我们经常听的音乐文件格式主要有:mp3,flac和wav等,但是大家有想过这些音频文件通过音频解码器解码后的数据格式是怎么样的?废话不多说,接下来介绍能被设备播放的音频原始数据格式PCM。
一、PCM音频
PCM音频,中文名称:脉冲编码调制,是用于将波形表示的模拟音频信号转换为数字1和0表示的数字音频信号,而不压缩也不丢失信息的处理技术。如下是使用Audacity音频处理软件截取1~2s的时间段内音频波形图:
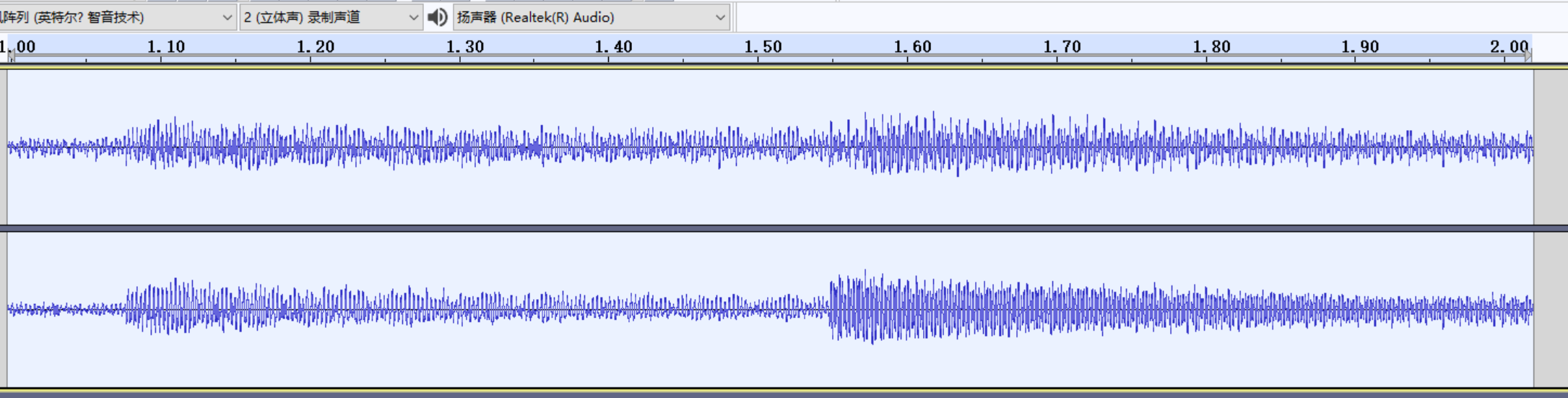
我们再对这个区间的波形图进行放大:
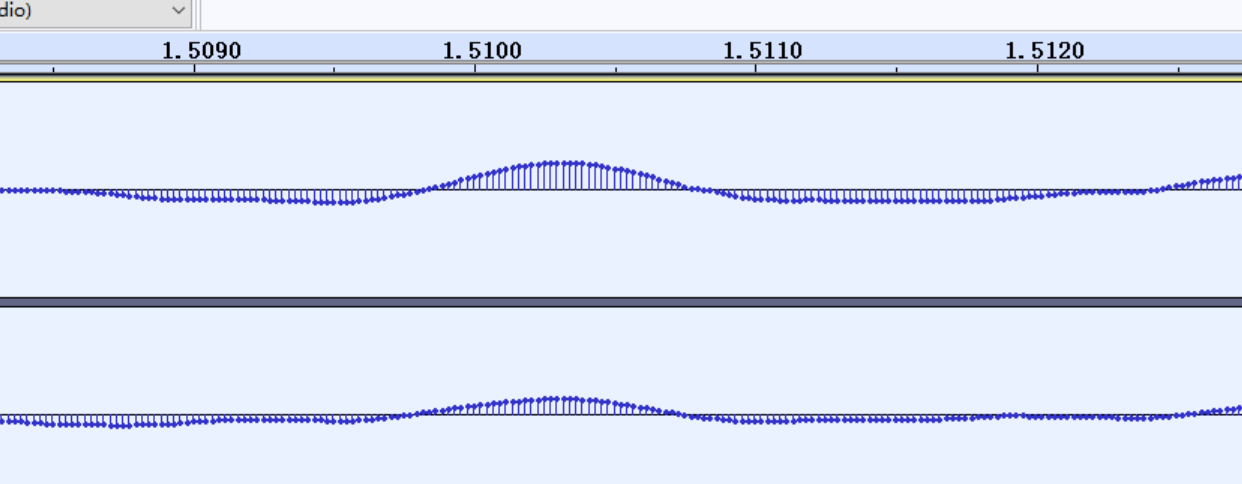
上面一个像火柴棒的是什么?它其实就是一个样本,这里就需要提到PCM音频中涉及的几个重要参数:样本,采样频率,位深和通道。
二、样本
样本:sample,将模拟音频信号振幅通过量化编码方式转换为数字音频信号的数据大小,如下图所示:

三、采样率
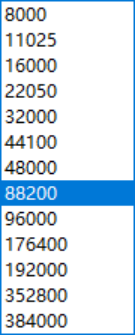
采样率:sampel rate,每秒钟采集的样本数,采样频率一般越大,转换失真越小。常见的采用率有:44100HZ,48000HZ和91KHZ。如下图是Audacity提供的采样率:
四、位深
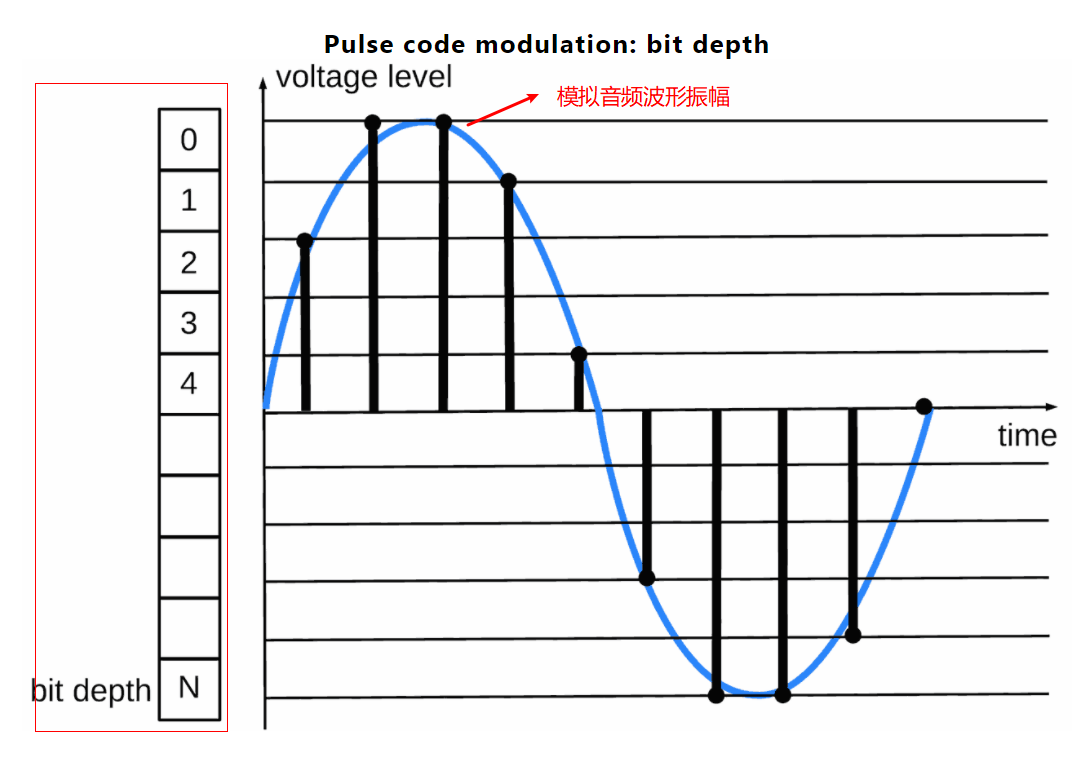
位深度:bit depth,定义了可以存储的数字电平的数量;位深越大,存储的信息越详细,保真度越好。如下图所示:
五、声道
声道:channel,表示音频采集源的个数,比如:单声道,采集源只有一个;双声道(立体声),采集源有两个,分别为左和右;多声道(环绕声),采集源有多个。声道越多,播放的音频效果越立体,但是存储的数据越大。
Audacity提供的声道列表如下:
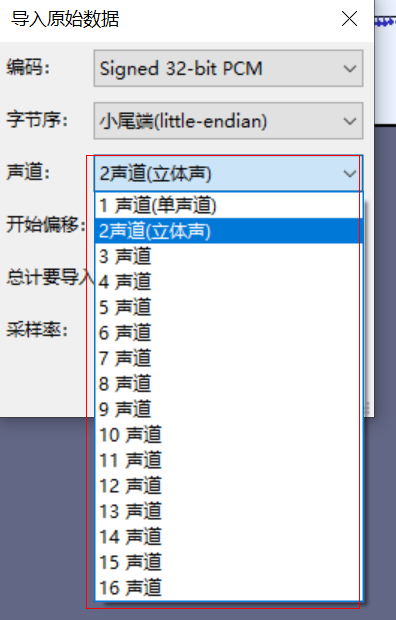
位深8bits的样本数据存放格式如下:
单声道:
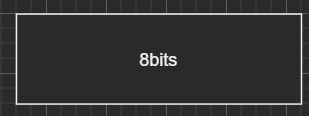
双声道:
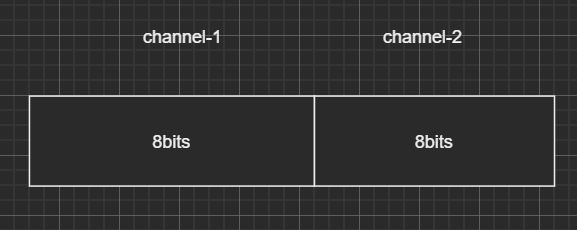
三声道:
对于多声道(大于一个声道)的PCM音频,在实际编码中,我们也按照单声道处理,统称为一个采样,如上面的单声道,双声道和三声道的一个采样大小分别为:8bits,18bits和24bits;可以将多声道分离为一个个单声道。
六、参数之间的关系
通过上面的介绍,我们可以得出如下关系:
- sample_bits = depth_bits
- channels_sample_bits = sample_bits* channel
- samples_bits_per_second = sample_rate * depth_bits * channel = sampe_rate * sample_bits * channel;
七、小试牛刀
PCM格式音频样本参数:44100HZ + 16bits + 2channel。
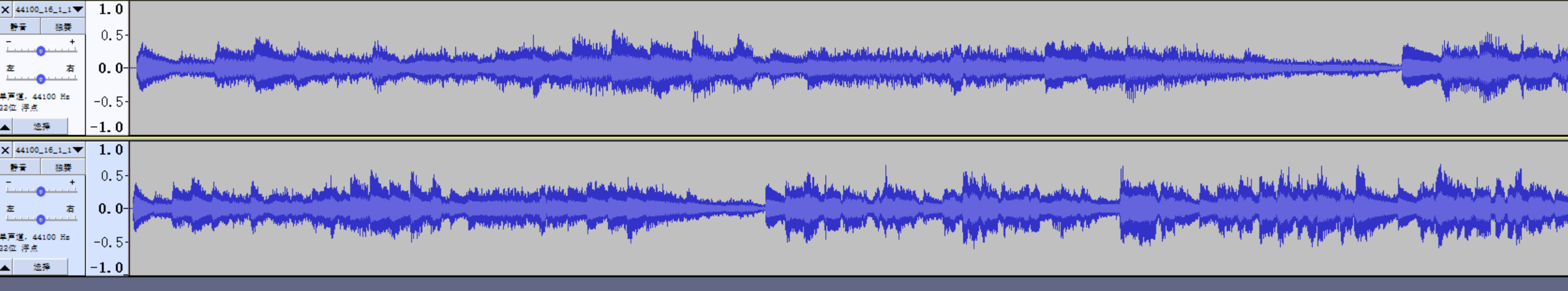
分离双声道为单声道:
1 void SeparateChannel() 2 { 3 const auto originalFilename = R"(44100_16_2.pcm)"; 4 ifstream inFStream(originalFilename, ios_base::binary); 5 6 if (!inFStream.is_open()) { 7 cout << "read <" << originalFilename << "> failed. "; 8 return; 9 } 10 const auto separateFilename1 = R"(44100_16_1_1.pcm)"; 11 const auto spearateFilename2 = R"(44100_16_1_2.pcm)"; 12 ofstream outFStream1(separateFilename1, ios_base::out | ios_base::binary); 13 ofstream outFStream2(spearateFilename2, ios_base::out | ios_base::binary); 14 auto fileBuf = inFStream.rdbuf(); 15 unique_ptr<char[]> buf = make_unique<char[]>(kSampleBitsPer / 8); 16 while (!inFStream.eof()){ 17 memset(buf.get(), 0xff, kSampleBitsPer / 8); 18 auto len = fileBuf->sgetn(buf.get(), kSampleBitsPer / 8); 19 20 if (len != kSampleBitsPer / 8) { 21 break; 22 } 23 24 outFStream1.write(buf.get(), kDstSampleBitsPer / 8); 25 outFStream2.flush(); 26 outFStream2.write(buf.get() + kDstSampleBitsPer / 8, kDstSampleBitsPer / 8); 27 outFStream2.flush(); 28 } 29 30 outFStream1.close(); 31 outFStream2.close(); 32 inFStream.close(); 33 }
生成音频文件波形图如下:
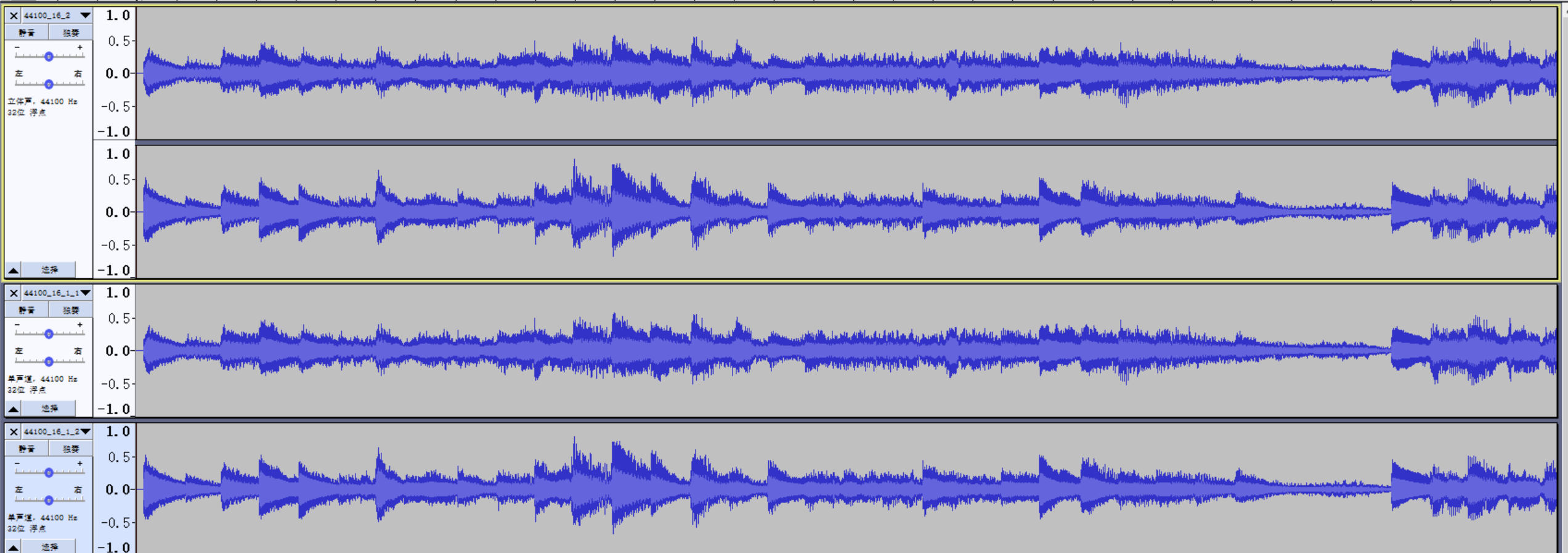
16bits转换为8bits
1 void SeparateBitsDeepth() 2 { 3 const auto originalFilename = R"(44100_16_1_1.pcm)"; 4 ifstream inFStream; 5 auto fileBuf = inFStream.rdbuf(); 6 fileBuf->open(originalFilename, ios_base::binary | ios_base::in); 7 if (!fileBuf->is_open()) { 8 cout << "read <" << originalFilename << "> failed. "; 9 return; 10 } 11 12 const auto outFStreamFilename1 = R"(44100_8_1.pcm)"; 13 ofstream outFStream(outFStreamFilename1, ios_base::binary); 14 unique_ptr<char[]> buf = make_unique<char[]>(kDstSampleBitsPer / 8); 15 while (!inFStream.eof()) { 16 memset(buf.get(), 0xff, kDstSampleBitsPer / 8); 17 auto len = fileBuf->sgetn(buf.get(), kDstSampleBitsPer / 8); 18 if (len != kDstSampleBitsPer / 8) { 19 break; 20 } 21 22 auto sample8BitsU = ((*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*>(buf.get()) >> 8)) + 128; // 这一步 23 outFStream.write(reinterpret_cast<char*>(&sample8BitsU), 1); 24 outFStream.flush(); 25 } 26 27 outFStream.close(); 28 inFStream.close(); 29 }


音量减半:
1 void Half() 2 { 3 const auto originalFilename = R"(44100_16_1_2.pcm)"; 4 ifstream inFStream; 5 auto fileBuf = inFStream.rdbuf(); 6 fileBuf->open(originalFilename, ios_base::binary | ios_base::in); 7 if (!fileBuf->is_open()) { 8 cout << "read <" << originalFilename << "> failed. "; 9 return; 10 } 11 12 const auto outFStreamFilename1 = R"(44100_16_1_2_half.pcm)"; 13 ofstream outFStream(outFStreamFilename1, ios_base::binary); 14 unique_ptr<char[]> buf = make_unique<char[]>(2); 15 while (!inFStream.eof()) { 16 memset(buf.get(), 0xff, 2); 17 auto len = fileBuf->sgetn(buf.get(), 2); 18 if (len != 2) { 19 break; 20 } 21 22 auto sampleL = reinterpret_cast<short*>(buf.get()); 23 *sampleL = *sampleL / 2; // 将样本数大小取一半 24 outFStream.write(buf.get(), 2); 25 outFStream.flush(); 26 } 27 28 outFStream.close(); 29 inFStream.close(); 30 }

音频双倍数:
1 void DoubleSpeed() 2 { 3 const auto originalFilename = R"(44100_16_1_1.pcm)"; 4 ifstream inFStream; 5 auto fileBuf = inFStream.rdbuf(); 6 fileBuf->open(originalFilename, ios_base::binary | ios_base::in); 7 if (!fileBuf->is_open()) { 8 cout << "read <" << originalFilename << "> failed. "; 9 return; 10 } 11 12 const auto outFStreamFilename1 = R"(44100_16_1_1_double_speed.pcm)"; 13 ofstream outFStream(outFStreamFilename1, ios_base::binary); 14 unique_ptr<char[]> buf = make_unique<char[]>(2); 15 int cnt = 0; 16 while (!inFStream.eof()) { 17 memset(buf.get(), 0xff, 2); 18 auto len = fileBuf->sgetn(buf.get(), 2); 19 if (len != 2) { 20 break; 21 } 22 // 奇数采样 23 if (++cnt % 2 != 0) { 24 outFStream.write(buf.get(), 2); 25 outFStream.flush(); 26 } 27 28 } 29 30 outFStream.close(); 31 inFStream.close(); 32 }
参考:
- https://samplerateconverter.com/educational/pcm-audio#what-pcm
- 视音频数据处理入门:PCM音频采样数据处理_雷霄骅(leixiaohua1020)的专栏-CSDN博客_pcm数据