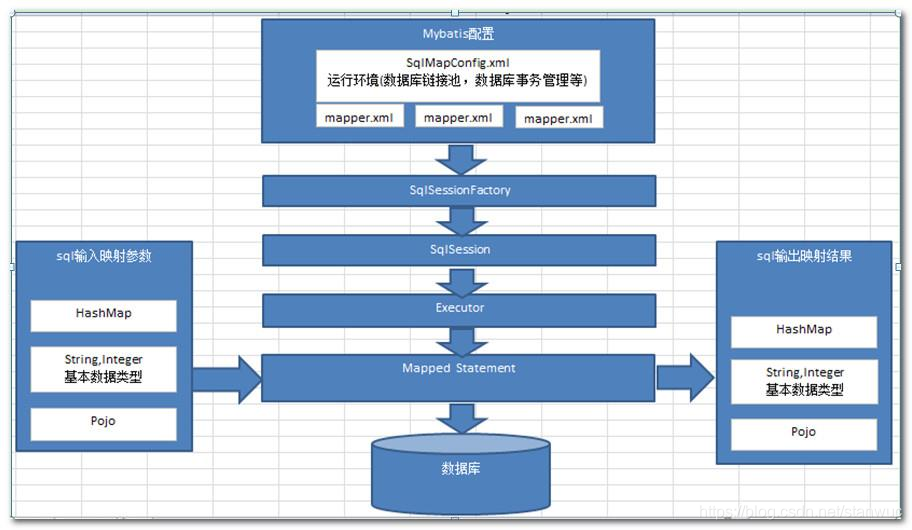
一、简介
1、基本概念
- mybatis 是一个半自动轻量级的一个 orm 框架
- 将 java 与 sql 分离,解决了 jdbc 的硬编码问题;
- sql 由开发人员控制,更加方便 sql 的修改调优;
2、入门程序
2.1 原始方法:通过 sqlsession 来操作数据库
- 建一个全局配置文件(mybatis-config.xml),配置数据源等运行环境信息;
- 建立一个 sql 的映射文件(mapper.xml),并将这个文件注册到全局配置中;
- 加载全局配置文件获得一个 sqlsessionfactory;
- 通过 factory 获得 sqlsession(非线程安全),一个sqlsession 维护一次会话;
- sqlsession通过 sql 的唯一标识符(id)调用方法执行 sql;
- 注意数据库的字段名和bean的字段名要相同才能顺利映射;
- 具体的配置文件可以参考后文;
public class MybatisTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); User user = sqlSession.selectOne("MyMapper.selectUser",1); System.out.println(user); } }
2.2 接口式编程(动态代理方式):通过 sqlsession 获得 mapper 接口的代理对象,通过代理对象来操作数据库
- 定义一个接口,接口中定义操作数据库的方法;
- 将接口和sql的映射文件绑定:xml的namespace是接口全限定名,sql的id是接口中的方法名;
- 为避免出错,最好mapper xml 文件和 mapper 接口放在同一个包下面,并且取同样的名字;
- idea 开发环境下,mapper xml 不能自动输出到 target 的目录下需要在 pom 文件中配置:
<build> <resources> <resource> <directory>src/main/java</directory> <includes> <include>**/*.properties</include> <include>**/*.xml</include> </includes> <filtering>false</filtering> </resource> <resource> <directory>src/main/resources</directory> <includes> <include>**/*.properties</include> <include>**/*.xml</include> </includes> <filtering>false</filtering> </resource> </resources> </build>
2.3 问题说明
2.3.1 无法完成数据库字段到 pojo 属性的映射的解决方法:
- sql 查询的时候给数据库字段起别名(别名就是pojo的属性名);
- 可以给 pojo 中的属性重新以数据库的字段命名;
- 当数据库的字段类似(user_name),pojo 属性名称是(userName)时,开启驼峰语法自动转换即可;
<!--配置全局属性--> <settings> <!-- 开启驼峰命名转换 :{name_id} -> {nameId} --> <setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/> </settings>
2.3.2 当使用 sqlsession 对数据库进行增删改的操作的时候,需要调用 commit 方法;
2.3.3 mybatis 的全局配置文件中各配置项的顺序是有约束的;
3、运行原理简介
(1)sqlsessionfactory 初始化
- 把配置文件所有的信息解析并保存在 configuration 中,并返回一个包含 configuration 的 defaultSqlSessionFactory 对象;
- 一个 mapperedStatement 代表一个增删改查的信息;
(2)sqlsession 对象获取
- 返回一个 defaultSqlSession 对象,里面包含了 configuration 和 executor;
- executor的两次包装:二级缓存开启的话会有一次包装;拦截器链会有一次包装;
(3)获取接口代理对象
- 调用 getMapper 方法实际上是从一个 mapperproxyfactory 的工厂类中获得 mapperproxy 对象,里面包含了defaultsqlsession;
(4)查询实现:
-
在四大对象的创建过程中都会有插件的介入;
二、配置文件
1、全局配置文件
(1)properties标签:url引入网络或者磁盘的资源;resource引入 classpath 下的资源;
(2)settings标签:设置一些mybatis运行时的重要参数
(3)typeAliases标签:就是给 java 类起别名用的
- 别名不分大小写;
- 可以单独起也可以批量起;
- 默认别名就是类名;
- 也可以使用注解来起别名(@alias);
- java 中的基本数据类型和一些常用的类已经取好了别名(基本类型就是前面加 _ ;引用类型就是原类名)
(4)typeHandlers标签:
- 就是处理 java 类型和数据库类型的转换的;
- 常用的类型 mybatis 都给默认处理了,不用我们自己去做;
- 当然是支持自定义的了;
(5)plugins标签:作用就是拦截四大对象(StatementHandler、ParameterHandler、ResultSetHandler、executor),改变他们的默认行为
(6)environments标签:
- 用来配置环境的,可以配置多个环境,在default属性里可以指定默认的环境;
- 每个环境都应包含:transactionManager 和 dataSource
(7)databaseIdProvider标签:
- 此标签就是用来标记 sql 语句作用的数据库的;
- 标签内通过property标签指定数据库的别名;
- 在相应的 sql 语句的标签上用databaseId引入数据库的别名;
- 注意:主配置文件里的标签的书写的顺序是有要求的,databaseIdProvider应该写在envir 和 mapper 之间;
(8)mappers标签:注册 sql 映射,里面具体的 mapper 的属性有三种写法:
- resource:classpath 路径下;
- url:网络资源或者磁盘资源;
- class:指定对应的映射的接口(条件是必须同包同名);
- 批量的注册直接用package 标签(条件是必须同包同名);
2、mapper文件概述
(1)CRUD测试(select、delete、update、insert标签)
(2)数据插入获得自增主键
1、mysql:支持自增主键
(1)useGeneratedKeys 和 keyProperty 属性配合使用即可获取到自增主键的值;
(2)使用 selectkey 标签也可以实现,不过 order 的属性值要设置为 after 才能获取得到;
<selectKey order="AFTER"keyProperty="id" resultType="String">select last_insert_id()</selectKey>
2、oracle:不支持自增主键,靠序列来完成
(1)在要执行的sql前用 selectKey 标签来实现;
(2)相关的三个属性分别是 keyProperty、resultType 和 order;
(3)有两种写法分别是 order 的属性值为 before 和 after;Oracle 用 before;
<selectKey keyColumn="id" keyProperty="id" order="BEFORE" resultType="int"> select max(id)+1 as myNo from emp </selectKey>
<!--序列实现自增主键-->
SQL >create sequence autoID increment by 1 start with 1 maxvalue 999999 cycle;
SQL >insert into tablename values(autoID.nextval,...);
(3)常见问题说明
1、int、long 和 boolean 类型的返回值我们可以直接用;
2、增删改后一定要 commit,否则对于数据库的修改不会生效;
3、mapper文件参数处理
(1)参数处理
- 单个参数:单个参数可以在 #{}中随意写;
- 多个参数(默认封装在 map 中):可以写 #{param1}和 #{param2};也可以写#{0}和#{1};还可以用注解 @Param("id")Integer id 指定名称;
- 多参数可以自己封装一个 map,在 mapper 文件中用 #{键值}取值;
- 业务相关的数据直接封装在 pojo 中;
- list 和 array 的处理:https://blog.csdn.net/zyxwvuuvwxyz/article/details/80238995
(2)关于 #{} 和 ${}两种取值方法:
- #{}是以预编译的形式来取参数的值的,可以防注入;而${}是直接拼接的;
- 只有在原生的 jdbc 不支持占位符的地方可以使用 ${},比如order by ${age};
- 当插入一个null值的时候,#{email} 在 mysql 中插入成功,在 oracle 中会插入失败,插入 null 值时会转化成 jdbcType 的 other 类型,oracle不支持此类型;解决:#{email,jdbcType=NULL}
4、mapper文件结果集映射
(1)resultType
- resultType的作用就是指定结果集的封装的规则;
- 结果集封装为 list 类型直接写 list 里数据类型即可;
- 封装为 map 单条记录直接写 map 的别名(map);多条记录 mapper xml文件写 pojo 的类型(pojo是map的值),对应接口方法上用注解@mapKey("pojo属性")指定map的键;
(2)resultMap
- resultMap也是用来定义结果集的封装规则的(表的列名和pojo 的属性名的对应关系);
- resultMap标签两个属性 type是pojo类型,id是唯一标识;表中的主键列用id 封装,普通列用 result 封装;
<resultMap id="myuser" type="com.stan.hello.User"> <!--<id column="id" property="id"></id>--> <result column="user_name" property="userName"></result> </resultMap> <select id="queryUserById" resultMap="myuser" parameterType="java.lang.String"> select * from tb_user where id = #{id} </select>
三、动态sql
1、if 判断
(1)OGNL(对象图导航语言):
- 有点类似于 jsp 中的 el 表达式,可以用来取参数的值并作一些基本的运算;
- OGNL使用:动态SQL表达式中(test等);${param}参数中;
(2)if 判断
<select id="queryUserList" resultType="com.stan.pojo.User"> select * from tb_user WHERE 1=1 <if test="name!=null and name.trim()!=''"> and name like '%${name}%' </if> </select>
<!--if 判断拼接 where 条件存在多余 and 的解决方法:加一个 1=1;使用where 或者 trim标签;-->
2、choose 分支选择
(1)语法:choose----when----when----otherwise-----choose;
(2)理解:类似于 java 中带break 的 switch语句,只匹配一个条件;
<select id="queryUserByNameOrAge" resultType="com.stan.pojo.User"> select * from tb_user WHERE 1=1 <choose> <when test="name!=null and name.trim()!=''"> and name like '%${name}%' </when> <when test="age!=null"> and age = #{age} </when> <otherwise> and name='allen' </otherwise> </choose> </select>
3、foreach 遍历
(1)遍历集合拼接 where 条件(如:in 集合):几个常用的属性 collection、item、separator、open、close、index(map的key)
List<User> queryUserByIds(@Param("ids") String[] ids); <select id="queryUserByIds" resultType="com.stan.pojo.User"> select * from tb_user where id in <foreach collection="ids" item="id" open="(" close=")" separator=","> #{id} </foreach> </select>
(2)数据批量插入
- mysql 第一种:在 values 后面用 foreach 遍历拼接 sql;
- mysql 第二种:直接整个插入语句来循环,需要在数据库的 url 后面传参开启多条语句执行的支持;
- oracle 第一种:用 plsql ,在begin 和 end 中来遍历;
- oracle 第二种:循环用 select 语句将集合中的值从伪表中查出,再用查出的结果进行插入;
4、其他标签
(1)where标签:自动去除 where 条件中多余的 and
<select id="queryUserByNameAndAge" resultType="com.stan.pojo.User"> select * from tb_user <where> <if test="name!=null and name.trim()!=''"> and name like '%${name}%' </if> <if test="age!=null"> and age = #{age} </if> </where> </select>
(2)set标签:在 update 语句中自动加上 set 和逗号分隔符
<update id="updateUser"> update tb_user <set> <if test="userName != null and userName.trim() != ''"> user_name=#{userName} </if> <if test="password != null and password.trim() != ''"> password=#{password} </if> </set> where id = #{id} </update>
(3)trim标签:自动加 set,自动去掉多余的逗号(仅针对示例)
update tb_user <trim prefix="set" suffixoverride="," suffix=" where id = #{id} "> <if test="userName != null and userName.length()>0"> user_name=#{userName} , </if> <if test="password != null and password.length()>0"> password=#{password} , </if> </trim>
(4)bind标签:作用就是将传入的参数赋值给一个变量方便以后的调用,连个属性name 和 value;
<select id="getEmpsTestInnerParameter" resultType="com.hand.mybatis.bean.Employee"> <bind name="bindeName" value="'%'+userName+'%'"/> SELECT * FROM tb_user <if test="userName!=null"> where user_name like #{bindeName} </if> </select>
5、补充说明
(1)内置参数:
- 除了我们传入的参数,还有内置的参数,这里的内置参数可以取到也可以判断
- _parameter:封装所有的参数,传入的参数一个就是这个参数本身,传入多个参数就是一个 map;
- databaseId:全局配置文件里面配置了 databaseproviderid这里可以取到;
- _parameter 和 if结合可以用来进行 where条件的拼接;
- databaseId 和 if 结合使用可以用来在一个 select 元素里写两个数据库的 sql;
(2)sql 片段:
- 用 sql 标签抽取可以重用的sql 片段方便以后在其他的sql 里用include标签用id引用,如查询字段的重用;
<sql id="commonSql">id,user_name,password</sql> <select id="queryUserById" resultMap="userResultMap"> select <include refid="commonSql"></include> from tb_user where id = #{id} </select>
四、缓存
1、介绍
(1)作用:就是提升查询的效率;
(2)分类:
- 一缓(本地缓存):session 级别的缓存,默认开启,session关闭则失效;
- 二缓(全局缓存):namespace级别的缓存,要手动开启;
2、一级缓存
(1)一级缓存失效的四种情况
- sqlsession 不同,不同的session 之间不能共享数据;
- 参数不同的情况;
- 两次相同的查询之间有 增删改 的操作;
- 第二次查询之前手动清空缓存;
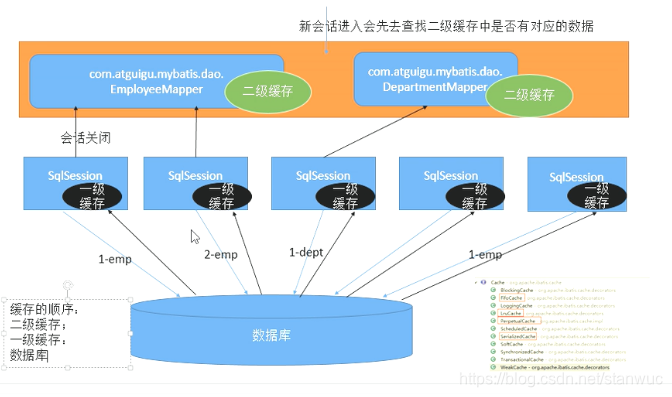
3、二级缓存
(1)作用:可以实现不同的 session 之间的数据共享,一个 namespace(一个接口)对应一个map(二级缓存);
(2)原理:
- 一次会话中查询的数据会默认保存在一级缓存中;
- 当对应的会话关闭的时候,如果开启了二级缓存,在session关闭清空缓存数据之前会将数据存到二级缓存中;
- 需要注意的是如果 session 没有关闭,一级缓存的数据是不会自动存到二级缓存中的;
(3)使用:
- 总开关(主配文件里的 setting)和分开关(sql映射文件里用 cache标签来开启)都要打开;
- select 标签里的 useCache 属性可以单独控制一个 select 是否使用二级缓存;
4、缓存原理和设置
(1)缓存相关设置
- 全局的 cacheEnabled 和 select 标签的 useCache 都是和二级缓存相关的设置,不会影响一级缓存;
- flashCache属性在增删改的标签里是默认开启,在 select 标签里是默认关闭的,这个属性为 true的话会清空一二级的缓存;
- session 的 clearcache 方法只会清除当前 session 的一级缓存;
- 全局 LocalcacheScope 可以用来关闭一级缓存(一般不用);
(2)原理图示
5、第三方缓存整合(ehcache)
(1)导入缓存的包和整合包;测试的时候采用的maven
<dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.caches</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-ehcache</artifactId> <version>1.1.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId> <artifactId>ehcache</artifactId> <version>2.10.5</version> </dependency>
(2)classpath 下编写 ehcache-xml 配置文件;
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://ehcache.org/ehcache.xsd"> <diskStore path="D:ehcache" /> <defaultCache maxElementsInMemory="1000" maxElementsOnDisk="10000000" eternal="false" overflowToDisk="false" timeToIdleSeconds="120" timeToLiveSeconds="120" diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120" memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"> </defaultCache> </ehcache>
(3)打开二级缓存的总开关,直接在mapper xml 中用 cache 标签引用;
<cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache" > <property name="timeToIdleSeconds" value="3600"/> <property name="timeToLiveSeconds" value="3600"/> <property name="maxEntriesLocalHeap" value="1000"/> <property name="maxEntriesLocalDisk" value="10000000"/> <property name="memoryStoreEvictionPolicy" value="LRU"/> </cache>
(4)另一个 mapper 可以用 cache-ref 标签来引用其他 mapper 的缓存策略;
<cache-ref namespace="com.stan.crud.UserDaoMapper"/>
(5)相关配置参数的说明
diskStore标签:指定数据在磁盘中的存储位置。 defaultCache标签:当借助CacheManager.add("demoCache")创建Cache时,EhCache便会采用<defalutCache/>指定的的管理策略 以下属性是必须的: maxElementsInMemory - 在内存中缓存的element的最大数目 maxElementsOnDisk - 在磁盘上缓存的element的最大数目,若是0表示无穷大 eternal - 设定缓存的elements是否永远不过期。如果为true,则缓存的数据始终有效,如果为false那么还要根据timeToIdleSeconds,timeToLiveSeconds判断 overflowToDisk - 设定当内存缓存溢出的时候是否将过期的element缓存到磁盘上 以下属性是可选的: timeToIdleSeconds - 当缓存在EhCache中的数据前后两次访问的时间超过timeToIdleSeconds的属性取值时,这些数据便会删除,默认值是0,也就是可闲置时间无穷大 timeToLiveSeconds - 缓存element的有效生命期,默认是0.,也就是element存活时间无穷大 diskSpoolBufferSizeMB 这个参数设置DiskStore(磁盘缓存)的缓存区大小.默认是30MB.每个Cache都应该有自己的一个缓冲区. diskPersistent - 在VM重启的时候是否启用磁盘保存EhCache中的数据,默认是false。 diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds - 磁盘缓存的清理线程运行间隔,默认是120秒。每个120s,相应的线程会进行一次EhCache中数据的清理工作 memoryStoreEvictionPolicy - 当内存缓存达到最大,有新的element加入的时候, 移除缓存中element的策略。默认是LRU(最近最少使用),可选的有LFU(最不常使用)和FIFO(先进先出)
6、mybatis 二级缓存的局限性
- mybatis 的二级缓存是基于 namespace 的,如果同一个 namaspace 下增删改的操作频繁的话,二级缓存会常常被清空,基本也就是没啥用了;
五、高级查询
1、高级查询 (示例:订单-用户-订单详情-商品)
(1)示例解读
- 一个订单只能属于一个人(一对一);
- 一个订单可以包含多个订单详情(一对多);
- 一个订单详情包含一个商品信息;
- 订单和商品(多对多);
(2)总结说明
- 一对一和一对多是单向关系,多对多是双向关系;
- 进行数据库设计的时候,双向的一对一关系的话通常主键相同即可(这种情况直接包含在一个表里会更简单);
- 一对多的关系是多方外键指向一方的主键;多对多的话需要建立中间表,将多对多转化为多对一,然后根据前面的原则进行建表;
(3)示例实现(resultMap)
1、具体的代码和数据库脚本参考:https://blog.csdn.net/hellozpc/article/details/80878563#12_1741
2、association 标签用法:可以用来实现一对一关联查询(Order 包含一个 User 属性);
<resultMap id="orderUserRM" type="com.stan.pojo.OrderUser" autoMapping="true"> <association property="user" javaType="com.stan.pojo.User" autoMapping="true"> <id property="id" column="user_id"></id> </association> </resultMap> <select id="queryOrderUserByOrderNumber" resultMap="orderUserRM" parameterType="String"> select * from tb_order o left join tb_user u on o.user_id = u.id where o.order_number = #{number} </select>
3、collection 标签用法:用 collection 标签实现集合类型属性的封装(一对多),属性 property为相应的集合属性名,而ofType 是集合元素类型;
<resultMap id="orderUserRM" type="com.stan.pojo.OrderUser" autoMapping="true"> <association property="user" javaType="com.stan.pojo.User" autoMapping="true"> <id property="id" column="user_id"></id> </association> <collection property="details" autoMapping="true" javaType="list" ofType="com.stan.pojo.OrderDetail" >
<!--这里的 OrderDetail 是订单和商品关系的媒介--> <id property="id" column="detial_id"></id> <association property="item" javaType="com.stan.pojo.Item" autoMapping="true"> <id property="id" column="item_id"></id> </association> </collection> </resultMap> <select id="queryOrderItemByOrderNumber" resultMap="orderUserRM2" parameterType="String"> select *,d.id as detial_id from tb_order o left join tb_user u on o.user_id = u.id left join tb_orderdetail d on o.id = d.order_id left join tb_item i on i.id = d.item_id where o.order_number = #{number} </select>
4、 其他说明:
- pojo包装pojo的情况,用resultMap实现关联查询,还可以设置 property 属性的时候,采取级联属性的写法(属性点属性);
- resultmap 标签有一个继承的属性(extends),可以用来继承另一个resultMap,达到复用的目的;
- sql 语句中如果出现 < > 等符号可以使用字符实体替代(<;>;)
2、延迟加载(分步查询)
(1)主配置文件设置
<!--延迟加载关联查询总开关,association和collection标签里的fetchType也是设置加载的模式的--> <setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/> <!--设置为true的话,只要get一个关联的属性,所有的关联查询都会发出--> <setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/>
(2)mapper xml 文件
<resultMap id="rm2" type="com.stan.pojo.OrderUser" autoMapping="true"> <association property="user" javaType="com.stan.pojo.User" autoMapping="true" select="queryUserById" column="user_id">
<!--这里的select指定关联的查询的 id,这里的column是传过去的参数-->
<!--多个参数的传递可以用map,就是这样的形式:{key1=col1,key2=col2}-->
</association> </resultMap> <select id="queryOrderByNumber" resultMap="rm2"> select * from tb_order where order_number = #{number} </select>
<!--这个方法不单独使用的话可以不在 mapper 接口中书写方法定义--> <select id="queryUserById" resultType="com.stan.pojo.User"> select * from tb_user where id = #{number} </select>
(3)mapper 接口
OrderUser queryOrderByNumber(@Param("number") String number);
(4)测试用例
@Test public void queryOrderByNumber() throws IOException { OrderMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(OrderMapper.class); OrderUser orderUser = mapper.queryOrderByNumber("201807010001"); System.out.println("----------------------"); System.out.println(orderUser.getOrderNumber()); System.out.println("--------------------"); System.out.println(orderUser.getUser()); }
(5)注意:延迟加载依赖于 cglib ,需要在 pom 文件中加入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>cglib</groupId> <artifactId>cglib</artifactId> <version>3.1</version> </dependency>
六、整合spring(SSM整合)
1、导包
(1)核心包:spring包、springmvc包、mybatis包、spring-mybatis整合包
(2)其他包:日志包、连接池包
2、mybatis 配置
(1)主要就是配全局 settings 等;
3、springMVC 配置
(1)controller 扫描;
(2)视图解析器;
(3)注解驱动;
(4)默认servlet 处理;
4、spring 配置
(1)包扫描;
(2)数据源的配置;
(3)事务管理(基于注解的事务);
(4)sqlSessionFactory配置;
(5)配置可以批量执行的 sqlSession;
(6)配置Mapper 接口的扫描(不可少);
5、web.xml配置
(1)全局参数配置 spring配置文件的路径;
(2)配置spring 监听;
(3)配置 springmvc 的DispatcherServlet;
(4)spring框架会自动加载 web-inf 下的配置文件,classpath 路径下的配置文件需要配置路径;
(5)SSM框架整合示例;
七、逆向工程
1、概念
- 就是根据数据库表自动生成 pojo、mapper 接口和 mapper xml 文件;
- 逆向工程常用的方法有:配置插件生成;使用 java 工程来生成;
2、使用(java工程)
(1)导包

(2)配置文件(mbg.xml)
(3)运行生成器 java 代码
3、注意事项
- mybatis 的SSM集成和逆向工程的具体使用方法和示例代码 github 上官方目录都有;
- 运行生成代码的时候很可能会找不到配置文件(mbg xml),直接右键 copy path 即可;
- 可以生成简单查询和复杂查询的代码,复杂查询的方式类似于 hibernate 的 QBC;
- or 条件的拼接代码示例
EmployeeExample example = new EmployeeExample(); Criteria criteria = example.createCriteria(); criteria.andLastNameLike("%e%"); criteria.andGenderEqualTo("1"); Criteria criteria2 = example.createCriteria(); criteria2.andEmailLike("%e%"); example.or(criteria2);
八、插件扩展
1、插件开发
(1)原理
- 四大对象的创建不是直接返回的,而是 intercepter 调用了 plugin 方法包装生成代理对象;
- 我们可以使用插件对四大对象进行包装生成代理对象,这样就可以拦截到四大对象的每一个执行;
(2)简单实现:单个插件
- 写一个类继承intercepter ,重写 intercept(拦截)、plugin(包装)、和 setProperties(属性设置)方法;
- 用 @intercepts 注解给插件签名;
- 在全局配置文件中引用插件;
(3)多个插件:拦截同一个对象同一个方法
- 包装:顺序包装;
- 执行:逆序执行;
- 特点:多个插件是对目标对象进行层层包装的;
(4)开发示例:
@Intercepts({@Signature(type= ParameterHandler.class,method = "setParameters",args = {PreparedStatement.class})})
public class MyIntercepter implements Interceptor {
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("要拦截的方法:"+invocation.getMethod());
MetaObject metaObject = SystemMetaObject.forObject(invocation.getTarget());
Object para = metaObject.getValue("parameterObject");
System.out.println("原来的参数是:"+para);
metaObject.setValue("parameterObject","5");
return invocation.proceed();
}
public Object plugin(Object o) {
System.out.println("包装的对象:"+o.toString());
return Plugin.wrap(o,this);
}
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
System.out.println(properties.getProperty("test"));
}
}
(5)PageHelper 插件使用:实现查询数据的分页功能
- 使用:导包 > 主配置文件注册插件 > mapper查询前设置参数 > 返回一个 page 对象其中包含很多分页信息(也可以用pageinfo包装查询结果);
<dependency> <groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId> <artifactId>pagehelper</artifactId> <version>4.1.4</version> </dependency>
<plugins> <plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageHelper"> <property name="dialect" value="mysql"/> <property name="offsetAsPageNum" value="false"/> <property name="rowBoundsWithCount" value="false"/> <property name="pageSizeZero" value="true"/> <property name="reasonable" value="false"/> <property name="supportMethodsArguments" value="false"/> <property name="returnPageInfo" value="none"/> </plugin> </plugins>
<select id="queryUserPage" resultType="com.stan.pojo.User"> select * from tb_user </select>
public List<User> queryUserPage();
@Test public void queryPage() throws IOException { Page<User> page = PageHelper.startPage(2,4); List<User> users = mapper.queryUserPage(); for (User user : users) { System.out.println(user); } System.out.println(page); }
2、扩展学习
(1)批量执行sql语句
- 正常使用就是在 openSession 传入 executorType;与 Spring 集成则是如下图所示配置;
- mybatis 主配置文件的 setting 里有一个批量执行的开关,但是不建议开启,因为会影响所有的sql执行;
(2)mybatis 调用存储过程:示例参考
(3)自定义类型处理器处理枚举类型
1、枚举类型
- 枚举的本质就是一个类;枚举的值本质就是枚举对象;枚举当然也可以有构造方法;
- 枚举类型包含 name(名)和 ordinal(suoyin),使用 mybatis 自带的类型处理器只能保存名字或者索引中的一个;
2、自定义类型处理器:参考示例
- 步骤:类继承typehandler > 重写相应方法(实质就是调用ps和rs 的 get 和 set 方法)> 主配置文件中注册;
- 注意:可以针对具体的字段设置 typehandler,但是必须保证保存和查询的 typeHandler 是一致的;
3、关于 mybatis 的注解开发
- 个人感觉注解开发还是将 sql 和 java 杂揉在一起了,不符合框架将 sql 和 java 分离的初衷,一般不建议使用,了解即可,小项目有快速开发的需求勉强可以考虑(个人感觉,不用参考);