转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/vedic/p/10737453.html
一、几个关键宏定义
CONFIG_DEBUG_LL、 CONFIG_DEBUG_LL_INCLUDE
容我慢慢道来, 首先要使能早期打印, menuconfig必须选中CONFIG_DEBUG_LL, 我们再慢慢梳理其他所以宏及代码
/* linux-3.10.65/arch/arm/kernel/Makefile */
obj-$(CONFIG_DEBUG_LL) += debug.o
obj-$(CONFIG_EARLY_PRINTK) += early_printk.o

我们选中“Kernel low-level debugging functions (read help!)” 在linux-3.10.65/arch/arm/Kconfig.debug 中就是DEBUG_LL
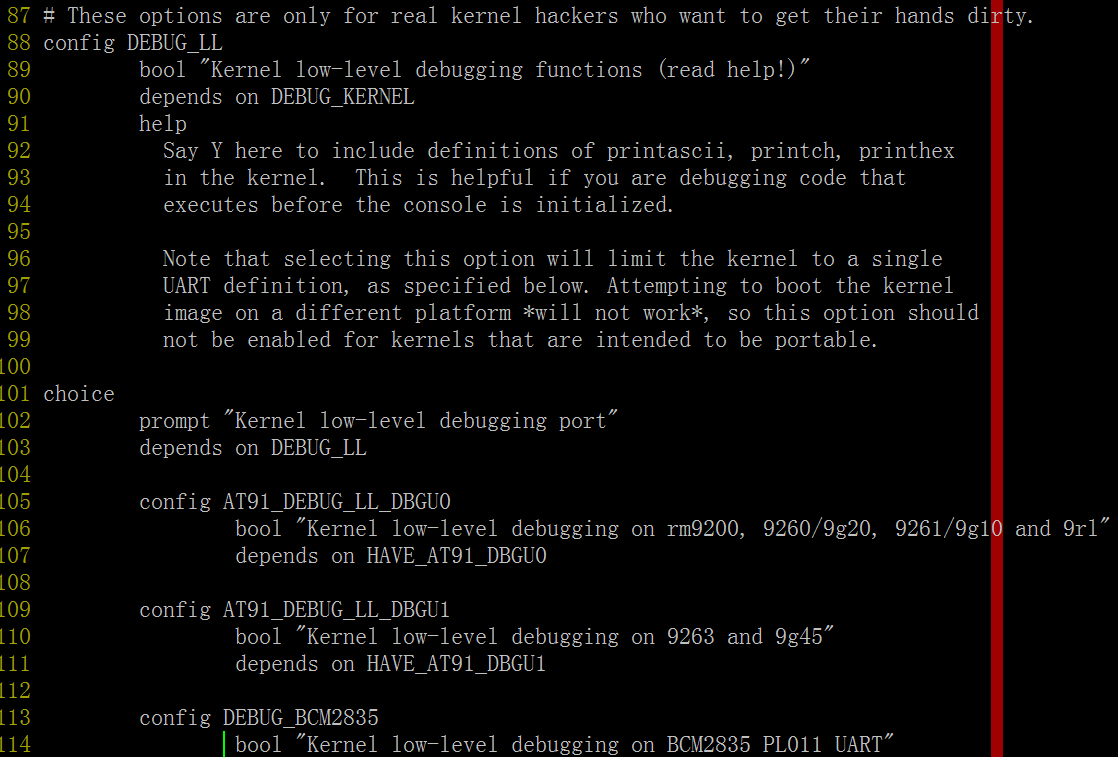
在这个选项中发现还有个依赖的子菜单“Kernel low-level debugging port”, 里面有一堆宏定义如AT91_DEBUG_LL_DBGU0、AT91_DEBUG_LL_DBGU1、
这几个子选项用来干嘛呢? 一是代码文件debug.S(obj-$(CONFIG_DEBUG_LL) += debug.o) 会根据子宏定义走不同的分支; 二是这个代码里会引用宏CONFIG_DEBUG_LL_INCLUDE,
这个宏在“linux-3.10.65/arch/arm/Kconfig.debug”中定义如下:
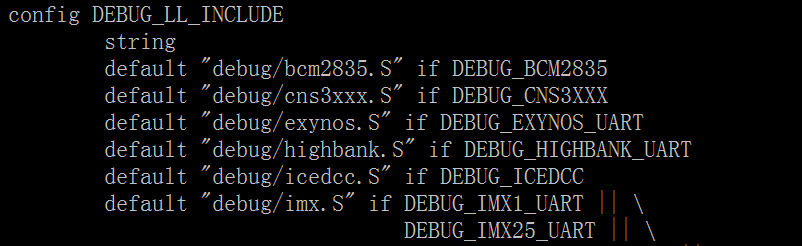
看到没? 子选项定义的DEBUG_BCM2835 在DEBUG_LL_INCLUDE中被依赖了, 也就是我们移植一个新平台, 需要在子选项定义新的宏, 然后在这添加依赖这个新宏对应的文件, 我们现在就这么做:
/* linux-3.10.65/arch/arm/Kconfig.debug */
choice
prompt "Kernel low-level debugging port"
depends on DEBUG_LL
+ config VEDIC_DEBUG_LL
+ bool "I just add a test macro"
config AT91_DEBUG_LL_DBGU0
bool "Kernel low-level debugging on rm9200, 9260/9g20, 9261/9g10 and 9rl"
depends on HAVE_AT91_DBGU0
config DEBUG_LL_INCLUDE
string
+ default "debug/vedic.S" if VEDIC_DEBUG_LL
default "debug/bcm2835.S" if DEBUG_BCM2835
default "debug/cns3xxx.S" if DEBUG_CNS3XXX
接下来我们在menuconfig选中VEDIC_DEBUG_LL宏和添加新文件vedic.S, 如下:

/* linux-3.10.65/.config */
+CONFIG_DEBUG_LL=y
+CONFIG_VEDIC_DEBUG_LL=y
+CONFIG_DEBUG_LL_INCLUDE="debug/vedic.S"
那这个vedic.S该怎么写呢? 我们看同目录下(linux-3.10.65/arch//arm/include/debug/)bcm2835.S文件写了什么:
/*
* Debugging macro include header
*
* Copyright (C) 2010 Broadcom
* Copyright (C) 1994-1999 Russell King
* Moved from linux/arch/arm/kernel/debug.S by Ben Dooks
*
* This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 as
* published by the Free Software Foundation.
*
*/
#define BCM2835_DEBUG_PHYS 0x20201000
#define BCM2835_DEBUG_VIRT 0xf0201000
.macro addruart, rp, rv, tmp
ldr
p, =BCM2835_DEBUG_PHYS
ldr
v, =BCM2835_DEBUG_VIRT
.endm
#include <asm/hardware/debug-pl01x.S>
没错, 就是提供一个函数而已 -> addruart(rp, rv, tmp) , 其实就是返回参数 -- 串口物理地址和串口虚拟地址, 为什么要提供虚拟地址呢? 因为在kernel C语言的第一个入口start_kernel()时, 汇编期间已经开启了MMU, CPU取的都是
虚拟地址; 该函数只是返回地址而已, 如果是开启MMU,返回虚拟地址还不够, 还要事前构建好页表, 不然根据虚拟地址也找不到物理地址。 至于具体在哪里构建页表, 待会说, 根据我目前的硬件平台, 提供文件代码如下:
/* linux-3.10.65/arch/arm/include/debug/vedic.S
* phy_addr is fixed of hardware, but virt_addr? Why 0xF5368000
*/
#define VEDIC_DEBUG_PHYS 0x70400000
#define VEDIC_DEBUG_VIRT 0xF5368000
.macro addruart, rp, rv, tmp
ldr
p, =VEDIC_DEBUG_PHYS
ldr
v, =VEDIC_DEBUG_VIRT
.endm
二、源码分析
为方便待会分批解释功能我先贴出debug.S源码:

1 /*
2 * linux/arch/arm/kernel/debug.S
3 *
4 * Copyright (C) 1994-1999 Russell King
5 *
6 * This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
7 * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 as
8 * published by the Free Software Foundation.
9 *
10 * 32-bit debugging code
11 */
12 #include <linux/linkage.h>
13 #include <asm/assembler.h>
14
15 .text
16
17 /*
18 * Some debugging routines (useful if you've got MM problems and
19 * printk isn't working). For DEBUGGING ONLY!!! Do not leave
20 * references to these in a production kernel!
21 */
22
23 #if !defined(CONFIG_DEBUG_SEMIHOSTING)
24 #include CONFIG_DEBUG_LL_INCLUDE
25 #endif
26
27 #ifdef CONFIG_MMU
28 .macro addruart_current, rx, tmp1, tmp2
29 addruart mp1, mp2,
x
30 mrc p15, 0,
x, c1, c0
31 tst
x, #1
32 moveq
x, mp1
33 movne
x, mp2
34 .endm
35
36 #else /* !CONFIG_MMU */
37 .macro addruart_current, rx, tmp1, tmp2
38 addruart
x, mp1
39 .endm
40
41 #endif /* CONFIG_MMU */
42
43 /*
44 * Useful debugging routines
45 */
46 ENTRY(printhex8)
47 mov r1, #8
48 b printhex
49 ENDPROC(printhex8)
50
51 ENTRY(printhex4)
52 mov r1, #4
53 b printhex
54 ENDPROC(printhex4)
55
56 ENTRY(printhex2)
57 mov r1, #2
58 printhex: adr r2, hexbuf
59 add r3, r2, r1
60 mov r1, #0
61 strb r1, [r3]
62 1: and r1, r0, #15
63 mov r0, r0, lsr #4
64 cmp r1, #10
65 addlt r1, r1, #'0'
66 addge r1, r1, #'a' - 10
67 strb r1, [r3, #-1]!
68 teq r3, r2
69 bne 1b
70 mov r0, r2
71 b printascii
72 ENDPROC(printhex2)
73
74 hexbuf: .space 16
75
76 .ltorg
77
78 #ifndef CONFIG_DEBUG_SEMIHOSTING
79
80 ENTRY(printascii)
81 addruart_current r3, r1, r2
82 b 2f
83 1: waituart r2, r3
84 senduart r1, r3
85 busyuart r2, r3
86 teq r1, #'
'
87 moveq r1, #'
'
88 beq 1b
89 2: teq r0, #0
90 ldrneb r1, [r0], #1
91 teqne r1, #0
92 bne 1b
93 mov pc, lr
94 ENDPROC(printascii)
95
96 ENTRY(printch)
97 addruart_current r3, r1, r2
98 mov r1, r0
99 mov r0, #0
100 b 1b
101 ENDPROC(printch)
102
103 #ifdef CONFIG_MMU
104 ENTRY(debug_ll_addr)
105 addruart r2, r3, ip
106 str r2, [r0]
107 str r3, [r1]
108 mov pc, lr
109 ENDPROC(debug_ll_addr)
110 #endif
111
112 #else
113
114 ENTRY(printascii)
115 mov r1, r0
116 mov r0, #0x04 @ SYS_WRITE0
117 ARM( svc #0x123456 )
118 THUMB( svc #0xab )
119 mov pc, lr
120 ENDPROC(printascii)
121
122 ENTRY(printch)
123 adr r1, hexbuf
