Spring和SpringMVC作为Bean管理容器和MVC层的默认框架,已被众多WEB应用采用,而实际使用时,由于有了强大的注解功能,很多基于XML的配置方式已经被替代,但是在实际项目中,同时配置Spring和SpringMVC时会出现一些奇怪的异常,比如Bean被多次加载,多次实例化,或者依赖注入时,Bean不能被自动注入,但是明明你已经将该Bean注册了的。找原因还是要看问题的根源,我们从容器说起。
在Spring整体框架的核心概念中,容器是核心思想,就是用来管理Bean的整个生命周期的,而在一个项目中,容器不一定只有一个,Spring中可以包括多个容器,而且容器有上下层关系,目前最常见的一种场景就是在一个项目中引入Spring和SpringMVC这两个框架,其实就是2个容器,Spring是根容器,SpringMVC是其子容器,并且在Spring根容器中对于SpringMVC容器中的Bean是不可见的,而在SpringMVC容器中对于Spring根容器中的Bean是可见的,也就是子容器可以看见父容器中的注册的Bean,反之就不行。理解这点很重要,因为这是一个规则,是Spring自己设定的,但是往下看,我们会发现有些地方它并不默认使用这个规则。
当我们使用注解时,对于Bean注册这个功能的实现就不需要在给每个Bean配置XML了,只要使用统一的如下配置即可。
|
1
|
<context:component-scan base-package=“com.test" /> |
根据Spring提供的参考手册,该配置的功能是扫描默认包下的所有的@Component注解,并且自动注册到容器中,同时也扫描@Controller,@Service,@Respository这三个注解,他们是继承自@Component。
除了以上我们使用的扫描配置,在项目中我们经常见到的就是<context:annotation-config/>这个配置,其实有了以上的配置,这个是可以省略掉的。
还有一个SpringMVC相关的是<mvc:annotation-driven />配置,经过验证,这个是必须要配置的,因为它是和@RequestMapping结合使用的,这里补充下SpringMVC框架相关的知识点。
HandlerMapping,是SpringMVC中用来处理Request请求URL到具体Controller的,其自身也分成很多种类;
HandlerAdapter,是SpringMVC中用来处理具体请求映射到具体方法的,其自身也分很多种类;
@RequestMapping这个注解的主要目的就是对具体的Controller和方法进行注册,以方便HandlerMapping用来处理请求的映射。但是@RequestMapping需要结合<mvc:annotation-driven />使用才能生效。
好了,有了以上基础知识的铺垫,我们看下现在这样的一个使用场景中,Spring与SpringMVC的容器冲突的原因在那里!
Spring配置文件applicationContext.xml,SpringMVC配置文件applicationContext-MVC.xml,这样项目中就有2个容器了,配置方式A,如下:
applicationContext.xml中配置了<context:component-scan base-package=“com.test" />,负责所有需要注册的Bean的扫描工作,applicationContext-MVC.xml中配置<mvc:annotation-driven />,负责springMVC相关注解的使用,启动项目发现,springMVC失效,无法进行跳转,开启log的DEBUG级别进行调试,发现springMVC容器中的请求好像没有映射到具体controller中;
配置方式B,如下:
为了快速验证效果,将<context:component-scan base-package=“com.test" />扫描配置到applicationContext-MVC.xml中,重启后,验证成功,springMVC跳转有效。
要想查看具体原因,翻看源码,从springMVC的DispatcherServlet开始看,在一个请求进来之后,发生了什么?漫长的查看之后,找到原因,如下。
springMVC初始化时,会寻找所有当前容器中的所有@Controller注解的Bean,来确定其是否是一个handler,而当前容器springMVC中注册的Bean中并没有@Controller注解的,注意,上面提及的配置方式A,所有的@Controller配置的Bean都注册在Spring这个父容器中了,看代码。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
protected void initHandlerMethods() { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Looking for request mappings in application context: " + getApplicationContext()); } String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts ? BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(getApplicationContext(), Object.class) : getApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class)); for (String beanName : beanNames) { if (isHandler(getApplicationContext().getType(beanName))){ detectHandlerMethods(beanName); } } handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods()); } |
在方法isHandler中会判断当前bean的注解是否是controller,代码如下:
|
1
2
3
|
protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) { return AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) != null; } |
在配置方式B中,springMVC容器中包括了所有的@Controller注解的Bean,所以自然就能找到了。
以上是原因,解决办法是什么?注意看initHandlerMethods()方法中,detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts这个Switch,它主要控制从那里获取容器中的bean,是否包括父容器,默认是不包括的。所以解决办法是有的,即在springMVC的配置文件中配置HandlerMapping的detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts属性为true即可(这里需要根据具体项目看使用的是哪种HandlerMapping),让其检测父容器的bean。如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping"> <property name="detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts"> <value>true</value> </property> </bean> |
以上已经有了2种解决方案了,但在实际工程中,会包括很多配置,根据不同的业务模块来划分,所以我们一般思路是各负其责,明确边界,Spring根容器负责所有其他非controller的Bean的注册,而SpringMVC只负责controller相关的Bean的注册。第三种方案如下:
Spring容器配置,排除所有@controller的Bean
|
1
2
3
|
<context:component-scan base-package="com.fsnip.open"> <context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/> </context:component-scan> |
SpringMVC容器配置,让其只包括@controller的Bean
|
1
2
3
|
<context:component-scan base-package="com.fsnip.open" use-default-filters="false"> <context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller" /> </context:component-scan> |
个人比较推荐第三种方案。引申一下,项目中使用事务的配置方案,也会在这种场景下失效,归根结底也是由于2个容器的可见性问题导致,可以结合具体问题按照上面的思路进行查找原因!
引用一下海涛的博客中的一张图。 原图地址http://jinnianshilongnian.iteye.com/blog/1602617
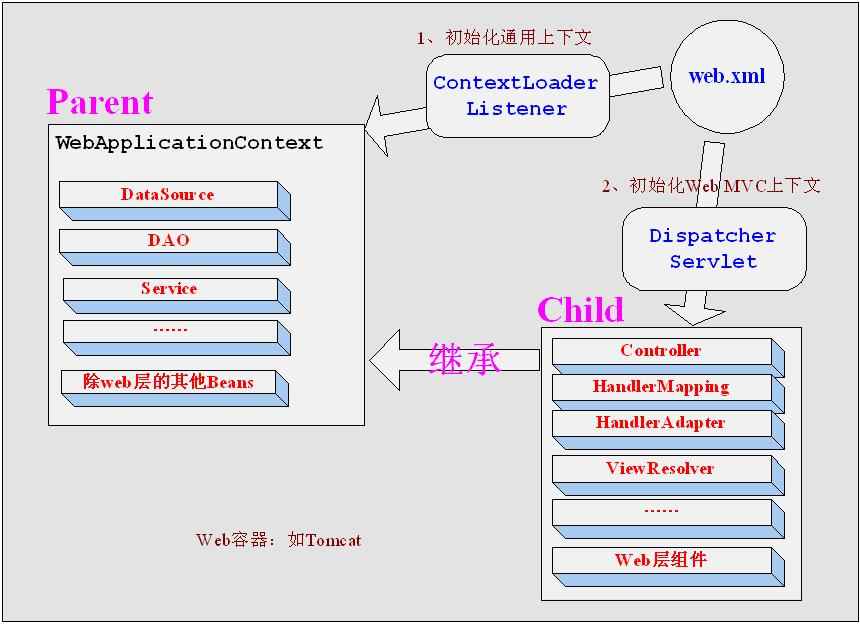
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/zyzcj/p/5286190.html