第11课 - enum, sizeof, typedef 分析

1. enum介绍
(1)enum是C语言中的一种自定义类型,和struct、union地位相同,格式如下:
1 // enum每个值的最后以逗号结尾 2 enum Color { 3 GREEN, 4 RED, 5 BLUE 6 };
// printf("%zu ", sizeof(enum Color)); ==> 输出的结果为4,表明enum类型的变量占用4字节
(2)enum定义的第一个值默认情况下为0,后一个的值在前一个值的基础上加1
(3)enum在程序中有两种用法: ① 定义常量 ② 定义离散的整型值类型

(4)enum中定义的值是C语言中真正意义的常量,在工程中enum多用于定义整型常量。下面的enum没有名字,不能用来定义枚举变量,仅仅用来定义常量。
1 enum { // 无名枚举,用于定义常量 2 ARRAY_SIZE = 10 3 }; 4 5 int array[ARRAY_SIZE] = {0}; // 使用ARRAY_SIZE定义数组大小 6 int i = 0; 7 8 for (i=0; i<ARRAY_SIZE; i++) { 9 array[i] = i + 1; 10 }
【enum的用法】
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 enum 4 { 5 ARRAY_SIZE = 10 //定义数组大小,ARRAY_SIZE是常量运行时无法改变 6 }; 7 8 enum Color 9 { 10 RED = 0x00FF0000, 11 GREEN = 0x0000FF00, 12 BLUE = 0x000000FF 13 }; 14 15 //打印,参数为枚举类型 16 void PrintColor(enum Color c) 17 { 18 switch( c ) 19 { 20 case RED: 21 printf("Color: RED (0x%08X) ", c); 22 break; 23 case GREEN: 24 printf("Color: GREEN (0x%08X) ", c); 25 break; 26 case BLUE: 27 printf("Color: BLUE(0x%08X) ", c); 28 break; 29 } 30 } 31 32 //初始化数据 33 void InitArray(int array[]) 34 { 35 int i = 0; 36 37 for(i=0; i<ARRAY_SIZE; i++) 38 { 39 array[i] = i + 1; 40 } 41 } 42 43 void PrintArray(int array[]) 44 { 45 int i = 0; 46 47 for(i=0; i<ARRAY_SIZE; i++) 48 { 49 printf("%d ", array[i]); 50 } 51 } 52 53 int main() 54 { 55 enum Color c = GREEN; //定义变量c并初始化为GREEN 56 57 int array[ARRAY_SIZE] = {0}; 58 59 PrintColor(c); 60 61 InitArray(array); 62 63 PrintArray(array); 64 65 return 0; 66 }
执行结果:
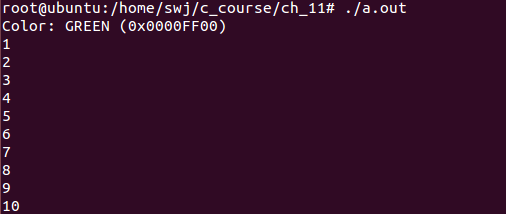
2. sizeof关键字的用法
(1)sizeof是C语言的一个内置关键字而不是函数,初学者往往因为sizeof后面的一对括号将其误认为是函数
(2)sizeof 用于计算 类型 或 变量 所占的内存大小
sizeof 用于类型:
sizeof(type)
sizeof 用于变量:
sizeof(var) 或 sizeof var // 这里sizeof与var之间使用空格间隔,也证明了sizeof是关键字而不是函数,函数是没有这种语法的
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 int main() 4 { 5 int var = 0; 6 7 printf("%zu ", sizeof(int)); // 4 8 printf("%zu ", sizeof(var)); // 4 9 printf("%zu ", sizeof var); // 4 10 11 return 0; 12 }
(3)sizeof 的值在编译期就已经确定。在编译过程中所有的sizeof将被具体的数值所替换,程序的执行过程与sizeof没有任何关系。看下面这段程序会输出什么?
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 int func() { 4 printf("This is test! "); 5 return 0; 6 } 7 8 int main() 9 { 10 int var = 0; 11 12 int size = sizeof(var++); // 在编译期直接替换为4 13 printf("var = %d, size = %d ", var, size); // var = 0, size = 4 14 15 size = sizeof(func()); // 因为func()的返回值类型为int,这里直接替换为4,func()并不会被执行 16 printf("size = %d ", size); 17 18 return 0; 19 }
执行结果:
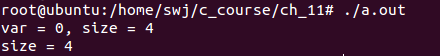
3. typedef的意义
(1)typedef 用于给一个已经存在的数据类型重命名,typedef 不能产生新的类型
(2)不能使用unsigned 和signed 修饰 typedef 重命名的类型
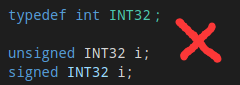
(3)typedef用法:
typedef type new_name;
其中type的定义可以在这条语句的后面出现,不必非要在这条语句的前面出现。编译器在处理这条语句时,只是将new_name认为是type的新名称,并不关心new_name的具体定义。
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 typedef int Int32; 4 5 struct _tag_point 6 { 7 int x; 8 int y; 9 }; 10 typedef struct _tag_point Point; // 前面先定义了类型,然后再重命名 11 12 typedef struct // struct没有名字,使用typedef重命名,这种用法很常见 13 { 14 int length; 15 int array[]; 16 } SoftArray; 17 18 19 // 这里先重命名,定义放在了后面,这样也是允许的 20 // 编译器在处理typedef时仅仅是给一个类型重命名,并不关心这个类型具体是什么样的 21 // 以后在程序中碰到ListNode就当做struct _tag_list_node 22 typedef struct _tag_list_node ListNode; //先重命名 23 struct _tag_list_node //再定义类型 24 { 25 ListNode* next; // 在链表中常看到这种写法 26 }; 27 28 int main() 29 { 30 Int32 i = -100; // int 31 // unsigned Int32 ii = 0; //不能使用signed、unsigned修饰 32 Point p; // struct _tag_point 33 SoftArray* sa = NULL; 34 ListNode* node = NULL; // struct _tag_list_node* 35 36 return 0; 37 }