最后容易造成内存问题的通常就是全局单例、全局缓存、长期存活的对象
引用计数(主要), 标记清除, 分代收集(辅助)
引用计数为0则会被gc回收。标记删除可以解决循环引用的问题。分代:0代--年轻代;1代--中年代;2代--老年代,存活越久被回收的频率越低。
通过gc机制基本解决内存回收的问题。
不要轻易实现对象的__del__方法,和循环引用一起使用容易造成内存泄露,无法回收
gc模块包括如下函数和属性:

gc.disable()关闭自动的垃圾回收,改为手动;
gc.get_count()查看0、1、2代的数量(创建的对象数量-销毁的对象数量)
gc.get_threshold()查看0、1、2代的阈值
gc.collect(*args, **kwargs)手动执行垃圾回收,参数可以为0、1、2,表示回收指定代的垃圾;没有参数,表示0、1、2代全部回收,返回不可达的对象数量,不可达的对象也是要被清楚的对象,会被标记清除
gc.set_debug(DEBUG_COLLECTABLE|DEBUG_LEAK|DEBUG_SAVEALL|DEBUG_STATS|DEBUG_UNCOLLECTABLE) 把所有的debug开关打开。估计后端的C语音是根据8个bit位来判断debug开关功能的。
sys.getrefcount(a)查看a的引用计数
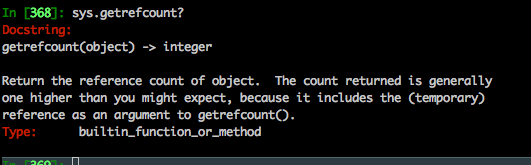
直接查看源代码说明:
def is_tracked(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Returns true if the object is tracked by the garbage collector.
Simple atomic objects will return false.
"""
pass
所以a=2没有被tracked,a=[2,2]被tracked

# encoding: utf-8 # module gc # from (built-in) # by generator 1.146 """ This module provides access to the garbage collector for reference cycles. enable() -- Enable automatic garbage collection. disable() -- Disable automatic garbage collection. isenabled() -- Returns true if automatic collection is enabled. collect() -- Do a full collection right now. get_count() -- Return the current collection counts. get_stats() -- Return list of dictionaries containing per-generation stats. set_debug() -- Set debugging flags. get_debug() -- Get debugging flags. set_threshold() -- Set the collection thresholds. get_threshold() -- Return the current the collection thresholds. get_objects() -- Return a list of all objects tracked by the collector. is_tracked() -- Returns true if a given object is tracked. get_referrers() -- Return the list of objects that refer to an object. get_referents() -- Return the list of objects that an object refers to. freeze() -- Freeze all tracked objects and ignore them for future collections. unfreeze() -- Unfreeze all objects in the permanent generation. get_freeze_count() -- Return the number of objects in the permanent generation. """ # no imports # Variables with simple values DEBUG_COLLECTABLE = 2 DEBUG_LEAK = 38 DEBUG_SAVEALL = 32 DEBUG_STATS = 1 DEBUG_UNCOLLECTABLE = 4 # functions def collect(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Run the garbage collector. With no arguments, run a full collection. The optional argument may be an integer specifying which generation to collect. A ValueError is raised if the generation number is invalid. The number of unreachable objects is returned. """ pass def disable(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Disable automatic garbage collection. """ pass def enable(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Enable automatic garbage collection. """ pass def freeze(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Freeze all current tracked objects and ignore them for future collections. This can be used before a POSIX fork() call to make the gc copy-on-write friendly. Note: collection before a POSIX fork() call may free pages for future allocation which can cause copy-on-write. """ pass def get_count(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return a three-tuple of the current collection counts. """ pass def get_debug(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Get the garbage collection debugging flags. """ pass def get_freeze_count(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return the number of objects in the permanent generation. """ pass def get_objects(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return a list of objects tracked by the collector (excluding the list returned). """ pass def get_referents(*objs): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ get_referents(*objs) -> list Return the list of objects that are directly referred to by objs. """ return [] def get_referrers(*objs): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ get_referrers(*objs) -> list Return the list of objects that directly refer to any of objs. """ return [] def get_stats(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return a list of dictionaries containing per-generation statistics. """ pass def get_threshold(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return the current collection thresholds. """ pass def isenabled(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Returns true if automatic garbage collection is enabled. """ pass def is_tracked(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Returns true if the object is tracked by the garbage collector. Simple atomic objects will return false. """ pass def set_debug(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Set the garbage collection debugging flags. flags An integer that can have the following bits turned on: DEBUG_STATS - Print statistics during collection. DEBUG_COLLECTABLE - Print collectable objects found. DEBUG_UNCOLLECTABLE - Print unreachable but uncollectable objects found. DEBUG_SAVEALL - Save objects to gc.garbage rather than freeing them. DEBUG_LEAK - Debug leaking programs (everything but STATS). Debugging information is written to sys.stderr. """ pass def set_threshold(threshold0, threshold1=None, threshold2=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ set_threshold(threshold0, [threshold1, threshold2]) -> None Sets the collection thresholds. Setting threshold0 to zero disables collection. """ pass def unfreeze(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Unfreeze all objects in the permanent generation. Put all objects in the permanent generation back into oldest generation. """ pass # classes class __loader__(object): """ Meta path import for built-in modules. All methods are either class or static methods to avoid the need to instantiate the class. """ @classmethod def create_module(cls, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Create a built-in module """ pass @classmethod def exec_module(cls, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Exec a built-in module """ pass @classmethod def find_module(cls, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Find the built-in module. If 'path' is ever specified then the search is considered a failure. This method is deprecated. Use find_spec() instead. """ pass @classmethod def find_spec(cls, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown pass @classmethod def get_code(cls, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return None as built-in modules do not have code objects. """ pass @classmethod def get_source(cls, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return None as built-in modules do not have source code. """ pass @classmethod def is_package(cls, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return False as built-in modules are never packages. """ pass @classmethod def load_module(cls, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Load the specified module into sys.modules and return it. This method is deprecated. Use loader.exec_module instead. """ pass def module_repr(module): # reliably restored by inspect """ Return repr for the module. The method is deprecated. The import machinery does the job itself. """ pass def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown pass __weakref__ = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default """list of weak references to the object (if defined)""" __dict__ = None # (!) real value is '' # variables with complex values callbacks = [] garbage = [] __spec__ = None # (!) real value is ''
参考:
1、https://foofish.net/python-gc.html
2、