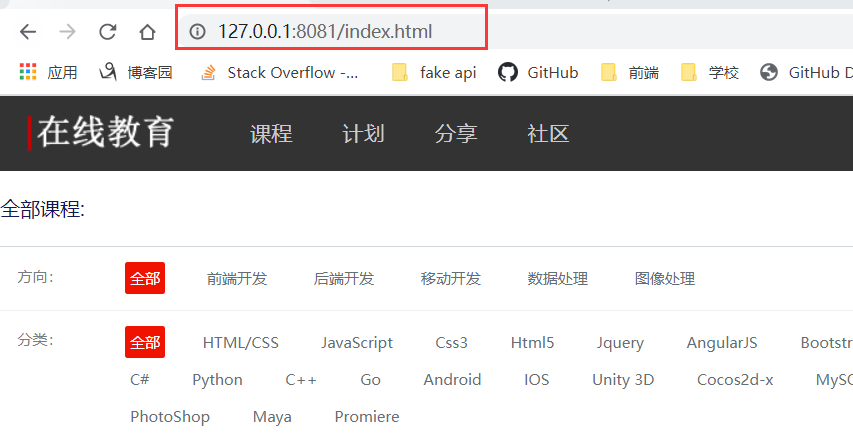
路由(Routing)是由一个URI(或者叫路径)和一个特定的HTTP 方法(GET、POST 等)组成的,涉及到应用如何响应客户端对某个网站节点的访问。
路由指的就是针对不同请求的URL,处理不同的业务逻辑。
route.js
const http = require('http');
const url = require('url')
const staticWeb = require('./web')
http.createServer(function (request, response) {
//创建静态Web服务
staticWeb(request,response,'./static')
//路由
let pathname = url.parse(request.url).pathname
if (pathname == '/') {
response.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': 'text/html;charset="utf-8"' });
response.end("<h3>执行首页逻辑</h3>");
}
else if(pathname=='/login'){
response.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': 'text/html;charset="utf-8"' });
response.end("<h3>执行登录逻辑</h3>");
}
else if(pathname=='/register'){
response.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': 'text/html;charset="utf-8"' });
response.end("<h3>执行注册逻辑</h3>");
}
else if(pathname=='/loginOut'){
response.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': 'text/html;charset="utf-8"' });
response.end("<h3>执行退出登录逻辑</h3>");
}
else{
response.writeHead(404, { 'Content-Type': 'text/html;charset="utf-8"' });
response.end("<h3>404 Not Found</h3>");
}
}).listen(8081);
console.log('Server running at http://127.0.0.1:8081/');
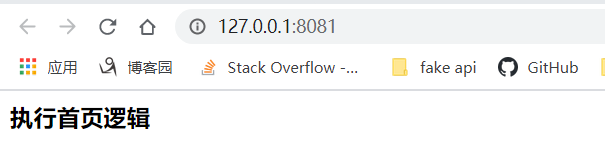
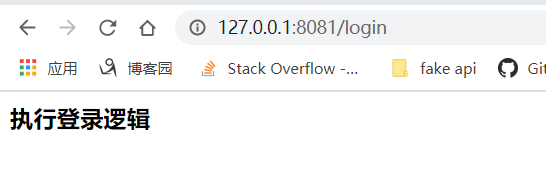

而直接访问静态资源文件会出现404,
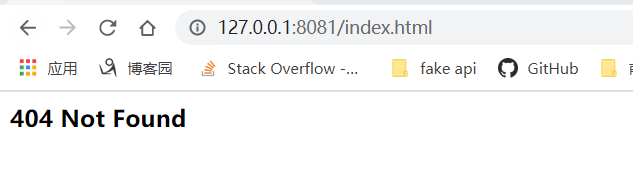
这是因为,静态文件的读取是异步的,还没有读取完成,先去匹配后端路由了,所以可以阻塞静态服务的读取,静态文件读取后再去匹配后端路由
web.js
const fs = require('fs')
const path = require('path')
const url = require('url')
let getMime = function (ext) {
let data = fs.readFileSync('./mime.json'); //同步方法,没有回调
let mime = JSON.parse(data.toString())[ext]
return mime;
}
module.exports = function staticWeb(req,res,staticPath){
let pathname = url.parse(req.url).pathname //先获取地址
pathname = pathname == '/' ? '/index.html' : pathname //根目录下定位到首页
let ext = path.extname(pathname) //获取文件后缀名
if (pathname != '/favicon.ico') {//过滤favicon的请求再读取
try {
let data = fs.readFileSync(staticPath + pathname)
console.log(staticPath + pathname)
if (data) {
let mime = getMime(ext) //获取文件类型
res.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': `${mime};charset="utf-8"` });
res.end(data);
}
} catch (error) {
console.log(error)
}
}
}
这里一定需要 try ... catch ,否则会不成功???
然后可以正常访问静态文件资源,不会报 404了: