面向对象&面向过程
面向过程:线性过程、第一步做什么、第二步做什么
面向对象:物以类聚、分类的思维模式、处理复杂的问题,多人协作,其本质是:以类的方式组织代码,以对象的方式封装数据。
值传递和引用传递
package oop;
// 值传递
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 1;
System.out.println(a);
change(10);
System.out.println(a);
}
public static void change(int a){
a = 10;
}
}
package oop;
// 引用传递
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person = new Person();
System.out.println(person.name);
change(person);
System.out.println(person.name);
}
public static void change(Person person){ //person对象是引用类型
person.name = "Java";
}
}
class Person{
String name;
}
创建对象&构造器
package oop.demo02;
public class Student {
// 属性
String name;
int age;
Student(String name, int age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
//方法
public void study(){
System.out.println(this.age + "的学生" +this.name + "在学习。");
}
}
package oop.demo02;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = new Student("小明",20);
student.study();
student.setName("小红");
student.age = 22;
student.study();
}
}
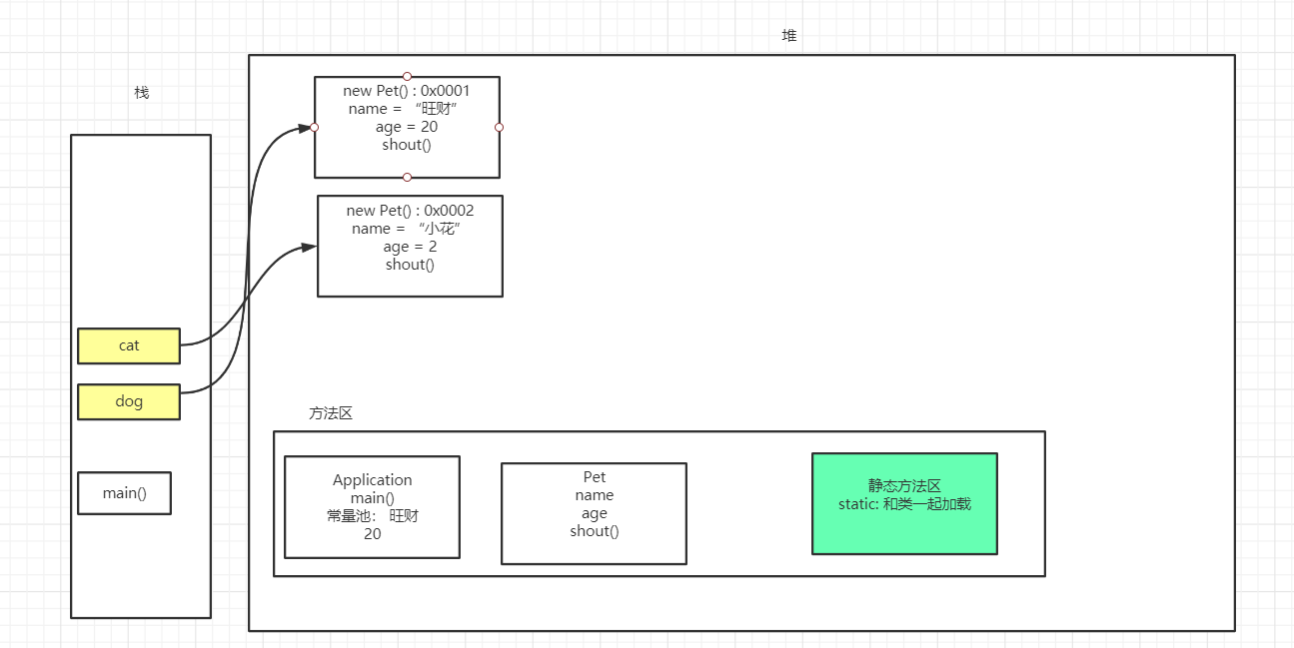
内存分析
package oop.demo03;
public class Pet {
String name;
int age;
public void shout(){
System.out.println(this.name + "今年" + this.age + "岁。");
}
}
package oop.demo03;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Pet dog = new Pet();
dog.name = "旺财";
dog.age = 20;
dog.shout();
Pet cat = new Pet();
cat.name = "小花";
cat.age = 2;
}
}
封装
封装: "高内聚、低耦合"。属性私有, get/set
package oop.demo04;
public class Student {
// 属性私有
private String name;
private int id;
private char sex;
private int age;
//get / set
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public char getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(char sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
if(age>120|| age<0){
this.age = 3;
}else{
this.age = age;
}
}
}
package oop.demo04;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student();
// s1.name 私有变量,只能通过get/set方法进行访问
s1.setName("老板");
s1.setAge(23);
System.out.println(s1.getName());
System.out.println(s1.getAge());
}
}
继承
extends关键字
Java只有单继承,没有多继承,多继承通过接口实现
继承是类和类之间的关系
object类
super和this
总结:
1. super调用父类的构造方法,必须在构造方法的第一个
1. super必须只能出现在子类的方法或者构造方法中
1. super和this不能同时调用构造方法
1. super vs this
1. this: 本身调用者对象
1. super 代表父类对象的引用
5. 前提
1. this: 没有继承也能使用
1. super只能在继承条件下才能使用
6. 构造方法
1. thist() 本类的构造
1. super() 父类的构造
package oop.demo05;
public class Person {
public Person(){
System.out.println("Person 无参构造。");
}
private int gupiao = 20_0000_0000;
public int money = 10_0000_0000;
protected String name = "kuangsheng";
public void say(){
System.out.println("说了一句话.");
}
public void print(){
System.out.println("Person");
}
private void print2(){
System.out.println("Person");
}
}
package oop.demo05;
public class Student extends Person{
public Student(){
super(); //默认调用父类无参构造
//this();
System.out.println("Student无参构造。。。");
}
private String name = "qingjiang";
public void test(String name){
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(this.name);
System.out.println(super.name);
}
public void print(){
System.out.println("Student");
}
public void test1(){
print();
this.print();
super.print();
//super.print2(); 私有的属性和方法无法被继承。
}
}
package oop.demo05;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = new Student();
student.say();
System.out.println(student.money);
//System.out.println(student.gupiao); 不能直接使用
//System.out.println(student.getGupiao());
student.test("秦疆");
student.test1();
}
}
方法重写
总结:重写需要有继承关系,子类重写父类的方法
- 方法名必须相同
- 参数列表必须相同
- 修饰符:范围可以扩大但不能缩小 ** public > protected > Default>private**
- 抛出异常: 范围可以被缩小但不能扩大
- 重写: 重写子类方法和父类方法方法名相同、方法体不同
- 为什么需要重写:父类的功能,子类不一定需要或者不一定满足!
package oop.demo05;
public class B {
public void test(){
System.out.println("B-- test");
}
}
package oop.demo05;
public class A extends B{
//重写
@Override //注解:有功能的注释
public void test() {
System.out.println("A-test");
}
}
package oop.demo05;
public class Application2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//静态方法方法的调用之和左边定义的数据类型有关
// 非静态的方法才能够重写
// private 方法不能重写
A a = new A();
a.test();
B b = new A();
b.test();
}
}
多态
注意:
a. 多态是方法的多态,属性没有多态
b. 父类和子类的多态, 有联系, 不能是猫和狗的多态,只能是猫狗和动物的多态
c. 类型转换异常: ClassCastException
d. 多态存在的条件:继承的关系,方法需要重写, 父类引用指向子类对象 Father f1 = new Son();
e. 那些方法不能重写:
1. static 方法, 属于类,不属于对象
2. final 常量
3. private方法
package oop.demo06;
public class Person {
public void run(){
System.out.println("run");
}
}
package oop.demo06;
public class Student extends Person {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("son");
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println("eat");
}
}
package oop.demo06;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//一个对象的实际类型是确定的
// new Person();
// new Student();
// 可以指向的引用类型就不确定了,可以是他的父类型
Student s1 = new Student();
Person s2 = new Student();
Object s3 = new Student();
s1.run();
s2.run(); // 子类重写父类方法后,执行子类的方法
s1.eat();
//对象能执行那边的方法,主要看对象左边的类型,和右边关系不大。
//s2.eat();
((Student) s2).eat(); // 强制类型转换,高转低
}
}