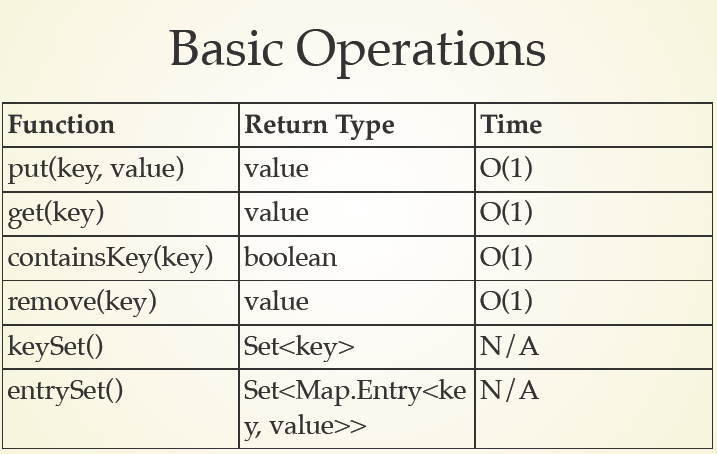
1、hashmap基本操作
2、hash function,equals函数,hashCode
3、练习题
1)Two Sum
Given an array of integers, return indices of the two numbers such
that they add up to a specific target.
You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution,
and you may not use the same element twice.
1、Two pointers 2、If return the two numbers, then HashSet will be enough 3、HashMap is needed to keep the mapping from number to index
方法一
1 public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int targer) { 2 HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); 3 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { 4 map.put(nums[i], i);//key:num[i], value:i 5 } 6 int[] result = new int[2]; 7 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { 8 int complement = target - nums[i]; 9 if (map.containsKey(complement) && map.get(complement) != i) { 10 return new int[] {i, map.get(complement)}; 11 } 12 } 13 return result; 14 } 15 16 public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int targer) { 17 HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); 18 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { 19 map.put(nums[i], i);//key:num[i], value:i 20 } 21 int[] result = new int[2]; 22 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { 23 int complement = target - nums[i]; 24 if (map.containsKey(complement) && map.get(complement) != i) { 25 result[0] = i; 26 result[1] = map.get(complement); 27 break; 28 } 29 } 30 return result; 31 }
方法二
1 public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) { 2 HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); 4 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { 5 int complement = target - nums[i]; 6 if (map.containsKey(complement && map.get(complement) != i)) { 7 return new int[] {i, map.get(complement)}; 8 } 9 map.put(nums[i], i);//假设result = {1,8},在找到1时,8还没有放进去,但是找到8时,1在hashmap里面,就找到了 10 } 11 return null; 12 }
1)Word Pattern
Given a pattern and a string str, find if str follows the same
pattern. Here follow means a full match, such that there is a
bijection between a letter in pattern and a non-empty word in str.
Examples:
1. pattern = "abba", str = "dog cat cat dog" should return true.
2. pattern = "abba", str = "dog cat cat fish" should return false.
3. pattern = "aaaa", str = "dog cat cat dog" should return false.
4. pattern = "abba", str = "dog dog dog dog" should return false.
Notes:
You may assume pattern contains only lowercase letters, and str
contains lowercase letters separated by a single space.
方法一
Keep a 1:1 mapping relationship HashMap is A->B, so two HashMaps are needed for A <-> B
1 public boolean wordPattern(String pattern, String str) { 2 HashMap<Character, String> map = new HaspMap<>(); 3 HashMap<String, Character> map_reverse = new HashMap<>(); 4 String[] words = str.split(" "); 5 if (pattern.length() != words.length) {//length() 6 return false; 7 } 8 for (int i = 0; i < pattern.length(); i++) { 9 char a = pattern.chatAt(i); 10 String b = words[i]; 11 if (!map.containsKey(a)) { 12 map.put(a, b); 13 } else if (!map.get(a).equals(b)) { 14 return false; 15 } 16 17 if (!map_reverse.containsKey(b)) { 18 map_reverse.put(b, a); 19 } else if (!map_reverse.get(b) != a) {//a is base type, can not use equals 20 return false; 21 } 22 } 23 return true; 24 }
方法二
Keep a 1:1 mapping relationship HashMap is A->B, so two HashMaps are needed for A <-> B Keep two A->B mappings at the same time
pattern -> index
string -> index
1 public boolean worPattern(String pattern, String str) { 2 HashMap<Character, Integer> mapPattern = new HashMap<>(); 3 HashMap<String, Integer> mapStr = new HashMap<>(); 4 String[] words = str.spilt(" "); 5 if (patterh.length() != words.length) { 6 return false; 7 } 8 for (int i = 0; i < pattern.length(); i++) { 9 int indexP = -1; 10 int indexS = -1; 11 Character a = pattern.charAt(i); 12 String b = word[i]; 13 if (mapPattern.containsKey(a)) { 14 indexP = mapPattern.get(a); 15 } else { 16 mapPattern.put(a, i); 17 } 18 19 if (mapStr.containsKey(b)) { 20 indexS = mapStr.get(b); 21 } else { 22 mapStr.put(b, i); 23 } 24 if (indexP != indexS) { 25 return false; 26 } 27 } 28 return true; 29 }
方法三
1 public boolean wordPattern(String pattern, String str) { 2 Map<Character, Integer> mappingPattern = new HashMap<>(); 3 Map<String, Integer> mappingStr = new HashMap<>(); 4 String[] words = str.split(" "); 5 if (pattern.length() != words.length) { 6 return false; 7 } 8 for (int i = 0; i < pattern.length(); i++) { 9 if (!Objects.equals(mappingPattern.put(pattern.charAt(i), i), 10 mappingStr.put(words[i], i))) { 11 return false; 12 } 13 } 14 return true; 15 }
习题三Group Anagrams
Given an array of strings, group anagrams together.
For example, given: ["eat", "tea", "tan", "ate", "nat", "bat"],
Return:
[
["ate", "eat","tea"],
["nat","tan"],
["bat"]
]
1 public ArrayList<String> anagrams(String[] strs) { 2 HashMap<String, ArrayList<String>> mapping = new HashMap<>(); 3 for (String str : strs) { 4 char[] array = str.toCharArray(); 5 Arrays.sort(array); 6 String newStr = new String(array);//排序后生成一个新字符串,作为key 7 if (!mapping.containsKey(newStr)) { 8 ArrayList<String> strList = new ArrayList<>(); 9 strList.add(str); 10 mapping.put(array, strList); 11 } else { 12 mapping.get(newStr).add(str); 13 } 14 } 15 ArrayList<String> result = new ArrayList<>(); 16 for (String str : mapping.keySet() {18 result.addAll(mapping.get(str));20 } 21 return result; 22 }