 77 if s == 0 78 { 79 y += 1 80 } 81 else if s == 1 82 { 83 x += 1 84 } 85 else if s == 2 86 { 87 pp = 1 88 } 89 else 90 { 91 pp = 0 92 } 93 return Pos(x, y, pp, cur.step + 1) 94 } 95 } 96 97 struct Pos 98 { 99 var x:Int = 0 100 var y:Int = 0 101 var s:Int = 0 102 var step:Int = 0 103 init(_ x:Int,_ y:Int,_ s:Int,_ step:Int) 104 { 105 self.x = x 106 self.y = y 107 self.s = s 108 self.step = step 109 } 110 }
236ms
1 class Solution { 2 func minimumMoves(_ grid: [[Int]]) -> Int { 3 let rows = grid.count, cols = grid[0].count 4 var queue = [(Int, Int, Int)]() 5 queue.append((0, 0, 0)) 6 7 var dist = [[[Int]]](repeating: [[Int]](repeating: [Int](repeating: Int.max, count: 2), count: cols), count: rows) 8 9 func valid(_ r: Int, _ c: Int) -> Bool { 10 return r >= 0 && r < rows && 0 <= c && c < cols 11 } 12 13 func bfs_check(_ q: inout [(Int, Int, Int)], _ r: Int, _ c: Int, _ dir: Int, _ curDist: Int) { 14 if curDist < dist[r][c][dir] { 15 dist[r][c][dir] = curDist; 16 q.append((r, c, dir)) 17 } 18 } 19 bfs_check(&queue, 0, 0, 0, 0) 20 while queue.count > 0 { 21 let (r, c, dir) = queue.removeFirst() 22 let curdist = dist[r][c][dir] 23 let r2 = dir == 0 ? r : r + 1 24 let c2 = dir == 0 ? c + 1 : c 25 26 if valid(r, c + 1) && valid(r2, c2 + 1) && grid[r][c + 1] == 0 && grid[r2][c2 + 1] == 0 { 27 bfs_check(&queue, r, c + 1, dir, curdist + 1) 28 } 29 30 if valid(r + 1, c) && valid(r2 + 1, c2) && grid[r + 1][c] == 0 && grid[r2 + 1][c2] == 0 { 31 bfs_check(&queue, r + 1, c, dir, curdist + 1) 32 } 33 34 if dir == 0 { 35 if valid(r + 1, c) && valid(r + 1, c + 1) && grid[r + 1][c] == 0 && grid[r + 1][c + 1] == 0 { 36 bfs_check(&queue, r, c, 1, curdist + 1) 37 } 38 } else { 39 if valid(r, c + 1) && valid(r + 1, c + 1) && grid[r][c + 1] == 0 && grid[r + 1][c + 1] == 0 { 40 bfs_check(&queue, r, c, 0, curdist + 1) 41 } 42 } 43 } 44 let answer = dist[rows - 1][cols - 2][0] 45 return answer < Int.max ? answer : -1 46 } 47 }