网格布局
网格布局由GridLayout所代表,它是Android 4.0 新增的布局管理器,因此需要在Android 4.0之后的版本中才能使用该布局管理器。如果希望在更早的Android平台上使用该布局管理器,则需要导入相应的支撑库。
GridLayout的作用类似于HTML中的table标签,它把整个容器划分成rows*columns个网格,每个网格可以放置一个组件。除此之外,也可以设置一个组件横跨多少列、一个组件纵跨多少行。
GridLayout提供了setRowCount(int)和setColumnCount(int)方法来控制该网格的行数量和列数量。
GridLayout常用的XML属性及相关方法
android:alignmentMode——setAlignmentMode(int)
设置该布局管理器采用的对齐模式
android:columnCount——setColumnCount(int)
设置该网络的列数量
android:columnOrderPreserved——setColumnOrderPreserved(boolean)
设置该网络容器是否保留列序号
android:rowCount——setRowCount(int)
设置该网络的行数量
android:rowOrderPreserved——setRowOrderPreserved(boolean)
设置该网络容器是否保留行序号
android:useDefaultMargins——setUseDefaultMargins(boolean)
设置该布局管理器是否使用默认的页边距
为了控制GridLayout布局容器中各子组件的布局分布,GridLayout提供了一个内部类:GridLayout.LayoutParams,该类提供了大量的XML属性来控制GridLayout布局容器中子组件的布局分布。
下面显示了GridLayout.LayoutParams常用的XML属性及相关方法
android:layout_column
设置该子组件在GridLayout的第几列
android:layout_columnSpan
设置该子组件在GridLayout横向上跨几列
android:layout_gravity——setGravity(int)
设置该子组件采用何种方式占据该网格的空间
android:layout_row
设置该子组件在GridLayout的第几行
android:layout_rowSpan
设置该子组件在GridLayout纵向上跨几行
计算器界面
效果图:
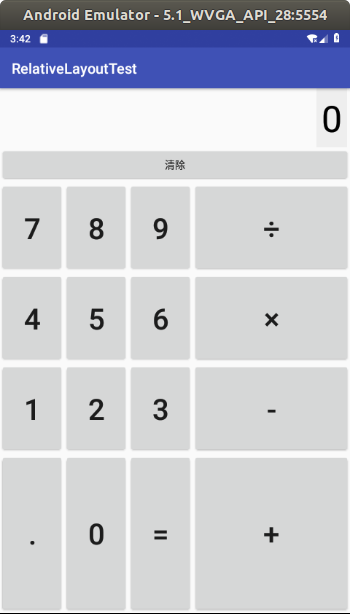
layout.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <GridLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:rowCount="6" android:columnCount="4" android:id="@+id/root"> <!--定义一个横跨4列的文本框,并设置该文本框的前景色、背景色等属性--> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_columnSpan="4" android:textSize="50sp" android:layout_marginLeft="2pt" android:layout_marginRight="2pt" android:padding="3pt" android:layout_gravity="right" android:background="#eee" android:textColor="#000" android:text="0"/> <!--定义一个横跨4列的按钮--> <Button android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_columnSpan="4" android:text="清除"/> </GridLayout>
MainActivity.java
1 package com.example.aimee.relativelayouttest; 2 3 import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity; 4 import android.os.Bundle; 5 import android.view.Gravity; 6 import android.widget.Button; 7 import android.widget.GridLayout; 8 import android.widget.LinearLayout; 9 10 public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { 11 12 GridLayout gridLayout; 13 LinearLayout linearLayout; 14 //定义16个按钮的文本 15 String[] chars = new String[]{ 16 "7","8","9","÷", 17 "4","5","6","×", 18 "1","2","3","-", 19 ".","0","=","+" 20 }; 21 22 @Override 23 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 24 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 25 setContentView(R.layout.layout); 26 gridLayout = (GridLayout) findViewById(R.id.root); 27 for (int i=0;i<chars.length;i++){ 28 Button bn = new Button(this); 29 bn.setText(chars[i]); 30 //设置该按钮的字号大小 31 bn.setTextSize(40); 32 //设置按钮四周的空白区域 33 bn.setPadding(5,35,5,35); 34 //指定该组件所在的行 35 GridLayout.Spec rowSpec = GridLayout.spec(i /4 + 2); 36 //指定该组件所在的列 37 GridLayout.Spec columnSpec = GridLayout.spec(i % 4); 38 GridLayout.LayoutParams params = new GridLayout.LayoutParams(rowSpec,columnSpec); 39 //指定该组件占满父容器 40 params.setGravity(Gravity.FILL); 41 gridLayout.addView(bn,params); 42 } 43 } 44 }