转自:https://blog.csdn.net/gqtcgq/article/details/53883546
C程序运行时,经常会碰到”segmentfault”错误。这是由于程序中非法访问内存导致的。当操作系统的内存保护机制发现进程访问了非法内存的时候会向此进程发送一个SIGSEGV信号,导致进程直接退出,并在shell中提示segment fault。
因此,可以通过设置SIGSEGV信号处理函数,在处理函数中调用backtrace系列函数得到异常时的函数调用栈信息。
一:backtrace
backtrace系列函数的原型如下:
-
-
-
int backtrace(void **buffer, int size);
-
char **backtrace_symbols(void *const *buffer, int size);
-
void backtrace_symbols_fd(void *const *buffer, int size, int fd);
backtrace函数通过指针数组buffer返回调用程序的回溯信息,也就是所谓的函数调用栈。buffer数组中的元素是void*类型,也就是栈中保存的返回地址。
size参数指定buffer中可以保存的地址的最大个数。如果实际的回溯信息大于size,则只返回最近的size个地址。
backtrace函数返回buffer中保存的地址个数,返回值不会大于size。如果返回值小于size,则说明所有的回溯信息都已经返回了,如果等于size,则有可能被截断了。
backtrace函数在buffer数组中返回的都是一些虚拟地址,不适于分析。backtrace_symbols函数可以将backtrace返回的buffer中的地址,根据符号表中的信息,转换为字符串(函数名+偏移地址)。size参数指明了buffer中的地址个数。
backtrace_symbols返回字符串数组的首地址,该字符串是在backtrace_symbols中通过malloc分配的,因此,调用者必须使用free释放内存。如果发生了错误,则backtrace_symbols返回NULL。
backtrace_symbols_fd类似于backtrace_symbols,只不过它是把字符串信息写到文件描述符fd所表示的文件中。backtrace_symbols_fd不会调用malloc函数。
注意,编译器的优化策略,可能导致得到的回溯信息不准确。而且,对于GUN编译器而言,必须使用-rdynamic链接选项,才能正确解析出符号名。
二:示例
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
static void sig_handler(int sig, siginfo_t *info, void *secret)
-
{
-
ucontext_t *uc = (ucontext_t*) secret;
-
-
void *buffer[BTSIZE];
-
char **strings;
-
int nptrs = 0;
-
-
printf("in sig_handler ");
-
printf("sig is %d, SIGSEGV is %d ", sig, SIGSEGV);
-
printf("info.si_signo is %d, info.si_addr is %p ",
-
info->si_signo, info->si_addr);
-
-
if (sig == SIGSEGV)
-
{
-
nptrs = backtrace(buffer, BTSIZE);
-
printf("backtrace() returned %d addresses ", nptrs);
-
-
strings = backtrace_symbols(buffer, nptrs);
-
if (strings == NULL)
-
{
-
perror("backtrace_symbols");
-
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
-
}
-
-
printf("backtrace: ");
-
int j = 0;
-
for (j = 0; j < nptrs; j++)
-
{
-
printf("[%d]%s ", j, strings[j]);
-
}
-
free(strings);
-
-
exit(0);
-
}
-
}
-
-
void fun3()
-
{
-
int *ptr = (int *)0x123;
-
printf("this is fun3 ");
-
-
*ptr = 0;
-
}
-
-
void fun2()
-
{
-
printf("this is fun2 ");
-
fun3();
-
}
-
-
void fun1()
-
{
-
printf("this is fun1 ");
-
fun2();
-
}
-
-
int main()
-
{
-
struct sigaction act;
-
sigemptyset(&act.sa_mask);
-
act.sa_flags = SA_SIGINFO;
-
act.sa_sigaction = sig_handler;
-
sigaction(SIGSEGV, &act, NULL);
-
-
fun1();
-
}
main函数中,使用sigaction设置SIGSEGV信号的处理函数,通过SA_SIGINFO标志,可以得到信号发生时的额外信息,比如引起信号的内存地址等。
在fun3函数中,尝试将内存地址为0x123的内存赋值为0,这是一个明显的非法内存访问,将导致SIGSEGV信号的产生。
在SIGSEGV信号处理函数sig_handler中,首先打印出引起异常的内存地址info->si_addr,然后调用backtrace和backtrace_symbols打印出栈帧。
结果如下:
[root@localhost test]# gcc -o testbacktrace testbacktrace.c
[root@localhost test]# ./testbacktrace
this is fun1
this is fun2
this is fun3
in sig_handler
sig is 11, SIGSEGV is 11
info.si_signo is 11, info.si_addr is 0x123
backtrace() returned 7 addresses
backtrace:
[0]./testbacktrace [0x80485d0]
[1][0xec8440]
[2]./testbacktrace [0x80486ba]
[3]./testbacktrace [0x80486d3]
[4]./testbacktrace [0x804872e]
[5]/lib/libc.so.6(__libc_start_main+0xdc) [0xa9cedc]
[6]./testbacktrace [0x80484a1]
打印出了info.si_addr的值为0x123。并且打印出了7个地址信息。通过objdump,对testbacktrace进行反汇编,可以得到如下信息:
080483e8 <__libc_start_main@plt>:
80483e8: ff 25 40 9a 04 08 jmp *0x8049a40
80483ee: 68 10 00 00 00 push $0x10
80483f3: e9 c0 ff ff ff jmp 80483b8 <_init+0x18>
08048480 <_start>:
...
8048497: 68 d5 86 04 08 push $0x80486d5
804849c: e8 47 ff ff ff call 80483e8 <__libc_start_main@plt>
80484a1: f4 hlt
...
08048554 <sig_handler>:
...
80485cb: e8 78 fe ff ff call 8048448 <backtrace@plt>
80485d0: 89 45 f8 mov %eax,0xfffffff8(%ebp)
0804867f <fun3>:
...
8048685: c7 45 fc 23 01 00 00 movl $0x123,0xfffffffc(%ebp)
804868c: c7 04 24 b1 88 04 08 movl $0x80488b1,(%esp)
8048693: e8 c0 fd ff ff call 8048458 <puts@plt>
8048698: 8b 45 fc mov 0xfffffffc(%ebp),%eax
804869b: c7 00 00 00 00 00 movl $0x0,(%eax)
80486a1: c9 leave
...
080486a3 <fun2>:
...
80486b0: e8 a3 fd ff ff call 8048458 <puts@plt>
80486b5: e8 c5 ff ff ff call 804867f <fun3>
80486ba: c9 leave
...
080486bc <fun1>:
...
80486c9: e8 8a fd ff ff call 8048458 <puts@plt>
80486ce: e8 d0 ff ff ff call 80486a3 <fun2>
80486d3: c9 leave
...
080486d5 <main>:
...
8048724: e8 ff fc ff ff call 8048428 <sigaction@plt>
8048729: e8 8e ff ff ff call 80486bc <fun1>
804872e: 81 c4 a4 00 00 00 add $0xa4,%esp
...
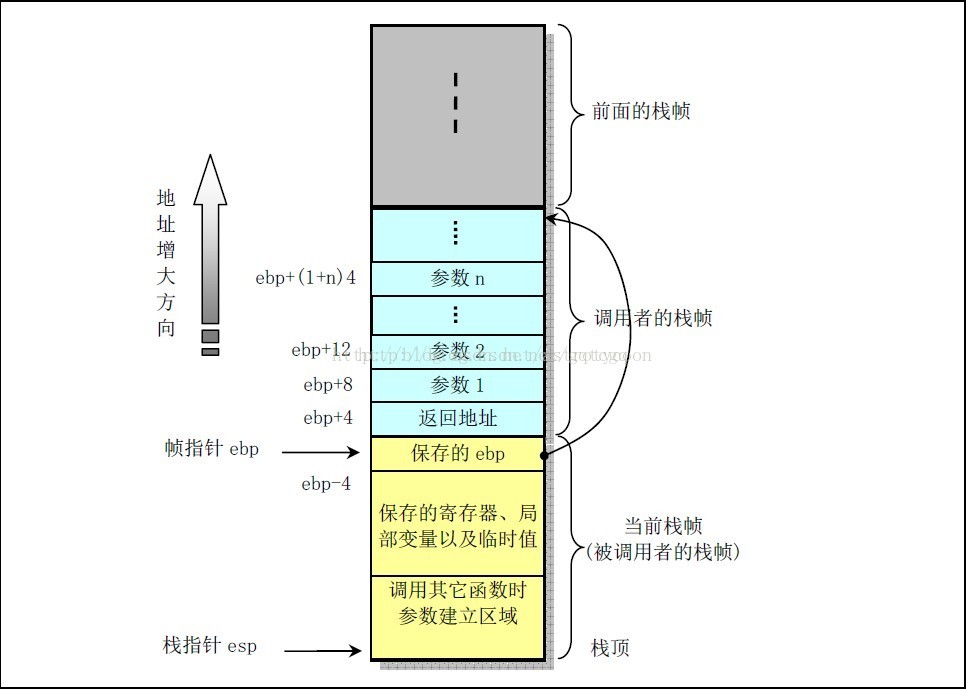
根据上面的反汇编信息,可知backtrace返回的7个地址信息,都是call指令后面紧跟着的指令地址。这是因为call指令在将子程序的起始地址送入指令寄存器(于是CPU的下一条指令就会转去执行子程序)之前,首先会将call指令的下一条指令的所在地址入栈。所以,函数调用时的栈内容如下:
backtrace返回的buffer中保存的地址,就是所有call指令后续紧跟的返回地址。
上面的结果,因为没有加”-rdynamic”链接选项,所以打印出来的都是虚拟地址。增加”-rdynamic”后的结果如下:
[root@localhost test]# gcc -o testbacktrace testbacktrace.c -rdynamic
[root@localhost test]# ./testbacktrace
this is fun1
this is fun2
this is fun3
in sig_handler
sig is 11, SIGSEGV is 11
info.si_signo is 11, info.si_addr is 0x123
backtrace() returned 7 addresses
backtrace:
[0]./testbacktrace [0x80487b0]
[1][0xda2440]
[2]./testbacktrace(fun2+0x17) [0x804889a]
[3]./testbacktrace(fun1+0x17) [0x80488b3]
[4]./testbacktrace(main+0x59) [0x804890e]
[5]/lib/libc.so.6(__libc_start_main+0xdc) [0x3daedc]
[6]./testbacktrace [0x8048681]
这样可以在不使用objdump的情况下,大体了解函数调用的关系了。
三:指令地址
上面通过backtrace可以大体得到”segmentfault”错误时的函数调用栈,然而仅凭backtrace还是不能得到引起异常的指令地址(甚至连引起异常的函数也无法得到)。
在Redis的源码中,看到了打印指令地址的方法。使用ucontext_t结构,打印出指令寄存器的内容。
代码如下:
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
static void *getMcontextEip(ucontext_t *uc) {
-
-
/* OSX < 10.6 */
-
-
return (void*) uc->uc_mcontext->__ss.__rip;
-
-
return (void*) uc->uc_mcontext->__ss.__eip;
-
-
return (void*) uc->uc_mcontext->__ss.__srr0;
-
-
-
/* OSX >= 10.6 */
-
-
return (void*) uc->uc_mcontext->__ss.__rip;
-
-
return (void*) uc->uc_mcontext->__ss.__eip;
-
-
-
/* Linux */
-
-
return (void*) uc->uc_mcontext.gregs[14]; /* Linux 32 */
-
-
return (void*) uc->uc_mcontext.gregs[16]; /* Linux 64 */
-
-
return (void*) uc->uc_mcontext.sc_ip;
-
-
-
return NULL;
-
-
}
-
-
static void sig_handler(int sig, siginfo_t *info, void *secret)
-
{
-
ucontext_t *uc = (ucontext_t*) secret;
-
-
void *buffer[BTSIZE];
-
char **strings;
-
int nptrs = 0;
-
-
printf("in sig_handler ");
-
printf("sig is %d, SIGSEGV is %d ", sig, SIGSEGV);
-
printf("info.si_signo is %d, info.si_addr is %p ",
-
info->si_signo, info->si_addr);
-
-
if (sig == SIGSEGV)
-
{
-
nptrs = backtrace(buffer, BTSIZE);
-
printf("backtrace() returned %d addresses ", nptrs);
-
-
if (getMcontextEip(uc) != NULL)
-
buffer[1] = getMcontextEip(uc);
-
-
strings = backtrace_symbols(buffer, nptrs);
-
if (strings == NULL) {
-
perror("backtrace_symbols");
-
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
-
}
-
-
printf("backtrace: ");
-
int j;
-
for (j = 0; j < nptrs; j++)
-
{
-
printf("[%d]%s ", j, strings[j]);
-
}
-
free(strings);
-
-
exit(0);
-
}
-
}
-
-
void fun3()
-
{
-
int *ptr = (int *)0x123;
-
printf("this is fun3 ");
-
-
*ptr = 0;
-
}
-
-
void fun2()
-
{
-
printf("this is fun2 ");
-
fun3();
-
}
-
-
void fun1()
-
{
-
printf("this is fun1 ");
-
fun2();
-
}
-
-
int main()
-
{
-
struct sigaction act;
-
sigemptyset(&act.sa_mask);
-
act.sa_flags = SA_SIGINFO;
-
act.sa_sigaction = sig_handler;
-
sigaction(SIGSEGV, &act, NULL);
-
-
fun1();
-
}
在使用sigaction函数设置SIGSEGV信号的处理函数时,使用SA_SIGINFO标志,可以得到信号发生时的更多信息。
当信号发生调用处理函数sig_handler时,传递给该函数的第三个参数,是一个ucontext_t类型的结构,该结构在头文件ucontext.h中定义,其中包含了信号发生时的CPU状态,也就是所有寄存器的内容。
函数getMcontextEip用于返回指令寄存器的内容。使用该内容,替换buffer[1]的内容。代码运行结果如下:
-
[root@localhost test]
-
[root@localhost test]# ./testbacktrace
-
this is fun1
-
this is fun2
-
this is fun3
-
in sig_handler
-
sig is 11, SIGSEGV is 11
-
info.si_signo is 11, info.si_addr is 0x123
-
backtrace() returned 7 addresses
-
backtrace:
-
[0]./testbacktrace [0x80487bb]
-
[1]./testbacktrace(fun3+0x1c) [0x804889f]
-
[2]./testbacktrace(fun2+0x17) [0x80488be]
-
[3]./testbacktrace(fun1+0x17) [0x80488d7]
-
[4]./testbacktrace(main+0x59) [0x8048932]
-
[5]/lib/libc.so.6(__libc_start_main+0xdc) [0xd6dedc]
-
[6]./testbacktrace [0x8048681]
可以看见buffer[1]的内容已经被替换成了信号发生时的指令寄存器内容。通过objdump,得到fun3的汇编指令如下:
-
08048883 <fun3>:
-
8048883: 55 push %ebp
-
8048884: 89 e5 mov %esp,%ebp
-
8048886: 83 ec 18 sub $0x18,%esp
-
8048889: c7 45 fc 23 01 00 00 movl $0x123,0xfffffffc(%ebp)
-
8048890: c7 04 24 b1 8a 04 08 movl $0x8048ab1,(%esp)
-
8048897: e8 98 fd ff ff call 8048634 <puts@plt>
-
804889c: 8b 45 fc mov 0xfffffffc(%ebp),%eax
-
804889f: c7 00 00 00 00 00 movl $0x0,(%eax)
-
80488a5: c9 leave
-
80488a6: c3 ret
地址0x804889f就是引起异常的指令地址。