Objective-C 基础语法详解
雨松MOMO原创文章如转载,请注明:转载至我的独立域名博客雨松MOMO程序研究院,原文地址:http://www.xuanyusong.com/archives/368
如果想从事iphone开发的话 Objective-C 这门语言就不得不学会 我们都知道C语言是没有面向对象的 而Object-C 则是ANSI C 的一个严格超集 它是具有面向对象的特性的 由于IPHONE 的成功 让这门语言现在非常的火热 今天笔者为大家介绍一下在xcode中 使用Objective-C 的基本语法。
1.打开mac系统中强大的Xcode软件 单击Create a new Xcode project 创建一个Xcode项目。

2. 选择“View-based Application” 因为只是介绍基本语法 所以 “View-based Application” 已经够用了 。 选择完后 点击Next 。

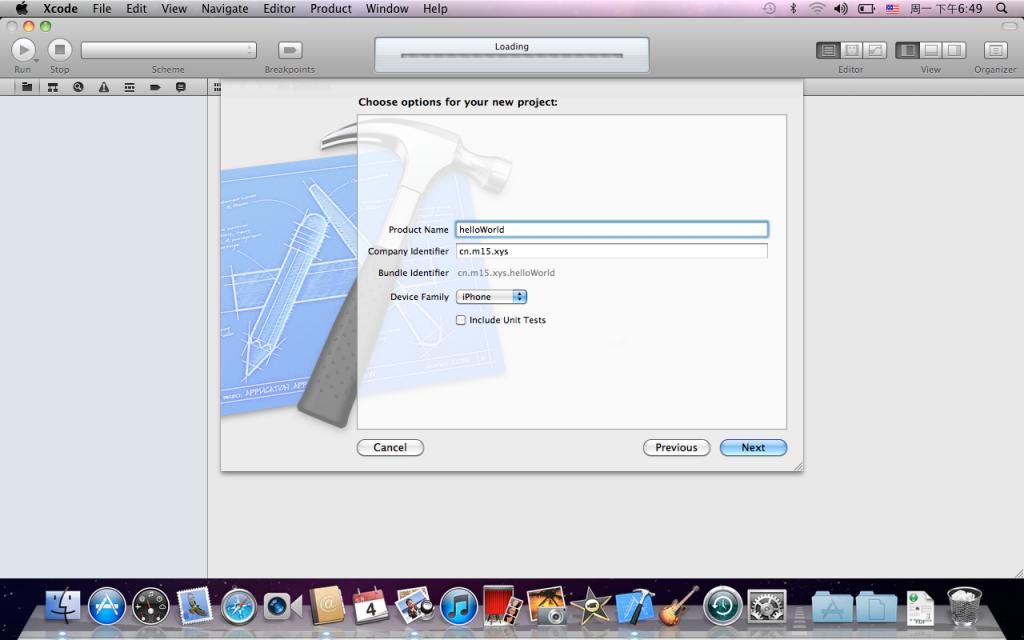
3.输入相应的信息后点击Next。
Product Name: 指产品名称 ,可以随意命名。
Company Identifier: 公司标识符,一般命名规则为 “com.公司名”
Bundle Identifier: 指包标识符,用于唯一标识应用程序,默认会根据公司标识符和产品名来组合生成
Device Family: 指该应用支持的设备类型,共三个选项:iPhone、iPad、Universal(即iPhone、iPad通用)
Include Unite Tests: 是否包含单元测试代码模板,如果勾选,Xcode会帮助生成单元测试代码模板
这样 我们的第一个项目就创建好了,接下来开始为大家介绍 Objective-C 的语法
在项目视图中 打开 helloWorldViewController.m文件 找到 - (void)viewDidLoad 方法 (这个方法每次启动程序都会调用 )
学过C++的朋友应该都知道 新写一个类会有 一个.h 声明类的变量 方法等 .cpp 用来实现方法 Objective-C 则也类似C++ .h 声明类的变量 方法 .m 用来实现方法
在c语言中 我们在控制台输出信息是用printf() Java语言则是 System.out.println() 而Objective-C 则是用 NSLog();

- //
- // helloWorldViewController.m
- // helloWorld
- //
- // Created by 宣雨松 on 11-7-4.
- // Copyright 2011年 __MyCompanyName__. All rights reserved.
- //
- #import "helloWorldViewController.h"
- #import "MyClass.h"//导入新写的类
- @implementation helloWorldViewController
- - (void)dealloc
- {
- [super dealloc];
- }
- - (void)didReceiveMemoryWarning
- {
- // Releases the view if it doesn't have a superview.
- [super didReceiveMemoryWarning];
- // Release any cached data, images, etc that aren't in use.
- }
- #pragma mark - View lifecycle
- // Implement viewDidLoad to do additional setup after loading the view, typically from a
- nib.
- - (void)viewDidLoad
- {
- [super viewDidLoad];
- //打印一个字符串
- NSLog(@"only log hello world");
- //字符串相加
- NSString *str;
- NSString *str1 = @"plusA ";
- NSString *str2 = @"+";
- NSString *str3 = @"plusB";
- // 把str1 str2 str3 相加后赋值给str %@ 表示是一个对象 这里也可以用 %d %s 在这里就不一一举例了。
- str = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@ %@ %@",str1,str2,str3];
- //打印出str
- NSLog(@"string plus %@",str);
- //self 好比C++ 或者 java 语言中的 this 指针 指向本类 这里调用了本类的 putString方法 将字符串"pass string"作为参数传递了进去
- [self putString:@"pass string"];
- //在内存中new了一个MyClass的对象 alloc是在内存中 分配内存 init 则是初始化 这样写 属于规定写法
- MyClass * myclass = [[MyClass alloc] init];
- // 用myclass指针调用 类中putclass方法 将字符串 "pass class string"作为参数传递进去
- [myclass putclass:@"pass class string"];
- //调用类中静态方法 将字符串"static pass class string "作为参数传递进去
- [MyClass staticPutClass:@"static pass class string"];
- }
- - (void)viewDidUnload
- {
- [super viewDidUnload];
- // Release any retained subviews of the main view.
- // e.g. self.myOutlet = nil;
- }
- - (BOOL)shouldAutorotateToInterfaceOrientation:(UIInterfaceOrientation)interfaceOrientation
- {
- // Return YES for supported orientations
- return (interfaceOrientation == UIInterfaceOrientationPortrait);
- }
- //自己写的类方法输出字符串
- -(void)putString:(NSString *)str
- {
- NSLog(@"%@",str);
- }
- @end
//这个类的声明
- #import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
- @interface helloWorldViewController : UIViewController {
- }
- -(void) putString:(NSString*)str;
- @end
- #import "MyClass.h"
- @implementation MyClass
- //方法前是-号的说明这是一个实力方法 必需本类new过才能调用
- -(void)putclass:(NSString *)str
- {
- NSLog(@"%@",str);
- }
- //方法前是+号的说明这是一个类方法 这种方法无权访问实例变量
- //这里声明了一个静态方法 无需本类new过也可以调用
- +(void)staticPutClass:(NSString *)str{
- NSLog(@"%@",str);
- }
- @end
MyClass类的声明
- #import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
- @interface MyClass :NSObject{
- }
- -(void) putclass : (NSString *) str;
- +(void) staticPutClass :(NSString *) str;
- @end
这样Objective-C 基本的语法就给大家介绍完了, 希望有兴趣的朋友可以和我一起讨论 我们可以一起进步。