1、python数据结构之元组
1.1、元组特点
(1)元组特点:有序,不可变;可以理解为不可变的列表;
(2)元组与列表的不同:
# 元组tuple,可hash,不可变数据类型,()表示;一般元组用来存储结构化数据,一般每个字段的意义不同;
import time print(time.localtime()) ''' (tm_year=2018, tm_mon=8, tm_mday=15, tm_hour=10, tm_min=40, tm_sec=4, tm_wday=2, tm_yday=227, tm_isdst=0) '''
# 列表list,不可hash,可变数据类型,[]表示;一般列表存储的是同类型的顺序数据;
l=list(range(6)) print(l) ''' [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5] '''
1.2、元组的定义与初始化
(1)元组的定义:
tuple() -> empty tuple
tuple(iterable) -> tuple initialized from iterable's items
t=tuple() # 工厂方法
t=() # 定义一个空元组
t=tuple(range(5))
t=(1,) # 定义一个元素的元组的时候一定记住后面跟一个逗号,否则定义的不是元组;
1 t1=(1) 2 t2=(1,) 3 print(type(t1),type(t2)) 4 ''' 5 <class 'int'> <class 'tuple'> 6 '''
1.3、元组的访问
# 元组的访问跟列表的访问方法一样,都是通过索引访问;
1.4、元组的查询
(1)index(value,[start,[stop])
通过值value,从指定区间查找元组内的元素是否匹配;
匹配到一个就返回索引;
匹配不到抛出异常valueError;
(2)count(value)
返回元组内匹配到value值的次数
# index和count的时间复杂度都是O(n),随着n的规模增大,效率越低;
2、python 字符串
2.1、字符串的定义与初始化
(1)字符串特点:有序可索引,可迭代,不可变数据类型;
(2)字符串定义与初始化:
1 class str(object): 2 """ 3 str(object='') -> str 4 str(bytes_or_buffer[, encoding[, errors]]) -> str
例如:
s1='hello world'
s2="I'm jerry" # 注意:如果内层有引号,则外层必须用不一样的;
s3=r'hello world' # 前面加r表示里面的所有字符都不做特殊处理
2.2、字符串连接
(1)字符串join连接
1 def join(self, iterable): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 2 """ 3 S.join(iterable) -> str 4 5 Return a string which is the concatenation of the strings in the 6 iterable. The separator between elements is S. # 元素之间的分隔符是S 7 """ 8 return ""
# 将可迭代对象连接起来,使用S作为分隔符;
# 返回一个新的字符串;
# 例如: str=‘hello’ ==>'@'.join(str) ==> h@e@l@l@o
(2)字符串'+'连接
# '+'将2个字符串连接在一起,返回一个新的字符串;本质上'+'调用的是__add__方法;
2.3、字符串分割
# 字符串的分割分为2中方法:
(1)split(sep=None, maxsplit=-1)
1 def split(self, sep=None, maxsplit=-1): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 2 """ 3 S.split(sep=None, maxsplit=-1) -> list of strings 4 5 Return a list of the words in S, using sep as the 6 delimiter string. If maxsplit is given, at most maxsplit 7 splits are done. If sep is not specified or is None, any 8 whitespace string is a separator and empty strings are 9 removed from the result. 10 """ 11 return []
# 从左至右,按照分隔符sep进行切分;
# 'sep=', 指定分隔符,默认空白字符串作为分隔符;
# 'maxsplit=',可以指定最大分割次数,如果不指定则遍历所有字符串进行分割;
str1='helloler'
lst1=str1.split('l',1) # 最大分割默认==>['he', 'loler']
lst2=str1.split('l') # ==> 最大分割1次['he', '', 'o', 'er']
# rsplit:从右至左分割;
s='00100110'
print(s.rsplit('0',1))
'''
['0010011', '']
'''
(2)partition(self, sep) , sep分隔符必须指定;
1 def partition(self, sep): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 2 """ 3 S.partition(sep) -> (head, sep, tail) # 根据分隔符分成三部分(一刀两断),返回一个tuple; 4 5 Search for the separator sep in S, and return the part before it, 6 the separator itself, and the part after it. If the separator is not 7 found, return S and two empty strings. 8 """
# 从左至右进行分割,遇到分隔符就把字符串分割成两部分,返回头部,分隔符,尾部组成的三元组;
# 如果没有找到分隔符,则返回字符串整体(头部),2个空元素的三元组;
# rpartition,从右至左开始切;
str1='helloler'
lst3=str1.partition('l') # ==>('he', 'l', 'loler') <class 'tuple'>
lst4=str1.rpartition('l') # ==>('hello', 'l', 'er')
print(lst3)
print(lst4)
'''
('hello', 'l', 'er')
('he', 'l', 'loler')
'''
2.4、字符串大小写
# str.upper() 全大写
# str.lower() 全小写
2.5、字符串排版
1 str1='hello ,world' 2 3 print(str1.title()) # 标题字符大写 4 ''' 5 Hello ,World 6 ''' 7 print(str1.center(20,'#')) # 宽度20个字符,str1居中打印,空白用#填充 8 ''' 9 ####hello ,world#### 10 ''' 11 print(str1.zfill(20)) # 宽度20,右对齐,空白字符用0填充 12 ''' 13 00000000hello ,world 14 ''' 15 print(str1.rjust(20,'@')) # 宽度20,右对齐,空白字符用@填充 16 ''' 17 @@@@@@@@hello ,world 18 ''' 19 print(str1.ljust(20,'@')) # 宽度20,左对齐,空白字符用@填充 20 ''' 21 hello ,world@@@@@@@@ 22 '''
2.6、字符串的修改
# 由于字符串是不可变数据类型,不能修改,这里的修改都是修改后返回新的字符串(原来字符串没有改变);
(1)replace(old,new[,count]) ==> new str
def replace(self, old, new, count=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ S.replace(old, new[, count]) -> str Return a copy of S with all occurrences of substring old replaced by new. If the optional argument count is given, only the first count occurrences are replaced. """ return ""
例如:
str1='hello ,world'
s=str1.replace('l','G',2) # 将字符串str1中的l替换为G,只替换1次;
print(s) # ==> heGGo ,world
(2)strip([chars]) ==> new str
# 从字符串的两端去除指定字符集chars中的所有字符;
# 如果chars没有被指定,则去除两端的空白字符;
# lstrip 从左边开始;
# rstrip 从右边开始;
1 def strip(self, chars=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 2 """ 3 S.strip([chars]) -> str 4 5 Return a copy of the string S with leading and trailing 6 whitespace removed. 7 If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead. 8 """ 9 return ""
2.7、字符串的查找与判断
## 字符串的查找
(1)find(sub[,start[,end]]) ==> int
# 在指定区间,从左至右,查找子串sub,找到立即返回索引,没找到返回-1;
(2)index(sub,[,start[,end]]) ==> int
# 类似于通过value查找索引号;
## 字符串的判断
(1)endswith(suffix,[,start[,end]]) ==>bool
# 在指定区间,字符串是否以suffix(词尾)结尾;
(2)startswith(prefix,[,start[,end]]) ==>bool
# 在指定区间,字符串是否以prefix(词首)开头;
## 字符串判断is系列
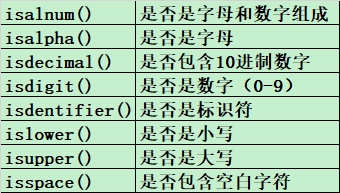
2.8、字符串格式化
# python中的格式化输入有2种:printf 风格和format(推荐使用)
(1)printf-style formatting,来自于c语言的风格
格式要求:
- 占位符:使用%和格式字符串组成,例如%s,%d等
- 占位符中可以插入修饰符,例如%03d表示,打印3个位置,不够前面补0;
- format % value,格式化字符串和被格式的值之间使用%分隔,如果要打印%则用%%
- vaule只能是一个对象,或者是一个和格式化字符串占位符数目相等的元组,或一个字典
print('my name is %s,my age is %03d, %d%% ' %('jerry',18,10)) ''' my name is jerry,my age is 018, 10% '''
(2)format(*args,**kwargs)
- "{}{xxx}".format(*args,**kwargs) ==> str
- args是位置参数,接受一个元组;
- **kwargs是关键字参数,接受一个字典;
- 花括号表示占位符
- {}表示按照顺序匹配位置参数,{n}表示取位置参数的索引为n的值;
1 print("{}{}".format('192.168.19.1',':8080')) # ==>192.168.19.1:8080 3 # args=('192.168.19.1','8080') 4 5 print("{server}{1}{0}".format(':8080','192.168.10.1',server='webserverIP:')) 6 # ==> webserverIP:192.168.10.1:8080 7 # args=('192.168.19.1','8080'), kwargs={server:'webserverIP:'} 8 9 print("{0[0]}is:{1[1]}:{0[1]}".format(('hello','world'),('19','20'))) 10 # hellois:20:world 11 # 0=args=('hello','world') args[0]='hello' args[1]='world' 12 # 1=args=('19','20') 13 14 from collections import namedtuple 16 Piont=namedtuple('p','x y') 17 p=Piont(4,5) 18 19 print("{0.x}:{0.y}".format(p)) 20 # ==> 4:5
1 print("{:#^30}".format('hello world')) # 长度为30个字符,居中,其他以#填充
2 '''
3 运行结果:#########hello world##########
4 '''
5 print("{:#>30}".format('hello world')) # 右对齐
6 '''
7 运行结果:###################hello world
8 '''
9 print("{:#<30}".format('hello world')) # 左对齐
10 '''
11 运行结果:hello world###################
12 '''
13 print("{:.2f}".format(1.34221)) # 通常都是配合 f 使用,其中.2表示长度为2的精度,f表示float类型
14 '''
15 运行结果:1.34
16 '''
17 print('{:,}'.format(9987733498273.0432))
18 '''
19 运行结果:9,987,733,498,273.043
20 '''
22 print("{:b}".format(10)) # 1010 二进制
23 print("{:o}".format(10)) # 12 八进制
24 print("{:x}".format(10)) # a 十六进制