一、启动流程的时候设置流程变量
1.1 案例
/** * 启动流程实例 */ @Test public void start() { Student student=new Student(); student.setId(1); student.setName("张三"); Map<String, Object> variables=new HashMap<String,Object>(); variables.put("days", 2); variables.put("date", new Date()); variables.put("reason", "发烧"); variables.put("student", student); ProcessInstance instance=processEngine.getRuntimeService() // 运行时Service .startProcessInstanceByKey("StudentLeaveProcess",variables); // 流程定义表act_re_procdef的KEY字段值 System.out.println("流程实例ID:"+instance.getId()); System.out.println("流程定义ID:"+instance.getProcessDefinitionId()); }
- 如上述例子流程启动之后,任何任务节点都可以通过excutionId获取到流程变量的值。

/** * 获取流程变量数据 */ @Test public void getVariableValues(){ RuntimeService runtimeService=processEngine.getRuntimeService(); String excutionId="52501"; Integer days=(Integer) runtimeService.getVariable(excutionId, "days"); Date date=(Date) runtimeService.getVariableLocal(excutionId, "date"); String reason=(String) runtimeService.getVariable(excutionId, "reason"); Student student=(Student) runtimeService.getVariable(excutionId, "student"); System.out.println("请假天数:"+days); System.out.println("请假日期:"+date); System.out.println("请假原因:"+reason); System.out.println("请假对象:"+student.getId()+","+student.getName()); }
二、完成任务的时候设置流程变量
2.1 需求
- 在完成某个任务节点之后设置流程变量,接下来的任务节点都可以使用这个流程变量。
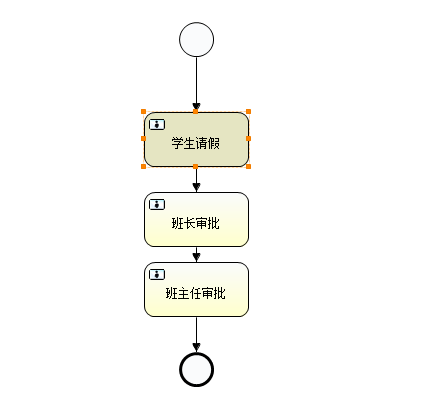 比如,当完成“学生请假”任务节点之后设置流程变量,然后在“班长审批”和“班主任审批”节点就可以获取该流程变量。
比如,当完成“学生请假”任务节点之后设置流程变量,然后在“班长审批”和“班主任审批”节点就可以获取该流程变量。
2.2 案例
/** * 完成任务 */ @Test public void test_completeTask2() { Student student=new Student(); student.setId(1); student.setName("张三"); Map<String, Object> variables=new HashMap<String,Object>(); variables.put("days", 2); variables.put("date", new Date()); variables.put("reason", "发烧"); variables.put("student", student); processEngine.getTaskService().complete("62504",variables); }
/** * 获取流程变量数据 */ @Test public void getVariableValues(){ RuntimeService runtimeService=processEngine.getRuntimeService(); String excutionId="62501"; Integer days=(Integer) runtimeService.getVariable(excutionId, "days"); Date date=(Date) runtimeService.getVariableLocal(excutionId, "date"); String reason=(String) runtimeService.getVariable(excutionId, "reason"); Student student=(Student) runtimeService.getVariable(excutionId, "student"); System.out.println("请假天数:"+days); System.out.println("请假日期:"+date); System.out.println("请假原因:"+reason); System.out.println("请假对象:"+student.getId()+","+student.getName()); }