题目:
Design a data structure that supports all following operations in averageO(1) time.
Note: Duplicate elements are allowed.
insert(val): Inserts an item val to the collection.remove(val): Removes an item val from the collection if present.getRandom: Returns a random element from current collection of elements. The probability of each element being returned is linearly related to the number of same value the collection contains.
Example:
// Init an empty collection. RandomizedCollection collection = new RandomizedCollection(); // Inserts 1 to the collection. Returns true as the collection did not contain 1. collection.insert(1); // Inserts another 1 to the collection. Returns false as the collection contained 1. Collection now contains [1,1]. collection.insert(1); // Inserts 2 to the collection, returns true. Collection now contains [1,1,2]. collection.insert(2); // getRandom should return 1 with the probability 2/3, and returns 2 with the probability 1/3. collection.getRandom(); // Removes 1 from the collection, returns true. Collection now contains [1,2]. collection.remove(1); // getRandom should return 1 and 2 both equally likely. collection.getRandom();
分析:
这道题是leetcode380的进阶版,也就是允许出现重复的元素。这里附上380的题解LeetCode 380. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1) 常数时间插入、删除和获取随机元素(C++/Java)。
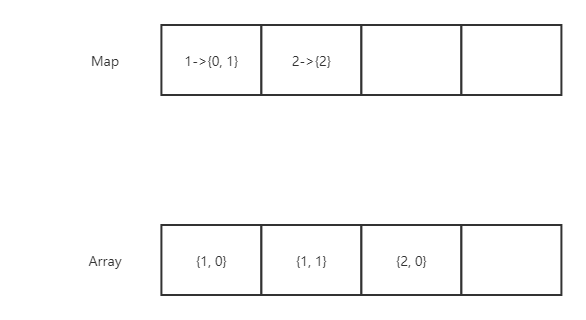
同样使用HashMap来支持插入和移除操作,利用数组来支持对数据的随机访问。只不过hashmap中val对应的是一个存放该元素在数组中索引的数组,当删除操作时,可以快速定位到该元素在数组的位置。
而数组中不只存放val,而是将val和该val在hashmap中对应的数组的索引,用来支持
我们来配合例子看一下:
依次执行
insert(1);insert(1);insert(2);
此时存储的情况如图:
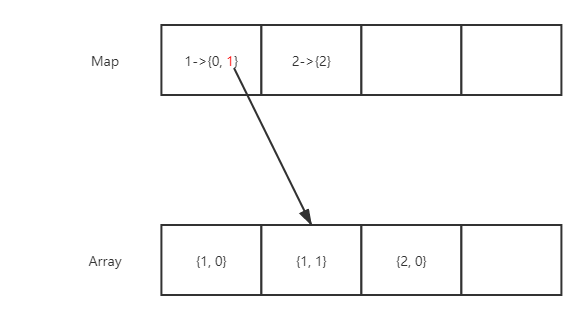
此时我们执行remove(1)的操作,我们首先通过map找到1这个元素对应的数组,取出数组中最后一个元素,表示的便是1这个元素在Array数组中的索引。
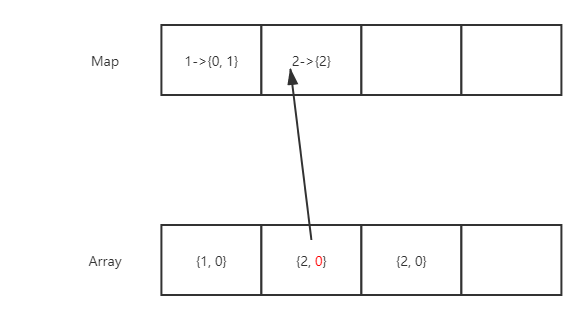
由于数组删除最后一个元素的时间复杂度为O(1)(不考虑扩容这种情况),我们将要删除的位置和数组中最后一个元素置换,或者是覆盖都可以。
然后我们再根据当前位置的这个元素去修改Map中数据,Array中元素的第二个值表示这个val在map中val对应的数组中的索引,此时我们要修改这个索引的值,改为array中调整后的索引值。最后在将无用的数据删除掉即可。
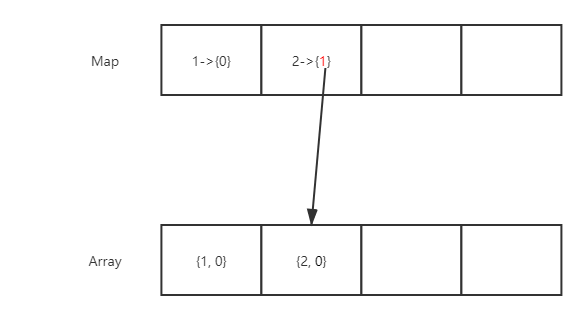
说着确实有些繁琐,不过通过实例配合图片过一遍应该比较好理解!
程序:
C++
class RandomizedCollection { public: /** Initialize your data structure here. */ RandomizedCollection() { } /** Inserts a value to the collection. Returns true if the collection did not already contain the specified element. */ bool insert(int val) { m[val].push_back(v.size()); v.emplace_back(val, m[val].size() - 1); return true; } /** Removes a value from the collection. Returns true if the collection contained the specified element. */ bool remove(int val) { if(!m.count(val)) return false; int lIndex = m[val].back(); auto entry = v.back(); v[lIndex] = entry; m[entry.first][entry.second] = lIndex; v.pop_back(); m[val].pop_back(); if(m[val].empty()) m.erase(val); return true; } /** Get a random element from the collection. */ int getRandom() { int index = rand() % v.size(); return v[index].first; } private: unordered_map<int, vector<int>> m; vector<pair<int, int>> v; };
Java
class RandomizedCollection { /** Initialize your data structure here. */ public RandomizedCollection() { } /** Inserts a value to the collection. Returns true if the collection did not already contain the specified element. */ public boolean insert(int val) { List<Integer> l = map.getOrDefault(val, new ArrayList<Integer>()); l.add(list.size()); map.put(val, l); list.add(new Pair<>(val, l.size()-1)); return true; } /** Removes a value from the collection. Returns true if the collection contained the specified element. */ public boolean remove(int val) { if(!map.containsKey(val)) return false; List<Integer> l = map.get(val); int lastIndex = l.get(l.size()-1); Pair<Integer, Integer> p = list.get(list.size()-1); list.set(lastIndex, p); List<Integer> cl = map.get(p.getKey()); cl.set(p.getValue(), lastIndex); map.put(p.getKey(), cl); list.remove(list.size()-1); l.remove(l.size()-1); if(l.size() == 0) map.remove(val); return true; } /** Get a random element from the collection. */ public int getRandom() { Random r = new Random(); int index = r.nextInt(list.size()); return list.get(index).getKey(); } private HashMap<Integer, List> map = new HashMap<>(); private ArrayList<Pair<Integer, Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>(); }