1、文件对象
文件和文件夹都是用File代表
①使用绝对路径或者相对路径创建File对象
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 绝对路径
File f1 = new File("d:/LOLFolder");
System.out.println("f1的绝对路径:" + f1.getAbsolutePath());
// 相对路径,相对于工作目录,如果在eclipse中,就是项目目录
File f2 = new File("LOL.exe");
System.out.println("f2的绝对路径:" + f2.getAbsolutePath());
// 把f1作为父目录创建文件对象
File f3 = new File(f1, "LOL.exe");
System.out.println("f3的绝对路径:" + f3.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
运行:
f1的绝对路径:d:LOLFolder
f2的绝对路径:E:projectStudyLOL.exe
f3的绝对路径:d:LOLFolderLOL.exe
②文件常用方法:
访问文件名或路径:
1)String getName() 返回File对象所表示的文件名或文件路径
2)String getPath() 返回File对象所对应的相对路径名。
3)File getAbsoluteFile() 返回File对象的绝对路径文件
4)String getAbsolutePath() 返回File对象所对应的绝对路径名
5)String getParent() 返回File对象所对应目录的父目录
6) boolean renameTo(File dest) 重命名File对象的文件或目录
文件检测:
1boolean exists() 判断File对象的文件或目录是否存在
2)bool canWrite() 判断File对象是否可写
3)boolean canRead()判断File对象是否可读
4)boolean isDirectory() 判断File对象是否是目录
5)boolean isFile() 判断File对象是否是文件
6)boolean isAbsolute() 判断File对象是否采用绝对路径
文件信息:
1)long length() ; File对象对应文件的长度
2)long lastNodified() File对象最后修改的时间
文件操作:
1)boolean createNewFile() ; 检查文件是否存在,当文件不存在时创建一个新的文件
2) boolean delete() 删除File对象所对应的文件或目录
目录操作:
1)boolean mkdir() 创建文件夹,如果父文件夹skin不存在,创建就无效
2)boolean f.mkdirs(); 创建文件夹,如果父文件夹skin不存在,就会创建父文件夹
3)String[] list() 列出File对象所有的子文件名和路径名
4)File[] listFile() 列出File对象的所有子文件或路径
5)static File[] listRoots() 列出系统所有的根路径
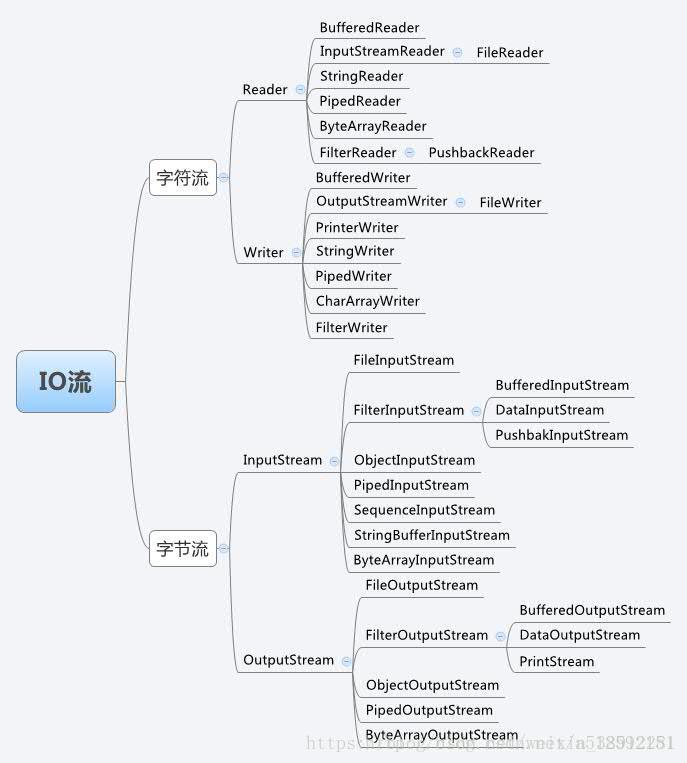
2、字节流、字符流
OutputStream字节输出流,抽象类
FileOutputStream 是OutputStream子类
InputStream字节输入流,抽象类
FileInputStream是InputStream子类
Reader字符输入流 ,抽象类
Writer字符输出流 ,抽象类
FileReader 是Reader子类
FileWriter 是Writer子类
简单的输入、输出操作:
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
FileReader fr = null;
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
fr = new FileReader(new File("d:\text\st01.txt"));
fw = new FileWriter(new File("d:\text\st02.txt"));
char[] c = new char[2];
int n = 0;
while ((n = fr.read(c)) != -1) {
String s = new String(c, 0, n);
System.out.println(s);
fw.write(s);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fr != null)
fr.close();
if(fw!=null)
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
标准的关闭流方式:
File f = new File("d:/lol.txt");
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(f);
byte[] all = new byte[(int) f.length()];
fis.read(all);
for (byte b : all) {
System.out.println(b);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 在finally 里关闭流
if (null != fis)
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
3、缓冲流
缓冲流在写入数据的时候,会先把数据写入到缓存区,直到缓存区达到一定的量(或关闭流),才把这些数据,一起写入到硬盘中去。
按照这种操作模式,就不会像字节流,字符流那样每写一个字节都访问硬盘,从而减少了IO操作
缓存流必须建立在一个存在的流的基础上
缓存字符输入流 BufferedReader 可以一次读取一行数据 String readLine()
PrintWriter 缓存字符输出流, 可以一次写出一行数据 viod println()
有的时候,需要立即把数据写入到硬盘,而不是等缓存满了才写出去。 这时候就需要用到void flush ()方法
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
BufferedReader br = null;
PrintWriter pw = null;
try {
// 准备文件lol.txt其中的内容是
// garen kill teemo
// teemo revive after 1 minutes
// teemo try to garen, but killed again
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File("d:\text\Student.txt")));
pw = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("d:\text\st02.txt")));
String s = "";
//每次读取一行 String readLine()
while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(s);
//每次写入一行 viod println()
pw.println(s);
//强制把缓存中的数据写入硬盘,无论缓存是否已满
pw.flush();
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
//判断并关闭流
if(br!=null)
br.close();
if(pw!=null)
pw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
运行:
garen kill teemo
teemo revive after 1 minutes
teemo try to garen, but killed again