一:集合了解
(一)确定性,互异性,无序性
确定性:对任意对象都能判定其是否属于某一个集合
互异性:集合内每个元素都是无差异的,注意是内容差异
无序性:集合内的顺序无关
(二)集合接口HashSet,TreeSet,LinkedHashSet
–HashSet (基于散列函数的集合,无序,不支持同步)
–TreeSet (基于树结构的集合,可排序的,不支持同步)
–LinkedHashSet(基于散列函数和双向链表的集合,可排序的,不支持同步
二:HashSet
(一)基础方法
–基于HashMap实现的,可以容纳null元素, 不支持同步
Set s = Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet(...));
–add 添加一个元素
–clear 清除整个HashSet
–contains 判定是否包含一个元素
–remove 删除一个元素 size 大小
–retainAll 计算两个集合交集
(二)HashSet实现
HashSet<Integer> hs = new HashSet<Integer>(); //<>是泛型编程,类似于C++模板
hs.add(null);
hs.add(10000);
hs.add(22);
hs.add(1010);
hs.add(50001010);
hs.add(101035);
hs.add(3);
System.out.println(hs.size());
if(!hs.contains(6)) {
hs.add(6);
}
System.out.println(hs.size());
hs.remove(4); //存在,则删除,不存在,则不操作
for(Integer item : hs) {
System.out.println(item);
}
7
8
null //无序性
10000
1010
3
22
6
50001010
101035
(三)性能测试:因为无序性,无索引操作。for效率高
public static void trverseByIterator(HashSet<Integer> hs) {
//使用迭代器遍历
System.out.println("==========迭代器遍历===========");
long startTime = System.nanoTime(); //获取开始时间,以纳秒为单位返回正在运行的Java虚拟机的高分辨率时间源的当前值。
Iterator<Integer> iter = hs.iterator(); //获取迭代指针
while(iter.hasNext()) {
iter.next();
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime-startTime;
System.out.println("iterator使用纳秒:"+duration);
}
public static void trverseByFor(HashSet<Integer> hs) {
//使用迭代器遍历
System.out.println("==========for索引遍历===========");
long startTime = System.nanoTime(); //获取开始时间,以纳秒为单位返回正在运行的Java虚拟机的高分辨率时间源的当前值。
for(Integer item : hs) {
;
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime(); //获取开始时间,以纳秒为单位返回正在运行的Java虚拟机的高分辨率时间源的当前值。
long duration = endTime-startTime;
System.out.println("for使用纳秒:"+duration);
}
==========迭代器遍历===========
iterator使用纳秒:5738665
==========for索引遍历===========
for使用纳秒:2721950
(四)retainAll交集测试
//测试交集
HashSet<String> hs1 = new HashSet<String>();
HashSet<String> hs2 = new HashSet<String>();
hs1.add("a");
hs1.add("b");
hs1.add("c");
hs2.add("c");
hs2.add("d");
hs2.add("e");
hs1.retainAll(hs2); //将交集保存在hs1中
for(String item : hs1) {
System.out.println(item);
}
三:LinkedHashSet(与HashSet一致)
–继承HashSet,也是基于HashMap实现的,可以容纳null元素,按照插入顺序有序
–不支持同步
Set s = Collections.synchronizedSet(new LinkedHashSet(...));
–方法和HashSet基本一致
add, clear, contains, remove, size
–通过一个双向链表维护插入顺序
四:TreeSet
(一)基本方法
–基于TreeMap实现的,不可以容纳null元素,不支持同步
SortedSet s = Collections.synchronizedSortedSet(new TreeSet(...));
–add 添加一个元素
–clear 清除整个TreeSe
–contains 判定是否包含一个元素
–remove 删除一个元素 size 大小
–根据compareTo方法或指定Comparator排序
(二)实现(有序,会自动排序,红黑树)
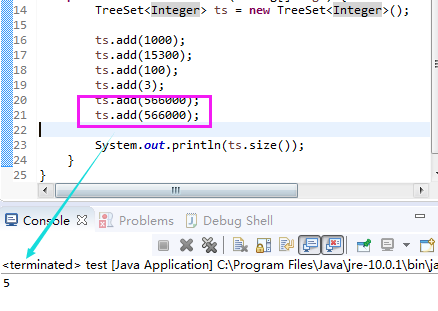
TreeSet<Integer> ts = new TreeSet<Integer>(); //<>是泛型编程,类似于C++模板
ts.add(1000);
ts.add(15300);
ts.add(100);
ts.add(3);
ts.add(566000);
if(!ts.contains(4)) {
ts.add(4);
}
for(Integer item : ts) {
System.out.println(item);;
}
(三)性能测试:for更加高效
==========迭代器遍历===========
iterator使用纳秒:9246423
==========for索引遍历===========
for使用纳秒:3366874
五:HashSet, LinkedHashSet, TreeSet对象比较(元素重复)《重点》
(一)HashSet和LinkedHashSet判定元素重复的原则
–判定两个元素的hashCode返回值是否相同,若不同,返回false
–若两者hashCode相同,判定equals方法,若不同,返回false;否则返回true。
–hashCode和equals方法是所有类都有的,因为Object类有
比较之前会先调用hashCode,之后是equals方法
1.正常执行,含重复
class Dog{
int age;
public Dog(int a) {
this.age=a;
}
}
public class CompareTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog d1=new Dog(10);
Dog d2=new Dog(10);
HashSet<Dog> hs=new HashSet<Dog>();
hs.add(new Dog(10));
hs.add(new Dog(1));
hs.add(new Dog(3));
hs.add(new Dog(10));
hs.add(new Dog(10));
System.out.println(hs.size());
}
}
Dog类本身没有hashCode方法,继承于Object,而Object类的hashCOde会返回对象信息和内存地址经过运算后的一个值。两个不同对象,其值必然不一致
2.实现对象的hashCode方法和equals方法实现去重
import java.util.*;
class Dog{
int age;
public Dog(int a) {
this.age=a;
}
public int getAge() {
return this.age;
}
public int hashCode() {
System.out.println("hashCode exec...");
return this.age;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj2) {
System.out.println("equals exec...");
if(0==this.age-((Dog)obj2).getAge())
return true;
else
return false;
}
}
public class CompareTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog d1=new Dog(10);
Dog d2=new Dog(10);
HashSet<Dog> hs=new HashSet<Dog>();
hs.add(new Dog(10));
hs.add(new Dog(1));
hs.add(new Dog(3));
hs.add(new Dog(10));
hs.add(new Dog(10));
System.out.println(hs.size());
}
}
hashCode exec...
hashCode exec...
hashCode exec...
hashCode exec...
equals exec...
hashCode exec...
equals exec...
3 //去重实现
先执行hashCode,只有hashCode通过,才会执行equals方法
public String toString() {
System.out.println("toString exec...");
return age+"";
}
要保持equals,hashCode和toString三位一体。都应该各自相同
(二) TreeSet去重
添加到TreeSet,需要实现Comparable接口,即实现compareTo方法
与hashCode和equals无关,只与compareTo有关


import java.util.*;
class Dog implements Comparable{
int age;
public Dog(int a) {
this.age=a;
}
public int getAge() {
return this.age;
}
public int hashCode() {
System.out.println("hashCode exec...");
return this.age;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj2) {
System.out.println("equals exec...");
if(0==this.age-((Dog)obj2).getAge())
return true;
else
return false;
}
public String toString() {
System.out.println("toString exec...");
return age+"";
}
public int compareTo(Object obj2) {
System.out.println("compareTo exec...");
return this.age - ((Dog)obj2).getAge();
}
}
public class CompareTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog d1=new Dog(10);
Dog d2=new Dog(10);
TreeSet<Dog> hs=new TreeSet<Dog>();
hs.add(new Dog(10));
hs.add(new Dog(1));
hs.add(new Dog(3));
hs.add(new Dog(10));
hs.add(new Dog(10));
System.out.println(hs.size());
}
}
View Code
compareTo exec...
compareTo exec...
compareTo exec...
compareTo exec...
compareTo exec...
compareTo exec...
compareTo exec...
compareTo exec...
3
可以知道,去重和hashCode与equals无关,不执行。而是直接去找compareTo方法
六:总结
(一)HashSet, LinkedHashSet, TreeSet的元素都只能是对象
(二)HashSet和LinkedHashSet判定元素重复的原则《重点》
–判定两个元素的hashCode返回值是否相同,若不同,返回false
–若两者hashCode相同,判定equals方法,若不同,返回false;否则返回true。
–hashCode和equals方法是所有类都有的,因为Object类有
(三)TreeSet判定元素重复的原则《重点》
–需要元素继承自Comparable接口
–比较两个元素的compareTo方法
(四)注意:对于基本类型的包装类。本来就实现了compareTo接口和其他比较方法,所以HashSet,LinkedHashSet,TreeSet中对于包装类是默认去重的