环境介绍:
nginx负载:1.135;后端web:1.131、1.132
1、下载 nginx_upstream_check_module模块
cd /usr/local/src
wget https://codeload.github.com/yaoweibin/nginx_upstream_check_module/zip/master
unzip master
#之前没安装依赖环境需要安装以下依赖包
yum -y install gcc zlib zlib-devel pcre-devel openssl openssl-deve
2、为nginx打补丁(之前已经安装过nginx了需要重新编译)
cd ../nginx-1.16.1/
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop
#根据自己的nginx版本选择对应的插件版本
patch -p1 </usr/local/src/nginx_upstream_check_module-master/check_1.16.1+.patch
patching file src/http/modules/ngx_http_upstream_hash_module.c patching file src/http/modules/ngx_http_upstream_ip_hash_module.c patching file src/http/modules/ngx_http_upstream_least_conn_module.c patching file src/http/ngx_http_upstream_round_robin.c patching file src/http/ngx_http_upstream_round_robin.h
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx-1.16.1 --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_stub_status_module --add-module=/usr/local/src/nginx_upstream_check_module-master/
make (注意:此处只make,编译参数需要和之前的一样)
mv /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx.bak
cp ./objs/nginx /usr/local/nginx/sbin/
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -V
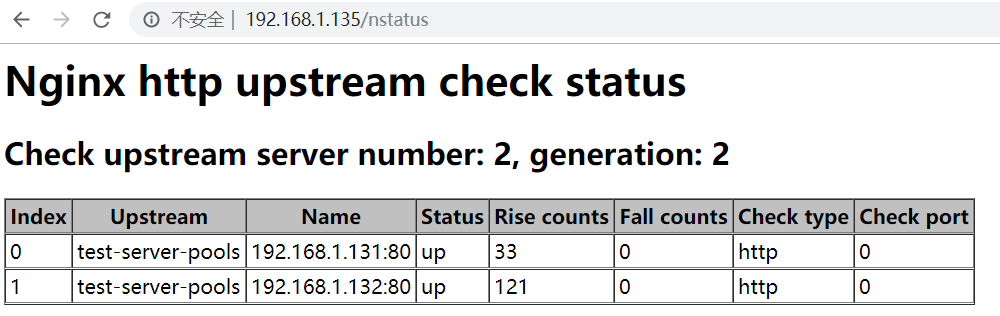
3、在nginx.conf配置文件中的upstream加入检查检查;
upstream test-server-pools { #ip_hash; server 192.168.1.131:80; server 192.168.1.132:80; check interval=3000 rise=2 fall=5 timeout=2000 type=http; #每3秒监测一次,2次正常则为UP,5次失败后为down,超时时间为2秒,检查类型为http; }
Syntax: check interval=milliseconds [fall=count] [rise=count] [timeout=milliseconds] [default_down=true|false] [type=tcp|http|ssl_hello|mysql|ajp] [port=check_port] Default: 如果没有配置参数,默认值是:interval=30000 fall=5 rise=2 timeout=1000 default_down=true type=tcp Context: upstream 该指令可以打开后端服务器的健康检查功能。 指令后面的参数意义是: interval:向后端发送的健康检查包的间隔。 fall(fall_count): 如果连续失败次数达到fall_count,服务器就被认为是down。 rise(rise_count): 如果连续成功次数达到rise_count,服务器就被认为是up。 timeout: 后端健康请求的超时时间。 default_down: 设定初始时服务器的状态,如果是true,就说明默认是down的,如果是false,就是up的。默认值是true,也就是一开始服务器认为是不可用,要等健康检查包达到一定成功次数以后才会被认为是健康的。 type:健康检查包的类型,现在支持以下多种类型 tcp:简单的tcp连接,如果连接成功,就说明后端正常。 ssl_hello:发送一个初始的SSL hello包并接受服务器的SSL hello包。 http:发送HTTP请求,通过后端的回复包的状态来判断后端是否存活。 mysql: 向mysql服务器连接,通过接收服务器的greeting包来判断后端是否存活。 ajp:向后端发送AJP协议的Cping包,通过接收Cpong包来判断后端是否存活。 port: 指定后端服务器的检查端口。你可以指定不同于真实服务的后端服务器的端口,比如后端提供的是443端口的应用,你可以去检查80端口的状态来判断后端健康状况。默认是0,表示跟后端server提供真实服务的端口一样。该选项出现于Tengine-1.4.0。